Difference between revisions of "GUARDIN"
| (20 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | ''GUARDIN'', a p53-inducible effector, is critical for guarding the de novo structure of DNA and genomic integrity. | |
| − | |||
==Annotated Information== | ==Annotated Information== | ||
| − | ===Name=== | + | ===Approved Name=== |
| − | + | Approved symbol:LNCTAM34A | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Approved name:long non coding transcriptional activator of miR34a | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | HGNC ID:HGNC:52548 | |
| − | + | Previous name:long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 1759 | |
| − | + | Alias symbol:GUARDIN | |
| + | |||
| + | RefSeq ID:NR_132738 | ||
| − | ''GUARDIN'' | + | Prev_symbol:LINC01759 |
| + | ===Characteristics=== | ||
| + | ''GUARDIN'' is located between the genes encoding miR-34a and hexose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase/glucose 1-dehydrogenase (H6PD).<ref name="ref1" /> | ||
| + | This region is part of the FRA1A(aphidicolin type, common, Fra(1)(P36)) fragile site that is frequently lost in human cancers.<ref name="ref2" /> ''GUARDIN'' silencing triggered apoptosis and senescence, enhanced cytotoxicity of additional genotoxic stress and inhibited cancer xenograft growth. GUARDIN may constitute a target for cancer treatment.<ref name="ref3" /> | ||
| + | ===Function=== | ||
| + | [[File:GUARDIN.jpg|right|thumb|400px|'''a, Expression of the lncRNA GUARDIN is induced upon DNA damage by direct p53 transcriptional activation in order to control genome stability by multiple mechanisms. b, Thanks to several miR-23a binding sites, GUARDIN is able to sequester this miRNA and to subsequently increase expression of TRF2, an essential factor devoted to capping and protection of telomere termini. c, GUARDIN also acts as a molecular scaffold to promote the interaction between BRCA1 and its partner BARD1, thus favouring the formation of this protein complex fundamental in DNA repair. The combinatorial effect of these different GUARDIN functions leads to cell survival, antagonizing the pro-apoptotic pathway promoted by p53 following DDR.'''<ref name="ref3" />]] | ||
| + | ''GUARDIN'' has a role in regulation of cell viability as it is necessary for preventing chromosome end-to-end fusion through maintaining the expression of telomeric repeat-binding factor 2 (TRF2) by sequestering microRNA-23a.<ref name="ref3" /> | ||
| + | ''GUARDIN'' modulates the cytotoxic effect of p53. <ref name="ref1" /> | ||
| + | ''GUARDIN'' interacts with BRCA1 and BARD1 and is essential for the stabilization of BRCA1. <ref name="ref1" /> | ||
| + | ''GUARDIN'' protects genomic integrity through TRF2 and BRCA1. <ref name="ref1" /> | ||
===Regulation=== | ===Regulation=== | ||
| − | + | ''GUARDIN'' expression is primarily regulated by wild-type p53, and is strongly induced following DNA damage <ref name="ref1" />. | |
| − | ''GUARDIN'' expression is primarily regulated by wild-type p53 | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
===Expression=== | ===Expression=== | ||
| − | ''GUARDIN'' expression is primarily regulated by wild-type p53. However, it was detectable in TP53-null cells and in tumours with mutations in TP53, albeit at low levels. | + | ''GUARDIN'' expression is primarily regulated by wild-type p53. However, it was detectable in TP53-null cells and in tumours with mutations in TP53, albeit at low levels.''GUARDIN'' transcripts were concurrently reduced in a proportion of colon cancers with gene copy number loss.<ref name="ref1" /> |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | ''GUARDIN'' transcripts were concurrently reduced in a proportion of colon cancers with gene copy number loss.<ref name="ref1" /> | ||
| + | ===Disease=== | ||
| + | *Colon cancer <ref name="ref1" /> | ||
| − | + | ==Labs working on this lncRNA== | |
* Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) Key Laboratory of Innate Immunity and Chronic Disease, CAS Centre for Excellence in Cell and Molecular Biology, Innovation Centre for Cell Signalling Network, School of Life Sciences, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, China | * Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) Key Laboratory of Innate Immunity and Chronic Disease, CAS Centre for Excellence in Cell and Molecular Biology, Innovation Centre for Cell Signalling Network, School of Life Sciences, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, China | ||
* Translational Research Institute, Henan Provincial People’s Hospital, Zhengzhou, China | * Translational Research Institute, Henan Provincial People’s Hospital, Zhengzhou, China | ||
* Department of Gene Therapy and Regulation of Gene Expression, Center for Applied Medical Research, University of Navarra, Pamplona, Spain | * Department of Gene Therapy and Regulation of Gene Expression, Center for Applied Medical Research, University of Navarra, Pamplona, Spain | ||
| − | + | ==References== | |
| − | < | + | <references> |
| − | <ref name="ref1"> Hu WL, Jin L, Xu A, Wang YF, Thorne RF, Zhang XD et al. GUARDIN is a p53-responsive long non-coding RNA that is essential for genomic stability[J]. Nature cell biology. 2018, 20(4):492-502.</ref>(1) | + | <ref name="ref1"> Hu WL, Jin L, Xu A, Wang YF, Thorne RF, Zhang XD et al. GUARDIN is a p53-responsive long non-coding RNA that is essential for genomic stability[J]. Nature cell biology. 2018, 20(4):492-502. |
| + | </ref>(1) | ||
<ref name="ref2"> Georgakilas AG, Tsantoulis P, Kotsinas A, Michalopoulos I, Townsend P & Gorgoulis VG. Are common fragile sites merely structural domains or highly organized “functional” units susceptible to oncogenic stress?[J]. Cellular and molecular life sciences. 2014, 71(23):4519-4544.</ref>(2) | <ref name="ref2"> Georgakilas AG, Tsantoulis P, Kotsinas A, Michalopoulos I, Townsend P & Gorgoulis VG. Are common fragile sites merely structural domains or highly organized “functional” units susceptible to oncogenic stress?[J]. Cellular and molecular life sciences. 2014, 71(23):4519-4544.</ref>(2) | ||
| − | <ref name="ref3"> Grossi E & Huarte M. A lncRNA GUARDINg genome integrity[J]. Nature cell biology. 2018, 20(4):371-372.</ref>(3) | + | <ref name="ref3"> Grossi E & Huarte M. A lncRNA GUARDINg genome integrity[J]. Nature cell biology. 2018, 20(4):371-372. |
| + | </ref>(3) | ||
</references> | </references> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Sequence== | ||
| + | >gi|102724571|ref|NR_132738.1|Homo sapiens GUARDIN, long non coding RNA | ||
| + | <dnaseq>ACCAGGCCCCGGGGCCGCGACGCGTCTCTCCAGCCCGGGATCCGGGGAGCTGGGCTGTCCCCAGACCGAC | ||
| + | GGGACAGCGGCATCTCCTCCACCTGAAAAGGAAAGAGGACCAGTTTGCAGGACTCCGAACTGGGCCCGCG | ||
| + | AGATCTCCACCTGCGCAAAACGAAAGGGCGGATTCTCCTTGGACTCACGAGGCAACCGCTCCCCGGGGTG | ||
| + | AGAACGGGGGACTCATTCCTCCGGCACTGGGAGAAGACGATTCTTTAGGAGGAGGACAGGGAAGCGAATG | ||
| + | CTACCCAGATGTCTCAGTATACTGGCTCGCGGCACATCGGGCAAATGAACCTATCAGATAACAACGGCAG | ||
| + | ATCAGATGCCTGAGCATTCAGAAGCAACAGCTGTGGAGCCCCCGTGGGTTCAGAAGGCCTGGTTCCCGTC | ||
| + | TCCAGAAGCCTGGCTCTCCTCCCTCCTGGGCCCACTACTTTGGCTTCTTGTTCCTACGTACAAGGAGTTG | ||
| + | CGAAGAAGGCAACTCTTCCCCTCCCTGAAGCCAAAGGAATGAAACAGACTAGGGCGGGAGAGGTGGCCAT | ||
| + | CCGTCATTAGTTGCGGCCATCAGTAACAGCAACAGGACACGGAACCTAAGGCTGTATCCATCCTGGGCCC | ||
| + | CCAGGGAAACATCAGCGGGAGCGGTACTAAGGAAGTGCTCATCTCTTAGAGACAAAGGCCCATGGAGGGG | ||
| + | AACAGTAACCATCCCCTCCCAATTCAGAAAATGTTAACATAAGCACTTCATTTCTCATGCAGATAACCAC | ||
| + | ATAAGTCTATTAATAAGAAAGAAAGAGAAAGAAAAAAAAGAAAAAGGAATCCATGCCAGCAGGGTATAGG | ||
| + | AATTGGTCTATAGGAGAAAGGGTCACCCACTGAAAGGTGGGCTGAATAGAATTCCTTGCCTGGGCTTTGA | ||
| + | GGTCCTGGCATGGAGAAGGCTGTAGAAATGCTGGCATCAGTGGAACCCTCAATAAACAGAATTCTTGTTA | ||
| + | AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA</dnaseq> | ||
Latest revision as of 14:02, 25 January 2021
GUARDIN, a p53-inducible effector, is critical for guarding the de novo structure of DNA and genomic integrity.
