Difference between revisions of "NR4A1AS"
(Created page with "NR4A1AS,an antisense lncRNA of NR4A1,is involved in colorectal cancer (CRC) development.<ref name="ref1" /> ==Annotated Information== ===Name===...") |
(→Labs working on this lncRNA) |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
Approved name:NR4A1 antisense RNA | Approved name:NR4A1 antisense RNA | ||
| − | HGNC ID | + | HGNC ID:54409 |
Alias symbol:NR4A1-AS1 | Alias symbol:NR4A1-AS1 | ||
RefSeq ID:NR_170321 | RefSeq ID:NR_170321 | ||
| − | + | ||
===Characteristics=== | ===Characteristics=== | ||
NR4A1AS located in the same primary transcript harboring miR-23a 27a 24-2 cluster is a stable, nuclear restricted and chromatin associated lncRNA.<ref name="ref1" /> | NR4A1AS located in the same primary transcript harboring miR-23a 27a 24-2 cluster is a stable, nuclear restricted and chromatin associated lncRNA.<ref name="ref1" /> | ||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
NR4A1AS up-regulates NR4A1 expression by forming RNA-RNA complexes and blocking UPF1-mediated mRNA destabilization<ref name="ref1" /> | NR4A1AS up-regulates NR4A1 expression by forming RNA-RNA complexes and blocking UPF1-mediated mRNA destabilization<ref name="ref1" /> | ||
===Expression=== | ===Expression=== | ||
| − | [[File: NR4A1AS. | + | [[File: NR4A1AS.png|thumb|550px|NR4A1 expression is increased in colorectal cancer (CRC) tissues and cells.<ref name="ref1"/>]] |
| − | NR4A1AS stabilized NR4A1 mRNA by forming RNA-RNA complexes via partial base-pairing and up-regulated NR4A1 expression in CRC cells.<ref name="ref1" /> | + | NR4A1AS stabilized NR4A1 mRNA by forming RNA-RNA complexes via partial base-pairing and up-regulated NR4A1 expression in CRC cells.<ref name="ref1" /> |
| + | |||
===Diseases=== | ===Diseases=== | ||
| − | Colorectal cancer<ref name="ref1" /> | + | Colorectal cancer<ref name="ref1" /> |
| + | |||
==Labs working on this lncRNA== | ==Labs working on this lncRNA== | ||
*Guangdong Key Laboratory of Systems Biology and Synthetic Biology for Urogenital Tumors, Institute of Translational Medicine, First Affiliated Hospital of Shenzhen University, Shenzhen Second People's Hospital, Shenzhen 518035, China.<ref name="ref1" /> | *Guangdong Key Laboratory of Systems Biology and Synthetic Biology for Urogenital Tumors, Institute of Translational Medicine, First Affiliated Hospital of Shenzhen University, Shenzhen Second People's Hospital, Shenzhen 518035, China.<ref name="ref1" /> | ||
| Line 39: | Line 41: | ||
*Department of General Surgery, First Affiliated Hospital of Shantou University Medical College, Shantou 515041, China.<ref name="ref1" /> | *Department of General Surgery, First Affiliated Hospital of Shantou University Medical College, Shantou 515041, China.<ref name="ref1" /> | ||
| − | *Department of Cell Biology and Genetics, Key Laboratory of Molecular Biology in High Cancer Incidence Coastal Chaoshan Area of Guangdong Higher Education Institutes, Shantou University Medical College, Shantou 515041, China tangaifa2018@email.szu.edu.cn huangdy@stu.edu.cn.</ref> | + | *Department of Cell Biology and Genetics, Key Laboratory of Molecular Biology in High Cancer Incidence Coastal Chaoshan Area of Guangdong Higher Education Institutes, Shantou University Medical College, Shantou 515041, China tangaifa2018@email.szu.edu.cn huangdy@stu.edu.cn.<ref name="ref1" /> |
| + | |||
| + | *Guangdong Key Laboratory of Systems Biology and Synthetic Biology for Urogenital Tumors, Institute of Translational Medicine, First Affiliated Hospital of Shenzhen University, Shenzhen Second People's Hospital, Shenzhen 518035, China tangaifa2018@email.szu.edu.cn huangdy@stu.edu.cn.<ref name="ref1" /> | ||
| − | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references> | <references> | ||
