Difference between revisions of "ENST00000609176.1"
(→Function) |
|||
| (23 intermediate revisions by 8 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | ''AIRN'' regulates genomic imprinting of a cluster of autosomal genes in cis. | |
==Annotated Information== | ==Annotated Information== | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
===Name=== | ===Name=== | ||
| − | AIRN | + | ''AIRN'' Antisense of IGF2R long noncoding RNA |
| − | |||
AIR | AIR | ||
| − | |||
IGF2RAS | IGF2RAS | ||
===Characteristics=== | ===Characteristics=== | ||
| − | + | Unspliced ''AIRN'' is transcribed from an antisense promoter located in intron 2 of the Igf2r (insulin-like growth-factor type-2 receptor) gene<ref name="ref1"/><ref name="ref2"/>. | |
| + | A number of spliced isoforms of ''AIRN'' varies in size from 500bp to ~1.4kb<ref name="ref3"/>. | ||
| + | ''AIRN'' long noncoding RNA is Imprinte and is expressed only from paternal allele<ref name="ref1"/><ref name="ref2"/>. | ||
| + | Unspliced ''AIRN'' is unstable, and is localised to the nucleus. Stable spliced isoforms of ''AIRN'' are found in nucleus and cytoplasm<ref name="ref3"/>. | ||
| − | + | ===Function=== | |
| − | + | ''AIRN'' Regulates genomic imprinting of a cluster of autosomal genes (Igf2r, Slc22a2 and Slc22a3) in cis, on mouse chromosome 17 <ref name="ref4"/>. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | Truncation of ''AIRN'' disrupts imprinting not only of Igf2r but also the nearby non-overlapping genes Slc22a2 and Slc22a3, leading to mice with a lower birth weight <ref name="ref4"/>. | |
| − | + | ''AIRN'' silences Igf2r through transcription alone and not via its RNA product<ref name="ref11"/><ref name="ref10"/>. | |
| − | + | [[File: Airn.png |right|thumb|500px| ''AIRN'' can silence Igf2r at any time by transcriptional overlap <ref name="ref10"/>]] | |
| + | ''AIRN'' forms a "cloud" over the imprinted DNA locus, binding to chromatin. | ||
| − | + | ''AIRN'' Recruits G9a histone methyltransferase to epigenetically silence Slc22a3 <ref name="ref5"/>. Slc22a3 and Slc22a2 are only imprinted at a specific time point in placental development. Outside of this time point the ''AIRN'' "cloud"/ ''AIRN'' chromatin binding and repressive histone modification are not found on these gene loci<ref name="ref5"/>. | |
| − | + | Although ''AIRN'' transcription can repress Igf2r at any time, it does so less efficiently when paternal Igf2r expression is high, as in late ESC differentiation <ref name="ref9"/>. Continuous ''AIRN'' expression is needed to maintain Igf2r silencing, but only until the paternal Igf2r promoter is methylated<ref name="ref9"/>. | |
===Regulation=== | ===Regulation=== | ||
| − | + | The unmethlyated imprint control region (ICR) acts as promoter for ''AIRN'', which then silence all imprinted genes in the cluster on that parental allele<ref name="ref4"/><ref name="ref11"/>. | |
===Expression=== | ===Expression=== | ||
| − | + | ''AIRN'' is expressed during embryonic development, in the placenta<ref name="ref1"/><ref name="ref2"/>, adult brain, lung and heart<ref name="ref3"/>. | |
| + | ''AIRN'' is also expressed in glial cells of the developing brain but not in neurons, explains lack of Igf2r imprinting in these neurons<ref name="ref6"/>. | ||
