Difference between revisions of "LncRNA-ATB"
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | '' | + | ''LncRNA-ATB'', a Long Noncoding RNA activated by TGF-β associated with poor prognosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) |
==Annotation== | ==Annotation== | ||
===Name=== | ===Name=== | ||
| − | '' | + | ''LncRNA-ATB'', Long Noncoding RNA activated by TGF-β <ref name="ref1" /> |
===Alias=== | ===Alias=== | ||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
===Characteristics=== | ===Characteristics=== | ||
| − | '' | + | ''LncRNA-ATB'' is a long noncoding RNA which is primarily activated by Transforming Growth Factor β (TGF-β) has been reported to be involved in specific physiological and pathological processes in human diseases, and could serve as biomarkers for cancers. ''LncRNA-ATB'' is poly (A)-negative and mainly located in the cytoplasm. ''LncRNA-ATB'' has no protein-coding potential since analysis of the sequences by ORF Finder from the National Center for Biotechnology Information failed to predict a protein of more than 55 amino acids. Moreover, ''lncRNA-ATB'' does not contain a valid Kozak sequence. <ref name="ref1" /> |
| + | |||
===Function=== | ===Function=== | ||
| − | '' | + | ''LncRNA-ATB'' downregulates E-cadherin (E-cad) and induces epithelial-to- mesenchymal transition thereby promoting the invasion-metastasis in carcinoma. <ref name="ref2" /> |
| − | '' | + | ''LncRNA-ATB'' also competitively binds the miR-200 family and then induces EMT and invasion by upregulating ZEB1 and ZEB2. lncRNA-ATB promotes EMT, HCC cell invasion, and metastatic organ colonization. ''LncRNA-ATB'' promotes organ colonization of disseminated tumor cells by binding IL-11 mRNA, autocrine induction of IL-11, and triggering STAT3 signaling. ''LncRNA-ATB'', as a mediator of TGF-β signaling, could predispose HCC patients to metastases and may serve as a potential target for antimetastatic therapies. <ref name="ref1" /> |
===Regulation=== | ===Regulation=== | ||
| − | '' | + | ''LncRNA-ATB'' is regulated by Transforming Growth Factor β (TGF-β). Studies indicated that a short-term TGF-β treatment was sufficient to activate ''lncRNA-ATB'', which implied that ''lncRNA-ATB'' may be a direct target of TGF-β/Smad pathway, but how TGF-β activates ''lncRNA-ATB'' requires further investigation.<ref name="ref1" /> Long non-coding RNA-activated by TGF-β was upregulated in colon cancer tissues compared with adjacent mucosa. ''LncRNA-ATB'' levels were also higher in metastatic cancer tissues <ref name="ref2" /> |
===Expression=== | ===Expression=== | ||
| − | High level expression of ''lncRNA-ATB'' is associated with liver cirrhosis in patients with HCC and poor prognosis. High expression of ''lncRNA-ATB'' is a robust predictor of poor survival. ''LncRNA-ATB'' was activated by TGF-β and induced EMT not only in HCC cells, but also in colorectal cancer and breast cancer cells. <ref name="ref1" /> Striking differences were observed in overall survival and disease-free survival in cases with both high ''lncRNA-ATB'' expression and low E-cad expression. Reduction of ''lncRNA-ATB'' increased expression of epithelial markers E-cad, ZO-1, and decreased expression of mesenchymal markers ZEB1 and N-cadherin (N-cad), and significantly influenced colon cancer cell progression.<ref name="ref2" /> LncRNA-ATB expression is also commonly increased in Coal Workers’ Pneumoconiosis (CWP) and significantly correlates with the TGF-β1 in CWP patients. Furthermore, elevated ''lncRNA-ATB'' was associated with CWP risk and may serve as a potential biomarker for CWP.<ref name="ref3" /> | + | [[File: lncrna-ATB.jpg|right|thumb|400px|'''Scatter plots of ''lncRNA-ATB'' expressions in different groups. Solid circles, healthy controls; Solid squares, healthy coal miners; Solid triangles, CWP patients. (* p < 0.05).''' <ref name="ref3" />.]] |
| + | High level expression of ''lncRNA-ATB'' is associated with liver cirrhosis in patients with HCC and poor prognosis. High expression of ''lncRNA-ATB'' is a robust predictor of poor survival. ''LncRNA-ATB'' was activated by TGF-β and induced EMT not only in HCC cells, but also in colorectal cancer and breast cancer cells. <ref name="ref1" /> Striking differences were observed in overall survival and disease-free survival in cases with both high ''lncRNA-ATB'' expression and low E-cad expression. Reduction of ''lncRNA-ATB'' increased expression of epithelial markers E-cad, ZO-1, and decreased expression of mesenchymal markers ZEB1 and N-cadherin (N-cad), and significantly influenced colon cancer cell progression.<ref name="ref2" /> ''LncRNA-ATB'' expression is also commonly increased in Coal Workers’ Pneumoconiosis (CWP) and significantly correlates with the TGF-β1 in CWP patients. Furthermore, elevated ''lncRNA-ATB'' was associated with CWP risk and may serve as a potential biomarker for CWP.<ref name="ref3" /> | ||
{| class='wikitable' style="text-align:center" | {| class='wikitable' style="text-align:center" | ||
Latest revision as of 05:06, 20 November 2018
