Difference between revisions of "ENST00000499008.3"
Chunlei Yu (talk | contribs) |
Qianpeng Li (talk | contribs) |
||
| (10 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | ''BDNF-AS''which is approximately 200 kb downstream from the BDNF promoter and is located on the positive strand of chromosome-11,represses BDNF sense RNA transcription. | + | ''BDNF-AS'' which is approximately 200 kb downstream from the BDNF promoter and is located on the positive strand of chromosome-11,represses BDNF sense RNA transcription. |
==Annotated Information== | ==Annotated Information== | ||
| − | === | + | ===Name=== |
''BDNF-AS'':BDNF antisense RNA 1 (HGNC nomenclature) | ''BDNF-AS'':BDNF antisense RNA 1 (HGNC nomenclature) | ||
''BDNF-AS1'', ''BT2A'', ''BT2B'', ''BT2C'', ''BT2D'', ''NCRNA00049'', "non-protein coding RNA 49" <ref name="ref1" /> | ''BDNF-AS1'', ''BT2A'', ''BT2B'', ''BT2C'', ''BT2D'', ''NCRNA00049'', "non-protein coding RNA 49" <ref name="ref1" /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | LncBook ID: HSALNT0288893. | ||
===Characteristics=== | ===Characteristics=== | ||
| − | [[File:Genomic organization of the human BDNF locus showing.jpg|right|thumb|400px'''Genomic organization of the human BDNF locus showing'''<ref name="ref1" />]] | + | [[File:Genomic organization of the human BDNF locus showing.jpg|right|thumb|400px|'''Genomic organization of the human BDNF locus showing'''<ref name="ref1" />]] |
''BDNF-AS'' is approximately 200 kb downstream from the BDNF promoter and it is located on the positive strand of chromosome-11. Transcription from this site gives rise to 16–25 splice variant long ncRNAs with 6–8 exons8. Exon-5 of ''BDNF-AS'', which contain 225-nucleotides of full complementarity to BDNF mRNA (overlapping) and exon-4 (non-overlapping) are common between all these variants . <ref name="ref1" /> | ''BDNF-AS'' is approximately 200 kb downstream from the BDNF promoter and it is located on the positive strand of chromosome-11. Transcription from this site gives rise to 16–25 splice variant long ncRNAs with 6–8 exons8. Exon-5 of ''BDNF-AS'', which contain 225-nucleotides of full complementarity to BDNF mRNA (overlapping) and exon-4 (non-overlapping) are common between all these variants . <ref name="ref1" /> | ||
| Line 14: | Line 16: | ||
===Function=== | ===Function=== | ||
| − | [[File:Antisense-mediated regulation of sense mRNA and protein.png|right|thumb| | + | [[File:Antisense-mediated regulation of sense mRNA and protein.png|right|thumb|400px|'''Antisense-mediated regulation of sense mRNA and protein'''<ref name="ref1" />]] |
''BDNF-AS'' tonically represses BDNF sense RNA transcription by altering chromatin structure at the BDNF locus, which in turn reduces endogenous BDNF protein and function<ref name="ref1" />. | ''BDNF-AS'' tonically represses BDNF sense RNA transcription by altering chromatin structure at the BDNF locus, which in turn reduces endogenous BDNF protein and function<ref name="ref1" />. | ||
| Line 20: | Line 22: | ||
''BDNF-AS'' represses chromatin by recruiting Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 (PRC2) to the BDNF promoter region<ref name="ref1" />. | ''BDNF-AS'' represses chromatin by recruiting Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 (PRC2) to the BDNF promoter region<ref name="ref1" />. | ||
| + | ''BDNF-AS'' siRNA induces activation of the BDNF–TrkB–PI3K/Akt pathway following hypoxia/reoxygenation(H/R)-induced neurotoxicity<ref name="ref2" />. | ||
===Expression=== | ===Expression=== | ||