| + | In human, IGF2R gene is predominantly nonimprinted and ''AIRN'' is typically not expressed; however, expression was identified in association with 16–40% of Wilms’ tumors<ref name="ref7"/>. | ||
| + | Bovine ''AIRN'' is not expressed in blastocyst-stage embryos. It is expressed in an increasing proportion of embryos around the time of maternal recognition of pregnancy and is expressed following implantation <ref name="ref8"/>. | ||
| − | + | ===Disease=== | |
| + | *Wilms’tumors <ref name="ref7"/>. | ||
| − | |||
| − | == | + | ==Labs working on this lncRNA== |
| − | + | *CeMM Research Center for Molecular Medicine of the Austrian Academy of Sciences, Lazarettgasse 14, 1090 Vienna, Austria. | |
| − | + | *Department of Molecular Genetics, The Netherlands Cancer Institute, Plesmanlaan 121, 1066CX, Amsterdam, The Netherlands. | |
| − | + | *Institute of Molecular Pathology, Vienna. | |
| + | *The Netherlands Cancer Institute (H5), Amsterdam. | ||
| − | === | + | ==References== |
| − | + | <references> | |
| + | <ref name="ref1"> Lyle, R., et al. (2000). "The imprinted antisense RNA at the Igf2r locus overlaps but does not imprint Mas1." Nat Genet 25(1): 19-21. </ref> | ||
| + | <ref name="ref2"> Wutz, A., et al. (1997). "Imprinted expression of the Igf2r gene depends on an intronic CpG island." Nature 389(6652): 745-749. </ref> | ||
| + | <ref name="ref3">Seidl, C. I., et al. (2006). "The imprinted Air ncRNA is an atypical RNAPII transcript that evades splicing and escapes nuclear export." EMBO J 25(15): 3565-3575.</ref> | ||
| + | <ref name="ref4"> Sleutels, F., et al. (2002). "The non-coding Air RNA is required for silencing autosomal imprinted genes." Nature 415(6873): 810-813.</ref> | ||
| + | <ref name="ref5"> Nagano, T., et al. (2008). "The Air noncoding RNA epigenetically silences transcription by targeting G9a to chromatin." Science 322(5908): 1717-1720. </ref> | ||
| + | <ref name="ref6">Yamasaki, Y., et al. (2005). "Neuron-specific relaxation of Igf2r imprinting is associated with neuron-specific histone modifications and lack of its antisense transcript Air." Hum Mol Genet 14(17): 2511-2520. </ref> | ||
| + | <ref name="ref7"> Yotova, I. Y., et al. (2008). "Identification of the human homolog of the imprinted mouse Air non-coding RNA." Genomics 92(6): 464-473. </ref> | ||
| + | <ref name="ref8">Farmer, W. T., et al. (2013). "Expression of antisense of insulin-like growth factor-2 receptor RNA non-coding (AIRN) during early gestation in cattle." Anim Reprod Sci 138(1-2): 64-73.</ref> | ||
| + | <ref name="ref9">Santoro, F., et al. (2013). "Imprinted Igf2r silencing depends on continuous Airn lncRNA expression and is not restricted to a developmental window." Development 140(6): 1184-1195. </ref> | ||
| + | <ref name="ref10"> Santoro, F. and F. M. Pauler (2013). "Silencing by the imprinted Airn macro lncRNA: transcription is the answer." Cell Cycle 12(5): 711-712.</ref> | ||
| + | <ref name="ref11">Latos, P.A., Pauler, F.M., Koerner, M.V., Senergin, H.B., Hudson, Q.J., Stocsits, R.R., Allhoff, W., Stricker, S.H., Klement, R.M., Warczok, K.E. et al. (2012) Airn transcriptional overlap, but not its lncRNA products, induces imprinted Igf2r silencing. Science, 338, 1469-1472.</ref> | ||