LncRNA-ATB, a Long Noncoding RNA activated by TGF-β associated with poor prognosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC)
Contents
Annotation
Name
LncRNA-ATB, Long Noncoding RNA activated by TGF-β [1]
Alias
NA
Characteristics
LncRNA-ATB is a long noncoding RNA which is primarily activated by Transforming Growth Factor β (TGF-β) has been reported to be involved in specific physiological and pathological processes in human diseases, and could serve as biomarkers for cancers. LncRNA-ATB is poly (A)-negative and mainly located in the cytoplasm. LncRNA-ATB has no protein-coding potential since analysis of the sequences by ORF Finder from the National Center for Biotechnology Information failed to predict a protein of more than 55 amino acids. Moreover, lncRNA-ATB does not contain a valid Kozak sequence. [1]
Function
LncRNA-ATB downregulates E-cadherin (E-cad) and induces epithelial-to- mesenchymal transition thereby promoting the invasion-metastasis in carcinoma. [2]
LncRNA-ATB also competitively binds the miR-200 family and then induces EMT and invasion by upregulating ZEB1 and ZEB2. lncRNA-ATB promotes EMT, HCC cell invasion, and metastatic organ colonization. LncRNA-ATB promotes organ colonization of disseminated tumor cells by binding IL-11 mRNA, autocrine induction of IL-11, and triggering STAT3 signaling. LncRNA-ATB, as a mediator of TGF-β signaling, could predispose HCC patients to metastases and may serve as a potential target for antimetastatic therapies. [1]
Regulation
LncRNA-ATB is regulated by Transforming Growth Factor β (TGF-β). Studies indicated that a short-term TGF-β treatment was sufficient to activate lncRNA-ATB, which implied that lncRNA-ATB may be a direct target of TGF-β/Smad pathway, but how TGF-β activates lncRNA-ATB requires further investigation.[1] Long non-coding RNA-activated by TGF-β was upregulated in colon cancer tissues compared with adjacent mucosa. LncRNA-ATB levels were also higher in metastatic cancer tissues [2]
Expression
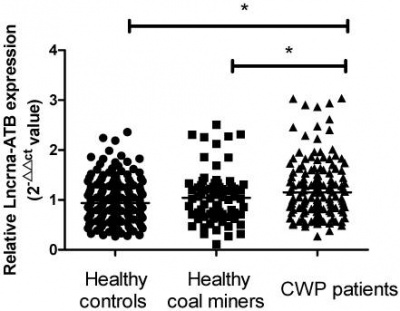
High level expression of lncRNA-ATB is associated with liver cirrhosis in patients with HCC and poor prognosis. High expression of lncRNA-ATB is a robust predictor of poor survival. LncRNA-ATB was activated by TGF-β and induced EMT not only in HCC cells, but also in colorectal cancer and breast cancer cells. [1] Striking differences were observed in overall survival and disease-free survival in cases with both high lncRNA-ATB expression and low E-cad expression. Reduction of lncRNA-ATB increased expression of epithelial markers E-cad, ZO-1, and decreased expression of mesenchymal markers ZEB1 and N-cadherin (N-cad), and significantly influenced colon cancer cell progression.[2] LncRNA-ATB expression is also commonly increased in Coal Workers’ Pneumoconiosis (CWP) and significantly correlates with the TGF-β1 in CWP patients. Furthermore, elevated lncRNA-ATB was associated with CWP risk and may serve as a potential biomarker for CWP.[3]
| Experiment | Forward primer | Reverse primer |
|---|---|---|
| qRT-PCR | 5'-CTTCACCAGCACCCAGAGA- 3' | 5'-AAGACAGAAAAACAGTTCCGAGTC- 3'[3] |
Diseases
- Breast cancer [1]
- Coal Workers’ Pneumoconiosis CWP [3]
- Colorectal cancer [2]
- Hepatocellular Carcinoma HCC [1]
Labs Working
- Department of Medical Genetics, Second Military Medical University, Shanghai, 200433, China
- The Third Department of Hepatic Surgery, Eastern Hepatobiliary Hospital, Second Military Medical University, Shanghai, 200433, China
- The Fifth Department of Hepatic Surgery, Eastern Hepatobiliary Hospital, Second Military Medical University, Shanghai, 200433, China
- Department of General Surgery, Shanghai Jiao Tong University Affiliated First People's Hospital, Shanghai, China
- Department of Occupational & Environmental Health, School of Public Health, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430030, China
- Key Laboratory of Environment and Health, Ministry of Education & Ministry of Environmental Protection, and State Key Laboratory of Environmental Health (Incubating), School of Public Health, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430030, China
- Long Hua Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Shenzhen 518109, China
Reference
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 Yuan J-h, Yang F, Wang F, Ma J-z, Guo Y-j, Tao Q-f et al. A Long Noncoding RNA Activated by TGF-β Promotes the Invasion-Metastasis Cascade in Hepatocellular Carcinoma[J]. Cancer Cell. 2014, 25(5):666-681.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Yue B, Qiu S, Zhao S, Liu C, Zhang D, Yu F et al. LncRNA-ATB mediated E-cadherin repression promotes the progression of colon cancer and predicts poor prognosis[J]. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology. 2016, 31(3):595-603.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Ma J, Cui X, Rong Y, Zhou Y, Guo Y, Zhou M et al. Plasma LncRNA-ATB, a Potential Biomarker for Diagnosis of Patients with Coal Workers' Pneumoconiosis: A Case-Control Study[J]. International journal of molecular sciences. 2016, 17(8):1367.