| − | BDNF mRNA levels are generally 10–100 fold higher than BDNF-AS transcript, except in testis, kidney and heart, which contain equal or higher levels of BDNF-AS. Both transcripts are expressed in brain, muscle and embryonic tissues. BDNF mRNA levels were relatively low in all post-natal tissues examined except in brain, bladder, heart and skeletal muscle.In rhesus monkey and mouse tissues, both transcripts are co-expressed in many tissues, which suggest BDNF-AS potential for regulation of BDNF mRNA<ref name="ref1" />. | + | ''BDNF-AS'' mRNA levels are generally 10–100 fold higher than ''BDNF-AS'' transcript, except in testis, kidney, and heart, which contain equal or higher levels of ''BDNF-AS''. Both transcripts are expressed in brain, muscle and embryonic tissues. BDNF mRNA levels were relatively low in all post-natal tissues examined except in brain, bladder, heart, and skeletal muscle. In rhesus monkey and mouse tissues, both transcripts are co-expressed in many tissues, which suggest ''BDNF-AS'' potential for regulation of BDNF mRNA<ref name="ref1" />. |
| + | BDNF expression was significantly downregulated in patients with cerebral | ||
| + | infarction, whereas the expression of ''BDNF-AS'' was significantly upregulated. In both human cortical neurons (HCN2) and human astrocytes, H/R significantly induced the expression of ''BDNF-AS'', but significantly decreased BDNF expression<ref name="ref2" />. | ||
{| class='wikitable' style="text-align:center" | {| class='wikitable' style="text-align:center" | ||
| Line 76: | Line 81: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | ===Diseases== | + | ===Diseases=== |
* Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease and Fragile X syndrome<ref name="ref1" />. | * Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease and Fragile X syndrome<ref name="ref1" />. | ||
| + | * Cerebral infarction<ref name="ref2" />. | ||
| − | + | ===Labs working on this lncRNA=== | |
| − | ==Labs working on this lncRNA== | ||
* Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences and Center for Therapeutic Innovation <ref name="ref1" />. | * Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences and Center for Therapeutic Innovation <ref name="ref1" />. | ||
| + | * Department of Neurology, Guangzhou Zengcheng People’s Hospital and Boji Hospital of Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, People’s Republic of China<ref name="ref2" />. | ||
| − | ==References== | + | ===References=== |
<references> | <references> | ||
<ref name="ref1"> Modarresi F, Faghihi MA, Lopez-Toledano MA, Fatemi RP, Magistri M, Brothers SP, et al. Inhibition of natural antisense transcripts in vivo results in gene-specific transcriptional upregulation[J]. Nature biotechnology. 2012,30(5):453-9 | <ref name="ref1"> Modarresi F, Faghihi MA, Lopez-Toledano MA, Fatemi RP, Magistri M, Brothers SP, et al. Inhibition of natural antisense transcripts in vivo results in gene-specific transcriptional upregulation[J]. Nature biotechnology. 2012,30(5):453-9 | ||
</ref>(1) | </ref>(1) | ||
| + | <ref name="ref2"> | ||
| + | Zhong J B, Li X, Zhong S M, et al. Knockdown of long noncoding antisense RNA brain-derived neurotrophic factor attenuates hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced nerve cell apoptosis through the BDNF–TrkB–PI3K/Akt signaling pathway[J]. Neuroreport, 2017, 28(14): 910-916. | ||
| + | </ref>(2) | ||
</references> | </references> | ||
Latest revision as of 14:35, 5 August 2019
BDNF-AS which is approximately 200 kb downstream from the BDNF promoter and is located on the positive strand of chromosome-11,represses BDNF sense RNA transcription.
Contents
Annotated Information
Name
BDNF-AS:BDNF antisense RNA 1 (HGNC nomenclature)
BDNF-AS1, BT2A, BT2B, BT2C, BT2D, NCRNA00049, "non-protein coding RNA 49" [1]
LncBook ID: HSALNT0288893.
