Difference between revisions of "MDS2"
(Created page with "==Annotated Information== ===Approved Symbol=== MDS2 ===Approved Name=== myelodysplastic syndrome 2 translocation associated ===Previous Symbols=== _ ===Synonyms=== _ ===Chrom...") |
|||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Annotated Information== | ==Annotated Information== | ||
===Approved Symbol=== | ===Approved Symbol=== | ||
| − | MDS2 | + | MDS2 (myelodysplastic syndrome 2 translocation associated) |
| − | |||
| − | myelodysplastic syndrome 2 translocation associated | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
===Chromosome=== | ===Chromosome=== | ||
1p36 | 1p36 | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
===OMIM ID=== | ===OMIM ID=== | ||
607305 | 607305 | ||
===RefSeq(supplied by NCBI)=== | ===RefSeq(supplied by NCBI)=== | ||
NR_027042 | NR_027042 | ||
| − | === | + | [[File:Analysis of the expression levels of genes surrounding MDS2 in the patient and in three unrelated normal bone marrow samples.png|right|thumb|400px|''' Analysis of the expression levels of genes surrounding MDS2 in the patient and in three unrelated normal bone marrow samples'''<ref name="ref1" />]] |
| − | + | ||
| + | ===Characteristics=== | ||
| + | The MDS2 gene is approximately 13 kb and is flanked by E2F2 and ID3 at its 5' end (telomeric) and by RPL11 and TCEB3 at its 3' end (centromeric) and gives rise to four alternatively spliced products.<ref name="ref1" /> | ||
| + | The predicted ETV6-MDS2 fusion product contains 58 amino acids, starting at the first ATG of ETV6 and ending in aTGA stop codon only four amino acids after ETV6 exon 2.<ref name="ref1" /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Expression=== | ||
| + | Oligonucleotide primers' sequences of MDS2 are showed as follow. | ||
| + | {| class='wikitable' style="text-align:center" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! | Primer | ||
| + | ! | Sequences | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | NG-R1 | ||
| + | | | GCGACAGCCAGGTCTTAA <ref name="ref1" /> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | NGex1-F1 | ||
| + | | | CCGCCTGTATCCGTGCCTGTT <ref name="ref1" /> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | NGex6-F1 | ||
| + | | | AGCAGTCCAGCTATGAGGGGAGGT <ref name="ref1" /> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | NGex6-R1 | ||
| + | | | TGGAGGCGACAGCCAGGTCTTAA <ref name="ref1" /> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | NGex6-F2 | ||
| + | | | GACCCTGGAGAGGCCATTAAGACCT <ref name="ref1" /> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | NGex6-R2 | ||
| + | | | GTCTTAATGGCCTCTCCAGGGTCAG <ref name="ref1" /> | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Disease=== | ||
| + | MyelodysplasticSyndrome <ref name="ref1" /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Labs working on this lncRNA== | ||
| + | * Department of Genetics, University of Navarra, Pamplona, Spain. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==References== | ||
| + | <references> | ||
| + | <ref name="ref1"> Odero, M.D., et al., A novel gene, MDS2, is fused to ETV6/TEL in a t(1;12)(p36.1;p13) in a patient with myelodysplastic syndrome. Genes Chromosomes Cancer, 2002. 35(1): p. 11-9. | ||
| + | </ref>(1) | ||
| + | </references> | ||
Latest revision as of 13:55, 13 November 2017
Contents
Annotated Information
Approved Symbol
MDS2 (myelodysplastic syndrome 2 translocation associated)
Chromosome
1p36
OMIM ID
607305
RefSeq(supplied by NCBI)
NR_027042
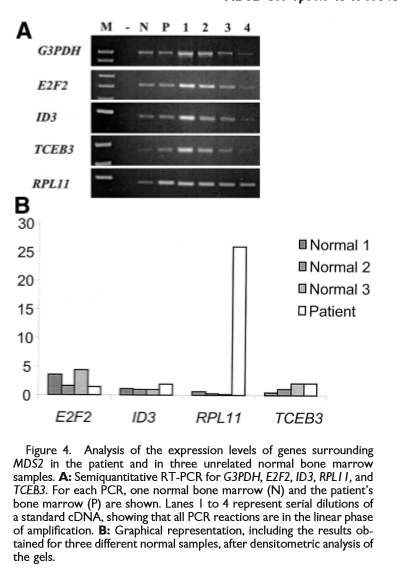
Analysis of the expression levels of genes surrounding MDS2 in the patient and in three unrelated normal bone marrow samples[1]
Characteristics
The MDS2 gene is approximately 13 kb and is flanked by E2F2 and ID3 at its 5' end (telomeric) and by RPL11 and TCEB3 at its 3' end (centromeric) and gives rise to four alternatively spliced products.[1] The predicted ETV6-MDS2 fusion product contains 58 amino acids, starting at the first ATG of ETV6 and ending in aTGA stop codon only four amino acids after ETV6 exon 2.[1]
Expression
Oligonucleotide primers' sequences of MDS2 are showed as follow.
| Primer | Sequences |
|---|---|
| NG-R1 | GCGACAGCCAGGTCTTAA [1] |
| NGex1-F1 | CCGCCTGTATCCGTGCCTGTT [1] |
| NGex6-F1 | AGCAGTCCAGCTATGAGGGGAGGT [1] |
| NGex6-R1 | TGGAGGCGACAGCCAGGTCTTAA [1] |
| NGex6-F2 | GACCCTGGAGAGGCCATTAAGACCT [1] |
| NGex6-R2 | GTCTTAATGGCCTCTCCAGGGTCAG [1] |
Disease
MyelodysplasticSyndrome [1]
Labs working on this lncRNA
- Department of Genetics, University of Navarra, Pamplona, Spain.