<ref name="ref1">Xie X, Lin J, Liu J, Huang M, Zhong Y, Liang B, Song X, Gu S, Chang X, Huang D, Tang A. A novel lncRNA NR4A1AS up-regulates orphan nuclear receptor NR4A1 expression by blocking UPF1-mediated mRNA destabilization in colorectal cancer. Clin Sci (Lond). 2019 Jul 15;133(13):1457-1473. doi: 10.1042/CS20181061.</ref>(1) | <ref name="ref1">Xie X, Lin J, Liu J, Huang M, Zhong Y, Liang B, Song X, Gu S, Chang X, Huang D, Tang A. A novel lncRNA NR4A1AS up-regulates orphan nuclear receptor NR4A1 expression by blocking UPF1-mediated mRNA destabilization in colorectal cancer. Clin Sci (Lond). 2019 Jul 15;133(13):1457-1473. doi: 10.1042/CS20181061.</ref>(1) | ||
</references> | </references> | ||
Latest revision as of 00:56, 20 February 2021
NR4A1AS,an antisense lncRNA of NR4A1,is involved in colorectal cancer (CRC) development.[1]
Contents
Annotated Information
Name
Approved symbol:NR4A1AS
Approved name:NR4A1 antisense RNA
HGNC ID:54409
Alias symbol:NR4A1-AS1
RefSeq ID:NR_170321
Characteristics
NR4A1AS located in the same primary transcript harboring miR-23a 27a 24-2 cluster is a stable, nuclear restricted and chromatin associated lncRNA.[1]
Function
NR4A1AS can make cell proliferation, migration and invasion.[1] NR4A1AS functions in tumor growth and metastasis of CRC cells at least partly through regulating NR4A1.[1]
Regulation
NR4A1AS up-regulates NR4A1 expression by forming RNA-RNA complexes and blocking UPF1-mediated mRNA destabilization[1]
Expression
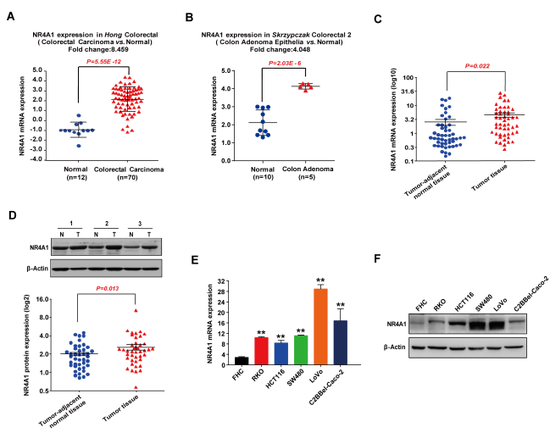
NR4A1AS stabilized NR4A1 mRNA by forming RNA-RNA complexes via partial base-pairing and up-regulated NR4A1 expression in CRC cells.[1]
Diseases
Colorectal cancer[1]
Labs working on this lncRNA
- Guangdong Key Laboratory of Systems Biology and Synthetic Biology for Urogenital Tumors, Institute of Translational Medicine, First Affiliated Hospital of Shenzhen University, Shenzhen Second People's Hospital, Shenzhen 518035, China.[1]
- Department of Cell Biology and Genetics, Key Laboratory of Molecular Biology in High Cancer Incidence Coastal Chaoshan Area of Guangdong Higher Education Institutes, Shantou University Medical College, Shantou 515041, China.[1]
- Department of Minimally Invasive Intervention, Peking University Shenzhen Hospital, Shenzhen 518036, China.[1]
- Department of Pathology, Shenzhen People's Hospital, Shenzhen 518000, China.[1]
- Department of Pathology and Central Laboratory, Shantou Central Hospital, Affiliated Shantou Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Shantou 515041, China.[1]
- Department of Urinary Surgery, Shenzhen Second People's Hospital, The First Affiliated Hospital of Shenzhen University, Health Science Center, Shenzhen 518035, China.[1]
- Department of General Surgery, First Affiliated Hospital of Shantou University Medical College, Shantou 515041, China.[1]
- Department of Cell Biology and Genetics, Key Laboratory of Molecular Biology in High Cancer Incidence Coastal Chaoshan Area of Guangdong Higher Education Institutes, Shantou University Medical College, Shantou 515041, China tangaifa2018@email.szu.edu.cn huangdy@stu.edu.cn.[1]
- Guangdong Key Laboratory of Systems Biology and Synthetic Biology for Urogenital Tumors, Institute of Translational Medicine, First Affiliated Hospital of Shenzhen University, Shenzhen Second People's Hospital, Shenzhen 518035, China tangaifa2018@email.szu.edu.cn huangdy@stu.edu.cn.[1]
References
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 1.14 1.15 1.16 Xie X, Lin J, Liu J, Huang M, Zhong Y, Liang B, Song X, Gu S, Chang X, Huang D, Tang A. A novel lncRNA NR4A1AS up-regulates orphan nuclear receptor NR4A1 expression by blocking UPF1-mediated mRNA destabilization in colorectal cancer. Clin Sci (Lond). 2019 Jul 15;133(13):1457-1473. doi: 10.1042/CS20181061.