Characteristics
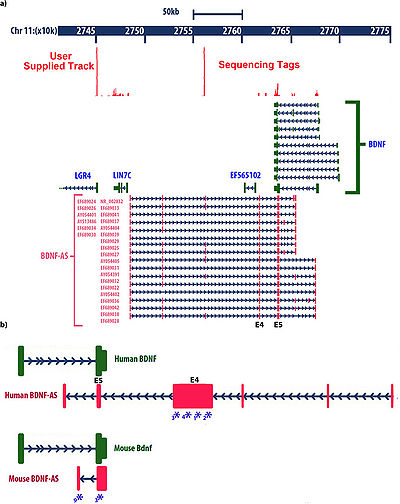
BDNF-AS is approximately 200 kb downstream from the BDNF promoter and it is located on the positive strand of chromosome-11. Transcription from this site gives rise to 16–25 splice variant long ncRNAs with 6–8 exons8. Exon-5 of BDNF-AS, which contain 225-nucleotides of full complementarity to BDNF mRNA (overlapping) and exon-4 (non-overlapping) are common between all these variants . [1]
It belongs to the category of "Antisense" in lncRNA classification[1].
Function

BDNF-AS tonically represses BDNF sense RNA transcription by altering chromatin structure at the BDNF locus, which in turn reduces endogenous BDNF protein and function[1].
BDNF-AS represses chromatin by recruiting Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 (PRC2) to the BDNF promoter region[1].
BDNF-AS siRNA induces activation of the BDNF–TrkB–PI3K/Akt pathway following hypoxia/reoxygenation(H/R)-induced neurotoxicity[2].
Expression
BDNF-AS mRNA levels are generally 10–100 fold higher than BDNF-AS transcript, except in testis, kidney, and heart, which contain equal or higher levels of BDNF-AS. Both transcripts are expressed in brain, muscle and embryonic tissues. BDNF mRNA levels were relatively low in all post-natal tissues examined except in brain, bladder, heart, and skeletal muscle. In rhesus monkey and mouse tissues, both transcripts are co-expressed in many tissues, which suggest BDNF-AS potential for regulation of BDNF mRNA[1].
BDNF expression was significantly downregulated in patients with cerebral infarction, whereas the expression of BDNF-AS was significantly upregulated. In both human cortical neurons (HCN2) and human astrocytes, H/R significantly induced the expression of BDNF-AS, but significantly decreased BDNF expression[2].
| Primer name | Sequence | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Human BDNF-AS siRNA-1 | GGCTCACCAGTTGTTTGTT | siRNA[1] |
| Scramble siRNA-1 | AGCTCGCCAGTCGTTTATT | Scrambled control[1] |
| Human BDNF-AS siRNA-2 | GCAATGTATCTTAGGCTCA | siRNA[1] |
| Human BDNF-AS siRNA-3 | GCTAATCTTACAACAGCAC | siRNA[1] |
| Scramble siRNA-3 | ACTAAGCTTACAGCAGCGC | Scrambled control[1] |
| Human BDNF-AS siRNA-4 | TCCCTACAAACATGTCAT | siRNA[1] |
| Scramble siRNA-4 | GCCCGACAAACAAGTCAAT | Scrambled control[1] |
| Control siRNA | CCUCUCCACGCGCAGUACATT | Non-targeting control[1] |
| Human BDNF-AS primer-F | AGTGGCTAATATTACAACAGCACAA | Real time PCR[1] |
| Human BDNF-AS primer-R | CTCAGTAGTCAAGTGCCTTTGGA | Real time PCR[1] |
| Human BDNF-AS probe | CCTCCTCTTCTCTTTCTGGTTAG | Real time PCR[1] |
Diseases
Labs working on this lncRNA
- Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences and Center for Therapeutic Innovation [1].
- Department of Neurology, Guangzhou Zengcheng People’s Hospital and Boji Hospital of Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, People’s Republic of China[2].
References
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 1.14 1.15 1.16 1.17 1.18 1.19 1.20 Modarresi F, Faghihi MA, Lopez-Toledano MA, Fatemi RP, Magistri M, Brothers SP, et al. Inhibition of natural antisense transcripts in vivo results in gene-specific transcriptional upregulation[J]. Nature biotechnology. 2012,30(5):453-9
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Zhong J B, Li X, Zhong S M, et al. Knockdown of long noncoding antisense RNA brain-derived neurotrophic factor attenuates hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced nerve cell apoptosis through the BDNF–TrkB–PI3K/Akt signaling pathway[J]. Neuroreport, 2017, 28(14): 910-916.
