Difference between revisions of "PRAL"
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
===Function=== | ===Function=== | ||
| + | [[File: PLAR.jpg|right|thumb|400px|'''Copy number deletion of genomic long noncoding RNA ''PRAL'' correlates with poor survival in HCC patients.''' <ref name="ref1" />.]] | ||
Somatic copy number variation of lncRNA-PRAL is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) growth and lncRNA-PRAL may serve as a potential target for antitumor therapy <ref name="ref1" />. LncRNA-PRAL could inhibit HCC growth and induce apoptosis in vivo and in vitro through p53 <ref name="ref1" />. The three stem-loop motifs at the 5' end of lncRNA-PRAL facilitates the combination of HSP90 and p53 and thus competitively inhibites MDM2-dependent p53 ubiquitination, resulting in enhanced p53 stability <ref name="ref1" />. | Somatic copy number variation of lncRNA-PRAL is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) growth and lncRNA-PRAL may serve as a potential target for antitumor therapy <ref name="ref1" />. LncRNA-PRAL could inhibit HCC growth and induce apoptosis in vivo and in vitro through p53 <ref name="ref1" />. The three stem-loop motifs at the 5' end of lncRNA-PRAL facilitates the combination of HSP90 and p53 and thus competitively inhibites MDM2-dependent p53 ubiquitination, resulting in enhanced p53 stability <ref name="ref1" />. | ||
| − | PRAL might be a tumor suppressor in lung cancer <ref name="ref2" />. The transcript level of PRAL is decreased in lung cancer in vivo and in vitro, and overexpression of PRAL inhibites cell proliferation by upregulating the expression of P53 <ref name="ref2" />. | + | ''PRAL'' might be a tumor suppressor in lung cancer <ref name="ref2" />. The transcript level of PRAL is decreased in lung cancer in vivo and in vitro, and overexpression of PRAL inhibites cell proliferation by upregulating the expression of P53 <ref name="ref2" />. |
===Expression=== | ===Expression=== | ||
| Line 28: | Line 29: | ||
==Labs working on this lncRNA== | ==Labs working on this lncRNA== | ||
| − | *Department of Medical Genetics, Second Military Medical University, Shanghai, 200433, China. | + | * Department of Medical Genetics, Second Military Medical University, Shanghai, 200433, China.<ref name="ref1" /> |
| − | *The Third Department of Hepatic Surgery, Eastern Hepatobiliary Hospital, Second Military Medical University, Shanghai, 200433, China. | + | * The Third Department of Hepatic Surgery, Eastern Hepatobiliary Hospital, Second Military Medical University, Shanghai, 200433, China.<ref name="ref1" /> |
| − | *Department of Epidemiology, Second Military Medical University, Shanghai, 200433, China.<ref name="ref1" /> | + | * Department of Epidemiology, Second Military Medical University, Shanghai, 200433, China.<ref name="ref1" /> |
| − | *Department of Surgery, Xi'an Red Cross Hospital, Affiliated to School of Medicine, Xi'an Jiao Tong University, Xi'an, Shanxi, China(mainland). | + | * Department of Surgery, Xi'an Red Cross Hospital, Affiliated to School of Medicine, Xi'an Jiao Tong University, Xi'an, Shanxi, China(mainland).<ref name="ref2" /> |
| − | *Maternal and Child Care Service Center of Changan District, Xi'an, Shanxi, China (mainland)<ref name="ref2" />. | + | * Maternal and Child Care Service Center of Changan District, Xi'an, Shanxi, China (mainland).<ref name="ref2" /> |
| + | * Hematology of Shanghai Xuhui Centre Hospital, Shanghai Clinical Centre of Chinese Acadymy of Sciences, CAS, Shanghai 200031, PR China.<ref name="ref3" /> | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Revision as of 02:37, 26 November 2018
Contents
Annotated Information
Name
PRAL:p53 regulation associated lncRNA
LncRNA-PRAL[1]
Characteristics
LncRNA-PRAL localizes on chromosome 17p13.1, and is transcribed with a poly A tail [1]. Most of the sequence of the lncRNA-PRAL overlaps in antisense with the 3' untranslated region of XAF1 protein-coding gene, which is known to regulate apoptosis[1].
Cellular Localization
LncRNA-PRAL is diffusely distributed both in the nucleus and cytoplasm, and localizes to both cytoplasmic and nuclear regions [1].
Function
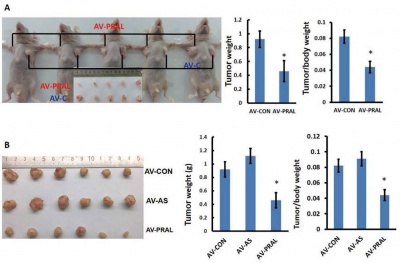
Somatic copy number variation of lncRNA-PRAL is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) growth and lncRNA-PRAL may serve as a potential target for antitumor therapy [1]. LncRNA-PRAL could inhibit HCC growth and induce apoptosis in vivo and in vitro through p53 [1]. The three stem-loop motifs at the 5' end of lncRNA-PRAL facilitates the combination of HSP90 and p53 and thus competitively inhibites MDM2-dependent p53 ubiquitination, resulting in enhanced p53 stability [1].
PRAL might be a tumor suppressor in lung cancer [2]. The transcript level of PRAL is decreased in lung cancer in vivo and in vitro, and overexpression of PRAL inhibites cell proliferation by upregulating the expression of P53 [2].
Expression
Expression level of PRAL is decreased in lung cancer [2].
PRAL is downregulated in primary multiple myeloma (MM) cells and cell lines [3].
Diseases
Labs working on this lncRNA
- Department of Medical Genetics, Second Military Medical University, Shanghai, 200433, China.[1]
- The Third Department of Hepatic Surgery, Eastern Hepatobiliary Hospital, Second Military Medical University, Shanghai, 200433, China.[1]
- Department of Epidemiology, Second Military Medical University, Shanghai, 200433, China.[1]
- Department of Surgery, Xi'an Red Cross Hospital, Affiliated to School of Medicine, Xi'an Jiao Tong University, Xi'an, Shanxi, China(mainland).[2]
- Maternal and Child Care Service Center of Changan District, Xi'an, Shanxi, China (mainland).[2]
- Hematology of Shanghai Xuhui Centre Hospital, Shanghai Clinical Centre of Chinese Acadymy of Sciences, CAS, Shanghai 200031, PR China.[3]
References
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.11 Zhou CC, Yang F, Yuan SX, Ma JZ, Liu F, Yuan JH, Bi FR, Lin KY, Yin JH, Cao GW, Zhou WP, Wang F, Sun SH. Systemic genome screening identifies the outcome associated focal loss of long noncoding RNA PRAL in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2016 Mar;63(3):850-63.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 Su P, Wang F, Qi B, Wang T, Zhang S. P53 Regulation-Association Long Non-Coding RNA (LncRNA PRAL) Inhibits Cell Proliferation by Regulation of P53 in Human Lung Cancer. Med Sci Monit. 2017 Apr 11;23:1751-1758.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Xiao G, Li Y, Wang Y, Zhao B, Zou Z, Hou S et al. LncRNA PRAL is closely related to clinical prognosis of multiple myeloma and the bortezomib sensitivity[J]. Experimental Cell Research. 2018.