Difference between revisions of "NONHSAT113149"
| (13 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Annotated Information== | ==Annotated Information== | ||
===Name=== | ===Name=== | ||
| − | 7SK | + | Approved symbol: RN7SK |
| + | |||
| + | Approved name: RNA component of 7SK nuclear ribonucleoprotein | ||
| + | |||
| + | HGNC ID: HGNC:10037 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Previous names: 7SK, 7SK small nuclear | ||
| + | |||
| + | Alias symbols: 7SK | ||
| + | |||
| + | RefSeq ID: NR_001445 | ||
| + | |||
| + | LncBook ID: [https://bigd.big.ac.cn/lncbook/transcript?transid=HSALNT0107279 HSALNT0107279] | ||
===Characteristics === | ===Characteristics === | ||
| + | [[File:Functional domains of 7SK RNA..png|right|thumb|Functional domains of 7SK RNA([https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19246988 (Diribarne 2009)])]] | ||
| + | |||
~330 nt in vertebrates*. Transcribed by RNAP III, GC-rich sequence forming conserved secondary structures (especially 3' and 5' stem-loop motifs). | ~330 nt in vertebrates*. Transcribed by RNAP III, GC-rich sequence forming conserved secondary structures (especially 3' and 5' stem-loop motifs). | ||
| + | |||
| + | The 7SK gene is located on chromosome 6, and chromosome 6 is the sole human chromosome that produces 7SK RNA ([https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8139910 (Driscoll 1994)]) | ||
7SK RNA is capped at its 5' end by BCDIN3, a specific methylase methylphosphate capping enzyme (MePCE) ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17643375 (Jeronimo 2007)]). | 7SK RNA is capped at its 5' end by BCDIN3, a specific methylase methylphosphate capping enzyme (MePCE) ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17643375 (Jeronimo 2007)]). | ||
| Line 18: | Line 34: | ||
===Regulation=== | ===Regulation=== | ||
| − | + | In the 7SK ribonucleoprotein, Larp7 binds directly to 3′ terminus of 7SK RNA ([https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18281698 (Krueger 2008)]) ([https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18483487 (Markert 2008)]), and prevents degradation of 7SK in vivo ([https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18281698 (Krueger 2008)]). | |
===Function=== | ===Function=== | ||
| − | + | [[File:Model of hLarp7 recognition of the 7SK.png|right|thumb|Model of hLarp7 recognition of the 7SK 3′end and mechanism of assembly of core 7SK RNP([https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29946027 (Eichhorn 2018)])]] | |
| − | 7SK snRNA | + | 7SK snRNA functions in transcriptional regulation by interacting with PTEF-B complex ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11713533 (Nguyen 2001)]) ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11713532 (Yang 2001)]), BAF chromatin-remodeling complex ([https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26878240 (Flynn 2016)]), or hnRNP R ([https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29507242 (Briese 2018)]). Consistently, it has been found highly enriched in isolated chromatin fractions, which may be related to its role in transcriptional regulation ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20404130 (Mondal 2010)]). In addition to its critical role for controlling transcription, 7SK snRNA is also involved in alternative splicing ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19416841 (Barboric 2009)]) and the localization of protein in nucleolus ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17381310 (He 2007)]). Therefore, 7SK snRNA has a variety of functions in the nuclear, playing important roles in cell growth and differentiation ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11713533 (Nguyen 2001)]) ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11713532 (Yang 2001)]), axon maintenance ([https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29507242 (Briese 2018)]) and vertebrate development ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19416841 (Barboric 2009)]). |
| − | 7SK | + | 7SK snRNA controls RNAP II activity by inhibiting P-TEFb elongation factor, which is a cdk-cyclin kinase that functions as both a general and an HIV-1 Tat-specific transcription factor ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11713533 (Nguyen 2001)]) ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11713532 (Yang 2001)]), with an impact on cell growth and differentiation. Specifically, 7SK snRNA functions as the central scaffold that coordinates protein-protein interactions and, by inhibiting P-TEFb kinase-mediated CTD phosphorylation, regulates RNAP II elongation ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11713533 (Nguyen 2001)]). |
