Difference between revisions of "LINC00665"
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
===Characteristics === | ===Characteristics === | ||
| + | Please input characteristics labs here. | ||
===Expression=== | ===Expression=== | ||
LINC00665 was Overexpressed in patients with HCC.<ref name="ref2" /> | LINC00665 was Overexpressed in patients with HCC.<ref name="ref2" /> | ||
| − | ==Function== | + | ===Function=== |
The target genes coregulated by LINC00665 and MIR378D2 mainly regulated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolism and response to calcium ion.<ref name="ref1" /> | The target genes coregulated by LINC00665 and MIR378D2 mainly regulated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolism and response to calcium ion.<ref name="ref1" /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | LINC00665 regulates pathways in the cell cycle to facilitate the development and progression of HCC through ten identified core genes: CDK1, BUB1B, BUB1, PLK1, CCNB2, CCNB1, CDC20, ESPL1, MAD2L1, and CCNA2.<ref name="ref2" /> | ||
==Labs working on this lncRNA== | ==Labs working on this lncRNA== | ||
Latest revision as of 07:37, 12 August 2019
Contents
Annotated Information
Name
Approved symbol: LINC00665
Approved name: long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 665
HGNC ID: HGNC:44323
RefSeq ID: NR_038278
LncBook ID: HSALNT0259139
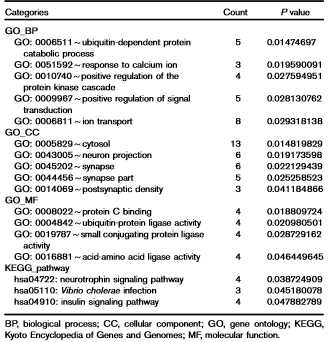
Enrichment of target genes coregulated by LINC00665 and MIR378D2[1]
Chromosome
19q13.12
Characteristics
Please input characteristics labs here.
Expression
LINC00665 was Overexpressed in patients with HCC.[2]
Function
The target genes coregulated by LINC00665 and MIR378D2 mainly regulated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolism and response to calcium ion.[1]
LINC00665 regulates pathways in the cell cycle to facilitate the development and progression of HCC through ten identified core genes: CDK1, BUB1B, BUB1, PLK1, CCNB2, CCNB1, CDC20, ESPL1, MAD2L1, and CCNA2.[2]
Labs working on this lncRNA
- Department of Oral Medicine, Beijing Stomatological Hospital bDepartment of Stomatology, Beijing Ditan Hospital cDepartment of Stomatology, Beijing Tongren Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China.[1]
- Department of Medical Ultrasonics, First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University, Nanning, Guangxi, China (mainland).[2]
- Department of Pathology, First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University, Nanning, Guangxi, China (mainland).[2]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Jia, H., X. Wang, and Z. Sun, Exploring the molecular pathogenesis and biomarkers of high risk oral premalignant lesions on the basis of long noncoding RNA expression profiling by serial analysis of gene expression. Eur J Cancer Prev, 2017.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Wen DY, Lin P, Pang YY, et al. Expression of the Long Intergenic Non-Protein Coding RNA 665 (LINC00665) Gene and the Cell Cycle in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Using The Cancer Genome Atlas, the Gene Expression Omnibus, and Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction[J]. Med Sci Monit, 2018, 24: 2786-2808.