LINC01138
Contents
Annotated Information
Approved Symbol

LINC01138 (long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 1138)
Previous Symbols
LINC00875
Synonyms
FLJ39739
Chromosome
1q21.2
RefSeq(supplied by NCBI)
NR_027468
LncBook transcript ID
HSALNT0014603
Disease
Prostate cancer
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)[1]
Expression
The expression level of LINC01138 is markedly increased in invasive extraprostatic tumors (pT3a, pT3b and T4 stages) as compared with intraprostatic localized tumors (pT2a , pT2b and pT2c stages).[2]
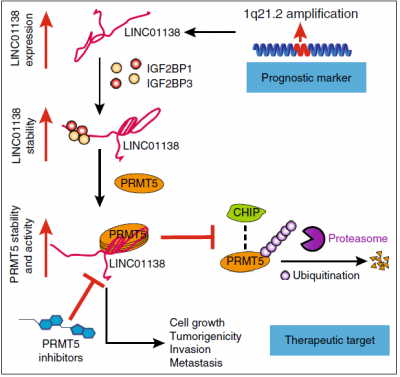
The LINC01138 locus is frequently amplified in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)[1].
Function
The high level of LINC01138 is correlated with a short biochemical recurrence-free survival times.[2] LINC01138 promotes the proliferation and inhibited apoptosis of PCa.[2] LINC01138 functions as an oncogenes in prostate cancer.[2]
LINC01138 is associated with the malignant features and poor outcomes of HCC patients. LINC01138 acts as an oncogenic driver that promotes cell proliferation, tumorigenicity, tumour invasion and metastasis by physically interacting with arginine methyltransferase 5 (PRMT5) and enhancing its protein stability by blocking ubiquitin/proteasome-dependent degradation in HCC[1].
Labs working on this lncRNA
- State Key Laboratory of Genetic Engineering, Shanghai Engineering Research Center Of Industrial Microorganisms, School of Life Science, Fudan University, Shanghai 200433, PR China.
- Fudan University Shanghai Cancer Center and Institutes of Biomedical Sciences, Department of Oncology, Shanghai Medical College, Fudan University, Shanghai 200032, China.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Li Z, Zhang J, Liu X, et al. The LINC01138 drives malignancies via activating arginine methyltransferase 5 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Nature communications, 2018, 9(1): 1572.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Wan, X., et al., Identification of androgen-responsive lncRNAs as diagnostic and prognostic markers for prostate cancer. Oncotarget, 2016. 7(37): p. 60503-60518.