| + | </references> | ||
| − | = | + | sequence = 100271873 |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ===Sequence=== | |
| − | + | >gi|100271873|ref|NR_047511.1|Homo sapiens antisense of IGF2R non-protein coding RNA (AIRN), transcript variant 1, long non-coding RNA | |
| − | + | <dnaseq>GAAAGCACACACCATGCTGGAAAGGAGAGAGAAGGAAAAACCCACTCCTAGCCACACAATGGTGGATCTT | |
| − | + | AATATCCAATGAAAAGAAAAAATTCTAATCTAGGTCACACACAATAACCCAATATAAAATGAACAAGACA | |
| − | + | TGATCAAGCAAATCAAAGAAAAATGTACATCAATAAATATGTTAAGACATGTTCAATGTTACTGGTGATC | |
| − | + | AAGGAATTTCAAATCAAGACCAAAATGGTATACCATTTACAACCATCCCTCTGGCAAAAATTAAATACCA | |
| − | + | AGTGTCAGCCATGAGGTGGCTCAGAGCTCTCCTGTATTGCTAGTGAAATGTTAACTGGTTCAACAACTAT | |
| − | + | GTAAGTCAGCAGGACATTATGTCCTAAAATTGAACATTCGTGTGCCCTATGACCTAGTTACTCCACTCAG | |
| − | + | GTCTATATAAAAGAGAAAACCATGCACATATGGAACATGCACAGCAGAAAATGTGAAAGAATATCTCATG | |
| − | + | CTCTTCAGAAGAGCAAAAACCTGGAAATGACCAAAGGCCCATCAACAGAAGAGTGGATAAATTAACTTCA | |
| − | + | GCAGATCCACACAAAATATCACAGCAGTCAGAAGGAATAAACCACAGTGAAAAACAACAATACGGTTGAT | |
| − | + | TTTTAGTAATATTACTGTTATCACTTAAGTCCCAAAAAGTTACACATAGGAAGATAACTTAGTTGCAAAC | |
| − | + | ACACAGATTTTTTTTTTTTGGAAATTAGATACAGTAAAAAAAAAAAAAAATTAATACAAGATGGGAGCTA | |
| − | + | ATGATTACTCCTAGCGAAAAGTGAAAGAGGAAAGAGTAAAACAGATAGTGGTTACTGCCAAGATCCTAGA | |
| − | + | TTTTTGTTGGAAACAGTGCTCGCTACATTATACAAAACAACTAATTTTTTAAAAGGAAAAAGGTTAGTCT | |
| + | ATGGATTAACACATGGCTCACTGTACGTGCCATGAGCTCGGGATGATAGCTGATCCAATCCCATATACAC | ||
| + | CTGAAGTCTTGGGGCAGGGGCGGACCACGAGTCAGCGCGCCCCCACAGCACCAGGCTGATGGCCCCGTGG | ||
| + | TTCTTCTGCCTGCAAGCAAAAGTCAGCCACGATCATCCTTCTCCATCTGCAACACCCAGGGTCTTTTCTA | ||
| + | AAACTTTTGCCCAGTCGGCTCAGCCAAAAGGACACAGAAGCCCTGCAGAGGCTCTGAAACCAAGCTGCCA | ||
| + | TGGCTCCCAGTTCGACATCATGTCACCGGAGCCTGCACAGATGAACCAAGCTTGCAACACGGGAGGAACC | ||
| + | TAAGCGCTGGACTGAGGAGCGGGACTGAAATAAGAAGCGCACACCACATGGCAAGATCCAGGATCCAATC | ||
| + | AGATAGAGCCCTGGTGTCATCTAATTGCAAGATCCAATCAGAACACACCTCATTACCTTATGGTATTGCC | ||
| + | AGACTATCAGGAGAGACCATAAATCAGATAAAAACATGAGTTGTATCCAAAACTCAACCAGGTATCATCT | ||
| + | TAAATATCCAACAGAATTC</dnaseq> | ||
Latest revision as of 05:40, 14 November 2018
AIRN regulates genomic imprinting of a cluster of autosomal genes in cis.
Contents
Annotated Information
Name
AIRN Antisense of IGF2R long noncoding RNA AIR IGF2RAS
Characteristics
Unspliced AIRN is transcribed from an antisense promoter located in intron 2 of the Igf2r (insulin-like growth-factor type-2 receptor) gene[1][2]. A number of spliced isoforms of AIRN varies in size from 500bp to ~1.4kb[3]. AIRN long noncoding RNA is Imprinte and is expressed only from paternal allele[1][2]. Unspliced AIRN is unstable, and is localised to the nucleus. Stable spliced isoforms of AIRN are found in nucleus and cytoplasm[3].
Function
AIRN Regulates genomic imprinting of a cluster of autosomal genes (Igf2r, Slc22a2 and Slc22a3) in cis, on mouse chromosome 17 [4].
Truncation of AIRN disrupts imprinting not only of Igf2r but also the nearby non-overlapping genes Slc22a2 and Slc22a3, leading to mice with a lower birth weight [4]. AIRN silences Igf2r through transcription alone and not via its RNA product[5][6].