At an early stage of the HIV transcription cycle, elongation is prevented as P-TEFb is recruited to the HIV-1 promoter in a catalytically inactive state bound to the 7SK snRNP and also the Tat trans-activator of transcription protein. The inhibitory 7SK snRNP may be displaced by the nascent TAR HIV RNA that also binds Tat protein, activating P-TEFb kinase and transcriptional elongation ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20562857 (D'Orso 2010)]). Displacement of 7SK may also be performed by cellular RNAs, as indicated by the 3'-untranslated region (~300-nt) of HIC mRNA, which forms complexes with P-TEFb and is necessary and sufficient for stimulation of P-TEFb-dependent transcription of the HIV promoter ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17925858 (Young 2007)]). | At an early stage of the HIV transcription cycle, elongation is prevented as P-TEFb is recruited to the HIV-1 promoter in a catalytically inactive state bound to the 7SK snRNP and also the Tat trans-activator of transcription protein. The inhibitory 7SK snRNP may be displaced by the nascent TAR HIV RNA that also binds Tat protein, activating P-TEFb kinase and transcriptional elongation ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20562857 (D'Orso 2010)]). Displacement of 7SK may also be performed by cellular RNAs, as indicated by the 3'-untranslated region (~300-nt) of HIC mRNA, which forms complexes with P-TEFb and is necessary and sufficient for stimulation of P-TEFb-dependent transcription of the HIV promoter ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17925858 (Young 2007)]). | ||
| − | 7SK | + | 7SK snRNA inhibits enhancer transcription by modulating nucleosome position. 7SK physically interacts with the BAF chromatin-remodeling complex, recruits BAF to enhancers and inhibits enhancer transcription by modulating chromatin structure ([https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26878240 (Flynn 2016)]). |
| + | |||
| + | In axons, 7SK snRNA interacts with hnRNP R to regulate its function in axon maintenance ([https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29507242 (Briese 2018)]). | ||
| + | |||
| + | 7SK snRNP (composed of 7SK snRNA, Hexim1, Larp7/Pip7S, and the P-TEFb subunits CycT1 and Cdk9) is not only critical for controlling transcription, but also for regulating alternative splicing coupled to transcription elongation ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19416841 (Barboric 2009)]). 7SK snRNP disintegration promotes inclusion of an alternative exon via the increased occupancy of P-TEFb, Ser2-phosphorylated (Ser2-P) RNAPII, and the splicing factor SF2/ASF at the minigene ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19416841 (Barboric 2009)]). | ||
| + | |||
| + | 7SK snRNA also inhibits APOBEC3C deaminase activity and sequesters it to the nucleolus, suggesting broader role for 7SK RNA in regulating key nuclear functions ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17381310 (He 2007)]). | ||
===Disease=== | ===Disease=== | ||
| Line 41: | Line 63: | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
| + | <references> | ||
| + | <ref name="ref1"> Shahriyari L. Effect of normalization methods on the performance of supervised | ||
| + | learning algorithms applied to HTSeq-FPKM-UQ data sets: 7SK RNA expression as a | ||
| + | predictor of survival in patients with colon adenocarcinoma. Brief Bioinform. | ||
| + | 2017 Nov 3. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbx153. | ||
| + | </ref>(1) | ||
| + | </references> | ||
[http://www.lncrnadb.org/7SK/ Annotation originally sourced from lncRNAdb]. | [http://www.lncrnadb.org/7SK/ Annotation originally sourced from lncRNAdb]. | ||
Latest revision as of 02:38, 12 August 2019
Contents
Annotated Information
Name
Approved symbol: RN7SK
Approved name: RNA component of 7SK nuclear ribonucleoprotein
HGNC ID: HGNC:10037
Previous names: 7SK, 7SK small nuclear
Alias symbols: 7SK
RefSeq ID: NR_001445
LncBook ID: HSALNT0107279
Characteristics
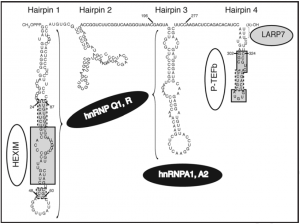
~330 nt in vertebrates*. Transcribed by RNAP III, GC-rich sequence forming conserved secondary structures (especially 3' and 5' stem-loop motifs).
The 7SK gene is located on chromosome 6, and chromosome 6 is the sole human chromosome that produces 7SK RNA ((Driscoll 1994))
7SK RNA is capped at its 5' end by BCDIN3, a specific methylase methylphosphate capping enzyme (MePCE) ((Jeronimo 2007)).
RNAP II was recently found to bind near 7SK promoter, as well as many other known Pol III genes, suggesting that RNAP II may also play a role in regulating their transcription ((Raha 2010)).
In invertebrates, 7SK homologs may have different sizes (such as >400 nt and ~130 nt in drosophilids and nematodes, respectively). ((Gruber 2008)) ((Marz 2009))
Expression
Nuclear, highly abundant (one of the most abundant small RNAs in vertebrate cells), first isolated from HeLa nuclear extracts, but ubiquitously expressed.
RNA sequencing from 11 humans tissues confirmed ubiquitous high expression of 7SK with expression in some tissues being higher than any mRNA ((Castle 2010)).
Regulation
In the 7SK ribonucleoprotein, Larp7 binds directly to 3′ terminus of 7SK RNA ((Krueger 2008)) ((Markert 2008)), and prevents degradation of 7SK in vivo ((Krueger 2008)).
