LINC01844
Contents
Annotated Information
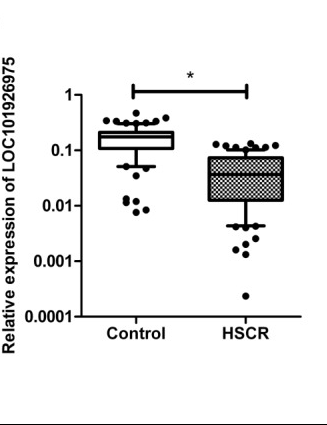
LOC101926975 is significantly downregulated in HSCR tissues compared control samples.[1]

(A) LOC101926975 was effectively knocked down in SK-N-BE(2) cells. Downregulation of LOC101926975 suppressed cell proliferation (B)and caused cell cycle arrest (C)without impact on cell apoptosis (D)or cell migration..[1]
Approved Symbol
LINC01844
Approved Name
long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 1844
Synonyms
LOC101926975
Chromosome
5q31.3
RefSeq ID
NR_110558
RefSeq(supplied by NCBI)
NR_110558
Characteristics
LOC101926975 locates on chromosome 5 (142745600-142760993) and it is near the gene FGF1.[1]
Expression
Compared with the control tissues, the expression of LOC101926975 is down-regulated in hirschsprung disease (HSCR) tissues.[1]
| Experiment | Forward primer | Reverse primer |
|---|---|---|
| qRT-PCR | 5'-AACCCAGTGTTCAAAACCCCA- 3' | 5'-GCAGGGGAAAATACCAGGGAA- 3'[1] |
Function
SiRNA experiment show that LOC101926975 knockdown inhibits cell proliferation and blocks the G0/G1 to S phase transition.[1] The expression correlation analysis shows LOC101926975 regulate the expression of FGF1.[1]
Labs working on this lncRNA
- Department of Pediatric Surgery, Nanjing Children's Hospital Affiliated Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing 210008; 2. State Key Laboratory of Reproductive Medicine, Institute of Toxicology, School of Public Health, Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing 211166, China.
- State Key Laboratory of Reproductive Medicine, Institute of Toxicology, School of Public Health, Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing 211166, China; 3. Key Laboratory of Modern Toxicology (Nanjing Medical University), Ministry of Education, China.