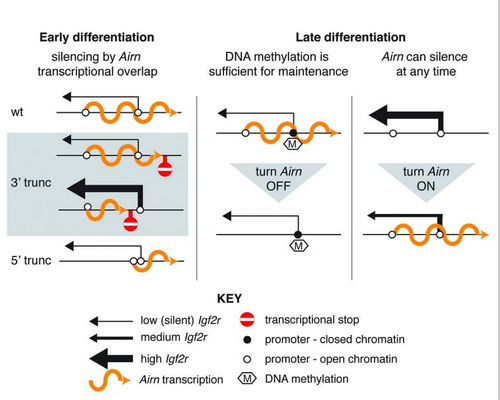
AIRN forms a "cloud" over the imprinted DNA locus, binding to chromatin.
AIRN Recruits G9a histone methyltransferase to epigenetically silence Slc22a3 [7]. Slc22a3 and Slc22a2 are only imprinted at a specific time point in placental development. Outside of this time point the AIRN "cloud"/ AIRN chromatin binding and repressive histone modification are not found on these gene loci[7].
Although AIRN transcription can repress Igf2r at any time, it does so less efficiently when paternal Igf2r expression is high, as in late ESC differentiation [8]. Continuous AIRN expression is needed to maintain Igf2r silencing, but only until the paternal Igf2r promoter is methylated[8].
Regulation
The unmethlyated imprint control region (ICR) acts as promoter for AIRN, which then silence all imprinted genes in the cluster on that parental allele[4][5].
Expression
AIRN is expressed during embryonic development, in the placenta[1][2], adult brain, lung and heart[3]. AIRN is also expressed in glial cells of the developing brain but not in neurons, explains lack of Igf2r imprinting in these neurons[9]. In human, IGF2R gene is predominantly nonimprinted and AIRN is typically not expressed; however, expression was identified in association with 16–40% of Wilms’ tumors[10]. Bovine AIRN is not expressed in blastocyst-stage embryos. It is expressed in an increasing proportion of embryos around the time of maternal recognition of pregnancy and is expressed following implantation [11].
Disease
- Wilms’tumors [10].
Labs working on this lncRNA
- CeMM Research Center for Molecular Medicine of the Austrian Academy of Sciences, Lazarettgasse 14, 1090 Vienna, Austria.
- Department of Molecular Genetics, The Netherlands Cancer Institute, Plesmanlaan 121, 1066CX, Amsterdam, The Netherlands.
- Institute of Molecular Pathology, Vienna.
- The Netherlands Cancer Institute (H5), Amsterdam.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Lyle, R., et al. (2000). "The imprinted antisense RNA at the Igf2r locus overlaps but does not imprint Mas1." Nat Genet 25(1): 19-21.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Wutz, A., et al. (1997). "Imprinted expression of the Igf2r gene depends on an intronic CpG island." Nature 389(6652): 745-749.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Seidl, C. I., et al. (2006). "The imprinted Air ncRNA is an atypical RNAPII transcript that evades splicing and escapes nuclear export." EMBO J 25(15): 3565-3575.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Sleutels, F., et al. (2002). "The non-coding Air RNA is required for silencing autosomal imprinted genes." Nature 415(6873): 810-813.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Latos, P.A., Pauler, F.M., Koerner, M.V., Senergin, H.B., Hudson, Q.J., Stocsits, R.R., Allhoff, W., Stricker, S.H., Klement, R.M., Warczok, K.E. et al. (2012) Airn transcriptional overlap, but not its lncRNA products, induces imprinted Igf2r silencing. Science, 338, 1469-1472.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Santoro, F. and F. M. Pauler (2013). "Silencing by the imprinted Airn macro lncRNA: transcription is the answer." Cell Cycle 12(5): 711-712.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Nagano, T., et al. (2008). "The Air noncoding RNA epigenetically silences transcription by targeting G9a to chromatin." Science 322(5908): 1717-1720.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Santoro, F., et al. (2013). "Imprinted Igf2r silencing depends on continuous Airn lncRNA expression and is not restricted to a developmental window." Development 140(6): 1184-1195.
