Difference between revisions of "LINC02864"
(→Characteristics) |
(→References) |
||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references> | <references> | ||
| − | <ref name="ref1">Yang J, Song H. Identification of long noncoding RNA RP11-169F17.1 and RP11-669N7.2 as novel prognostic biomarkers of stomach adenocarcinoma based on integrated bioinformatics analysis. Epigenomics. 2019 Aug;11(11):1307-1321. doi: 10.2217/epi-2019-0115. Epub 2019 Aug 1. PMID: 31368349./ref>(1) | + | <ref name="ref1">Yang J, Song H. Identification of long noncoding RNA RP11-169F17.1 and RP11-669N7.2 as novel prognostic biomarkers of stomach adenocarcinoma based on integrated bioinformatics analysis. Epigenomics. 2019 Aug;11(11):1307-1321. doi: 10.2217/epi-2019-0115. Epub 2019 Aug 1. PMID: 31368349.</ref>(1) |
</references> | </references> | ||
Latest revision as of 00:47, 21 February 2021
LINC02864 is closely related to H. pylori infectioninduced gastric cancer based on ceRNA hypothesis. [1]
Contents
Annotated Information
Name
Approved symbol:LINC02864
HGNC ID:54480
Approved name:long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 2864
Alias symbol:RP11-169F17.1
RefSeq ID:NR_034133
Characteristics
location:18q22.3
Function
LINC02864 act as novel prognostic biomarkers of stomach adenocarcinoma and also play an important role in H. pylori infection-induced gastric diseases.[1] LINC02864 is associated with cell motility, proliferation, differentiation, cycle and death.[1]
Regulation
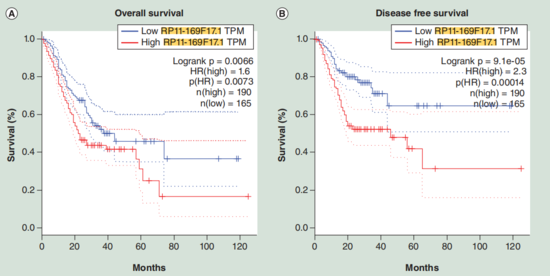
LINC02864 is frequently upregulated and associated with poor prognosis of stomach adenocarcinoma patients. [1]
Expression
LINC02864 level in stomach adenocarcinoma is signifi- cant positively associated with CDK6, and LINC02864 level is significantly correlated to the expressions of E2F3, CDK4 and CDC25A.[1]
Diseases
Stomach adenocarcinoma[1]
Labs working on this lncRNA
- The Key Laboratory of Endemic & Ethnic Diseases, Guizhou Medical University, Ministry of Education, Guiyang 550004, PR China.[1]
- The State Key Laboratory of Functions & Applications of Medicinal Plants, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550014, PR China.[1]
- The Key Laboratory of Medical Molecular Biology, Guizhou Medical University, Guizhou Province, Guiyang 550004, PR China.[1]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 1.9 Yang J, Song H. Identification of long noncoding RNA RP11-169F17.1 and RP11-669N7.2 as novel prognostic biomarkers of stomach adenocarcinoma based on integrated bioinformatics analysis. Epigenomics. 2019 Aug;11(11):1307-1321. doi: 10.2217/epi-2019-0115. Epub 2019 Aug 1. PMID: 31368349.