Function
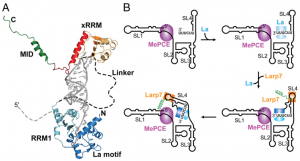
7SK snRNA functions in transcriptional regulation by interacting with PTEF-B complex ((Nguyen 2001)) ((Yang 2001)), BAF chromatin-remodeling complex ((Flynn 2016)), or hnRNP R ((Briese 2018)). Consistently, it has been found highly enriched in isolated chromatin fractions, which may be related to its role in transcriptional regulation ((Mondal 2010)). In addition to its critical role for controlling transcription, 7SK snRNA is also involved in alternative splicing ((Barboric 2009)) and the localization of protein in nucleolus ((He 2007)). Therefore, 7SK snRNA has a variety of functions in the nuclear, playing important roles in cell growth and differentiation ((Nguyen 2001)) ((Yang 2001)), axon maintenance ((Briese 2018)) and vertebrate development ((Barboric 2009)).
7SK snRNA controls RNAP II activity by inhibiting P-TEFb elongation factor, which is a cdk-cyclin kinase that functions as both a general and an HIV-1 Tat-specific transcription factor ((Nguyen 2001)) ((Yang 2001)), with an impact on cell growth and differentiation. Specifically, 7SK snRNA functions as the central scaffold that coordinates protein-protein interactions and, by inhibiting P-TEFb kinase-mediated CTD phosphorylation, regulates RNAP II elongation ((Nguyen 2001)).
At an early stage of the HIV transcription cycle, elongation is prevented as P-TEFb is recruited to the HIV-1 promoter in a catalytically inactive state bound to the 7SK snRNP and also the Tat trans-activator of transcription protein. The inhibitory 7SK snRNP may be displaced by the nascent TAR HIV RNA that also binds Tat protein, activating P-TEFb kinase and transcriptional elongation ((D'Orso 2010)). Displacement of 7SK may also be performed by cellular RNAs, as indicated by the 3'-untranslated region (~300-nt) of HIC mRNA, which forms complexes with P-TEFb and is necessary and sufficient for stimulation of P-TEFb-dependent transcription of the HIV promoter ((Young 2007)).
7SK snRNA inhibits enhancer transcription by modulating nucleosome position. 7SK physically interacts with the BAF chromatin-remodeling complex, recruits BAF to enhancers and inhibits enhancer transcription by modulating chromatin structure ((Flynn 2016)).
In axons, 7SK snRNA interacts with hnRNP R to regulate its function in axon maintenance ((Briese 2018)).
7SK snRNP (composed of 7SK snRNA, Hexim1, Larp7/Pip7S, and the P-TEFb subunits CycT1 and Cdk9) is not only critical for controlling transcription, but also for regulating alternative splicing coupled to transcription elongation ((Barboric 2009)). 7SK snRNP disintegration promotes inclusion of an alternative exon via the increased occupancy of P-TEFb, Ser2-phosphorylated (Ser2-P) RNAPII, and the splicing factor SF2/ASF at the minigene ((Barboric 2009)).
7SK snRNA also inhibits APOBEC3C deaminase activity and sequesters it to the nucleolus, suggesting broader role for 7SK RNA in regulating key nuclear functions ((He 2007)).
Disease
colon adenocarcinoma [1]
Evolution
Please input evolution information here.
Labs working on this lncRNA
Please input related labs here.
References
- ↑ Shahriyari L. Effect of normalization methods on the performance of supervised learning algorithms applied to HTSeq-FPKM-UQ data sets: 7SK RNA expression as a predictor of survival in patients with colon adenocarcinoma. Brief Bioinform. 2017 Nov 3. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbx153.
Annotation originally sourced from lncRNAdb.
Basic Information
| Transcript ID |
NONHSAT113149 |
| Source |
NONCODE4.0 |
| Same with |
, |
| Classification |
intergenic |
| Length |
332 nt |
| Genomic location |
chr6+:52860418..52860749 |
| Exon number |
1 |
| Exons |
52860418..52860749 |
| Genome context |
|
| Sequence |
000001 GGATGTGAGG GCGATCTGGC TGCGACATCT GTCACCCCAT TGATCGCCAG GGTTGATTCG GCTGATCTGG CTGGCTAGGC 000080
000081 GGGTGTCCCC TTCCTCCCTC ACCGCTCCAT GTGCGTCCCT CCCGAAGCTG CGCGCTCGGT CGAAGAGGAC GACCATCCCC 000160 000161 GATAGAGGAG GACCGGTCTT CGGTCAAGGG TATACGAGTA GCTGCGCTCC CCTGCTAGAA CCTCCAAACA AGCTCTCAAG 000240 000241 GTCCATTTGT AGGAGAACGT AGGGTAGTCA AGCTTCCAAG ACTCCAGACA CATCCAAATG AGGCGCTGCA TGTGGCAGTC 000320 000321 TGCCTTTCTT TT |