Contents
Annotated Information
Approved Name
Approved symbol:LNCTAM34A
Approved name:long non coding transcriptional activator of miR34a
HGNC ID:HGNC:52548
Previous name:long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 1759
Alias symbol:GUARDIN
RefSeq ID:NR_132738
Prev_symbol:LINC01759
Characteristics
GUARDIN is located between the genes encoding miR-34a and hexose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase/glucose 1-dehydrogenase (H6PD).[1] This region is part of the FRA1A(aphidicolin type, common, Fra(1)(P36)) fragile site that is frequently lost in human cancers.[2] GUARDIN silencing triggered apoptosis and senescence, enhanced cytotoxicity of additional genotoxic stress and inhibited cancer xenograft growth. GUARDIN may constitute a target for cancer treatment.[3]
Function
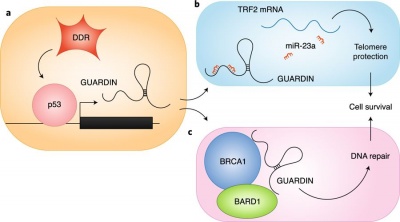
GUARDIN has a role in regulation of cell viability as it is necessary for preventing chromosome end-to-end fusion through maintaining the expression of telomeric repeat-binding factor 2 (TRF2) by sequestering microRNA-23a.[3] GUARDIN modulates the cytotoxic effect of p53. [1] GUARDIN interacts with BRCA1 and BARD1 and is essential for the stabilization of BRCA1. [1] GUARDIN protects genomic integrity through TRF2 and BRCA1. [1]
Regulation
GUARDIN expression is primarily regulated by wild-type p53, and is strongly induced following DNA damage [1].
Expression
GUARDIN expression is primarily regulated by wild-type p53. However, it was detectable in TP53-null cells and in tumours with mutations in TP53, albeit at low levels.GUARDIN transcripts were concurrently reduced in a proportion of colon cancers with gene copy number loss.[1]
Disease
- Colon cancer [1]
Labs working on this lncRNA
- Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) Key Laboratory of Innate Immunity and Chronic Disease, CAS Centre for Excellence in Cell and Molecular Biology, Innovation Centre for Cell Signalling Network, School of Life Sciences, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, China
- Translational Research Institute, Henan Provincial People’s Hospital, Zhengzhou, China
- Department of Gene Therapy and Regulation of Gene Expression, Center for Applied Medical Research, University of Navarra, Pamplona, Spain
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 Hu WL, Jin L, Xu A, Wang YF, Thorne RF, Zhang XD et al. GUARDIN is a p53-responsive long non-coding RNA that is essential for genomic stability[J]. Nature cell biology. 2018, 20(4):492-502.
- ↑ Georgakilas AG, Tsantoulis P, Kotsinas A, Michalopoulos I, Townsend P & Gorgoulis VG. Are common fragile sites merely structural domains or highly organized “functional” units susceptible to oncogenic stress?[J]. Cellular and molecular life sciences. 2014, 71(23):4519-4544.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Grossi E & Huarte M. A lncRNA GUARDINg genome integrity[J]. Nature cell biology. 2018, 20(4):371-372.
Sequence
>gi|102724571|ref|NR_132738.1|Homo sapiens GUARDIN, long non coding RNA
000081 CATCTCCTCC ACCTGAAAAG GAAAGAGGAC CAGTTTGCAG GACTCCGAAC TGGGCCCGCG AGATCTCCAC CTGCGCAAAA 000160
000161 CGAAAGGGCG GATTCTCCTT GGACTCACGA GGCAACCGCT CCCCGGGGTG AGAACGGGGG ACTCATTCCT CCGGCACTGG 000240
000241 GAGAAGACGA TTCTTTAGGA GGAGGACAGG GAAGCGAATG CTACCCAGAT GTCTCAGTAT ACTGGCTCGC GGCACATCGG 000320
000321 GCAAATGAAC CTATCAGATA ACAACGGCAG ATCAGATGCC TGAGCATTCA GAAGCAACAG CTGTGGAGCC CCCGTGGGTT 000400
000401 CAGAAGGCCT GGTTCCCGTC TCCAGAAGCC TGGCTCTCCT CCCTCCTGGG CCCACTACTT TGGCTTCTTG TTCCTACGTA 000480
000481 CAAGGAGTTG CGAAGAAGGC AACTCTTCCC CTCCCTGAAG CCAAAGGAAT GAAACAGACT AGGGCGGGAG AGGTGGCCAT 000560
000561 CCGTCATTAG TTGCGGCCAT CAGTAACAGC AACAGGACAC GGAACCTAAG GCTGTATCCA TCCTGGGCCC CCAGGGAAAC 000640
000641 ATCAGCGGGA GCGGTACTAA GGAAGTGCTC ATCTCTTAGA GACAAAGGCC CATGGAGGGG AACAGTAACC ATCCCCTCCC 000720
000721 AATTCAGAAA ATGTTAACAT AAGCACTTCA TTTCTCATGC AGATAACCAC ATAAGTCTAT TAATAAGAAA GAAAGAGAAA 000800
000801 GAAAAAAAAG AAAAAGGAAT CCATGCCAGC AGGGTATAGG AATTGGTCTA TAGGAGAAAG GGTCACCCAC TGAAAGGTGG 000880
000881 GCTGAATAGA ATTCCTTGCC TGGGCTTTGA GGTCCTGGCA TGGAGAAGGC TGTAGAAATG CTGGCATCAG TGGAACCCTC 000960
000961 AATAAACAGA ATTCTTGTTA AAAAAAAAAA AAAAAAAAAA AAA