- ↑ Yamasaki, Y., et al. (2005). "Neuron-specific relaxation of Igf2r imprinting is associated with neuron-specific histone modifications and lack of its antisense transcript Air." Hum Mol Genet 14(17): 2511-2520.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Yotova, I. Y., et al. (2008). "Identification of the human homolog of the imprinted mouse Air non-coding RNA." Genomics 92(6): 464-473.
- ↑ Farmer, W. T., et al. (2013). "Expression of antisense of insulin-like growth factor-2 receptor RNA non-coding (AIRN) during early gestation in cattle." Anim Reprod Sci 138(1-2): 64-73.
sequence = 100271873
Sequence
>gi|100271873|ref|NR_047511.1|Homo sapiens antisense of IGF2R non-protein coding RNA (AIRN), transcript variant 1, long non-coding RNA
000081 GAAAAGAAAA AATTCTAATC TAGGTCACAC ACAATAACCC AATATAAAAT GAACAAGACA TGATCAAGCA AATCAAAGAA 000160
000161 AAATGTACAT CAATAAATAT GTTAAGACAT GTTCAATGTT ACTGGTGATC AAGGAATTTC AAATCAAGAC CAAAATGGTA 000240
000241 TACCATTTAC AACCATCCCT CTGGCAAAAA TTAAATACCA AGTGTCAGCC ATGAGGTGGC TCAGAGCTCT CCTGTATTGC 000320
000321 TAGTGAAATG TTAACTGGTT CAACAACTAT GTAAGTCAGC AGGACATTAT GTCCTAAAAT TGAACATTCG TGTGCCCTAT 000400
000401 GACCTAGTTA CTCCACTCAG GTCTATATAA AAGAGAAAAC CATGCACATA TGGAACATGC ACAGCAGAAA ATGTGAAAGA 000480
000481 ATATCTCATG CTCTTCAGAA GAGCAAAAAC CTGGAAATGA CCAAAGGCCC ATCAACAGAA GAGTGGATAA ATTAACTTCA 000560
000561 GCAGATCCAC ACAAAATATC ACAGCAGTCA GAAGGAATAA ACCACAGTGA AAAACAACAA TACGGTTGAT TTTTAGTAAT 000640
000641 ATTACTGTTA TCACTTAAGT CCCAAAAAGT TACACATAGG AAGATAACTT AGTTGCAAAC ACACAGATTT TTTTTTTTTG 000720
000721 GAAATTAGAT ACAGTAAAAA AAAAAAAAAA TTAATACAAG ATGGGAGCTA ATGATTACTC CTAGCGAAAA GTGAAAGAGG 000800
000801 AAAGAGTAAA ACAGATAGTG GTTACTGCCA AGATCCTAGA TTTTTGTTGG AAACAGTGCT CGCTACATTA TACAAAACAA 000880
000881 CTAATTTTTT AAAAGGAAAA AGGTTAGTCT ATGGATTAAC ACATGGCTCA CTGTACGTGC CATGAGCTCG GGATGATAGC 000960
000961 TGATCCAATC CCATATACAC CTGAAGTCTT GGGGCAGGGG CGGACCACGA GTCAGCGCGC CCCCACAGCA CCAGGCTGAT 001040
001041 GGCCCCGTGG TTCTTCTGCC TGCAAGCAAA AGTCAGCCAC GATCATCCTT CTCCATCTGC AACACCCAGG GTCTTTTCTA 001120
001121 AAACTTTTGC CCAGTCGGCT CAGCCAAAAG GACACAGAAG CCCTGCAGAG GCTCTGAAAC CAAGCTGCCA TGGCTCCCAG 001200
001201 TTCGACATCA TGTCACCGGA GCCTGCACAG ATGAACCAAG CTTGCAACAC GGGAGGAACC TAAGCGCTGG ACTGAGGAGC 001280
001281 GGGACTGAAA TAAGAAGCGC ACACCACATG GCAAGATCCA GGATCCAATC AGATAGAGCC CTGGTGTCAT CTAATTGCAA 001360
001361 GATCCAATCA GAACACACCT CATTACCTTA TGGTATTGCC AGACTATCAG GAGAGACCAT AAATCAGATA AAAACATGAG 001440
001441 TTGTATCCAA AACTCAACCA GGTATCATCT TAAATATCCA ACAGAATTC