Basic Information
| Transcript ID |
ENST00000499008.3 |
| Source |
Gencode19 |
| Same with |
lnc-METTL15-4:4,NONHSAT018493,BDNF-AS |
| Classification |
intergenic |
| Length |
2324 nt |
| Genomic location |
chr11+:27528399..27699354 |
| Exon number |
8 |
| Exons |
27528399..27528445,27561567..27561663,27605816..27605884,27661392..27661552,27679788..27680009,27680718..27680775,27696844..27697687,27698529..27699354 |
| Genome context |
|
| Sequence |
000001 ATCGCGAGAT CAGGAAGGTG GCCGAGTGTG TCGCCGCGGC CATCAGGCAC TTCTCCTTCC TGCCCTTGTA TGAAGAAGGA 000080 000081 TGTGTTTGCT TCCCCTTGTG CCATGATTGT AAATTTCCTG AGGCCTCCTC AGCCCTGCAG AACTGGGGTT ATAGCCATGT 000160 000161 GACTGATCTT CGTCCAAGAA TATGTAAAGA AAAAGTGTTG AGTTGGCTTT TAGGGCTAGA GCAATGTATC TTAGGCTCAC 000240 000241 TTAAGGAAGC TGTAGAGATG AGCCCAAGGA GGGAAACCAG AAGAGCCCCC CAGGCTCACC AGTTGTTTGT TGGCTCCCTA 000320 000321 CAAACATGTC ATTCAAGTGG CTAATCTTAC AACAGCACAA ATTCATCTAA CCAGAAAGAG AAGAGGAGGC TCCAAAGGCA 000400 000401 CTTGACTACT GAGCATCACC CTGGACGTGT ACAAGTCTGC GTCCTTATTG TTTTCTTCAT TGGGCCGAAC TTTCTGGTCC 000480 000481 TCATCCAACA GCTCTTCTAT CACGTGTTCG AAAGTGTCAG CCAATGATGT CAAGCCTCTT GAACCTGCCT TGGGCCCATT 000560 000561 CACGCTCTCC AGAGTCCCAT GGGTCCGCAC ACCTGGAGAT ACTCTATTAT AGCAAAGAAG AAAGATAATT TCATTGAGCC 000640 000641 ATCCTGTTTT ACAGTATTGA ATTATTACCA CAAGGTACCA ACCATATATG CATACTTAAT AGGGTATTTT GTCAAAACTA 000720 000721 TGCATGAAGG TCATTTGTTT GAGATGTCAG AACATTTTCC CGTGAGAAGA TCTCATTGGG CATTGAAACA GAACCACATG 000800 000801 CTCTTCAGAC CAGCAACCGC GACTACCAAA TACTCCTCTG TCAACTCTAC TTGAGTAAGA ACGCTTTCAA TTAAGGCCTA 000880 000881 AGTGTCAACA TGCCTTTAAA AAAAATCGTG GTGACACAAA ATCTTTCTTT TTAGCACCCA ACAGAATCCC TTCAAAGCCT 000960 000961 CGTGGTCTGA CACCCTATGC TACGTGACTT GTGACCCATC CATTTGTCAT GTTCTTCGGG AATGTGGCTA AGGGGCTAAG 001040 001041 ATGTGACTTG AAAAGAAAGG TAGAACAAGA TCATCTCAAA TTTATTATCA AGGAATAGTT CAGAAAACGA CTTCAGACCA 001120 001121 CAGAGACAGC AGAACAGATG GTCCGGCATG GATAGAGCAT CAGACACTCA CAGACTGTGC CAACAAGAGC CATCGAGTCA 001200 001201 AAACAGCCAA AGGAAGGAGG GTCATGGAAT GGGTTCTCTC ACACCAAACT GATGCCCAGA GGCCCTCAGC ATGAATAACA 001280 001281 AAGGCAACCA GACCCACAAG CCATACTGAG TGGATACAAA ACCTATACCT AGGCTGACAT CCCAAATGTG TGTGGCAAGT 001360 001361 TAGATGATGA TGGCACAAAA GACAGAACAC CTTGCTTCTG G |