DLGAP1-AS1
The cancerogenic effects of DLGAP1-AS1 in HCC cells could be effectuated via activating Wnt/β-catenin pathway by positively regulating CDK8 and LRP6, downstream genes of miR-26a/b-5p.[1]
Contents
Annotated Information
Name
Approved symbol:DLGAP1-AS1
Approved name:DLGAP1 antisense RNA 1
HGNC ID:31676
Previous name:DLGAP1 antisense RNA 1 (non-protein coding)
Alias symbol:HsT914|FLJ35776
RefSeq ID:NR_024101
LncBook ID:HSALNG0119714
Characteristics
Located in chr18
Function
DLGAP1-AS1 in facilitating HCC progression and EMT in vitro and in vivo.[1]
Regulation
DLGAP1-AS1 serve as a molecular sponge to sequester the HCC-inhibitory miRNAs, miR-26a-5p and miR-26b-5p, thus enhancing the level of an oncogenic cytokine IL-6, which could activate JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway and reciprocally elevate the transcriptional activity of DLGAP1-AS1, thus forming a positive feedback loop.[1] The cancerogenic effects of DLGAP1-AS1 in HCC cells could be effectuated via activating Wnt/β-catenin pathway by positively regulating CDK8 and LRP6, downstream genes of miR-26a/b-5p.[1]
Expression
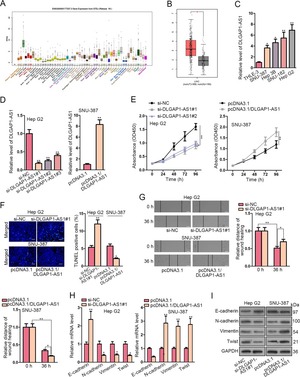
DLGAP1-AS1 was shown to be upregulated in HCC cell lines and capable to promote HCC progression and EMT.[1]
Diseases
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)[1]
Labs working on this lncRNA
- Department of General Surgery, Guangdong Provincial People's Hospital, Guangdong Academy of Medical Sciences, 106 Zhongshan Er Road, Guangzhou, 510080, China.[1]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 Lin Y, Jian Z, Jin H, Wei X, Zou X, Guan R, Huang J. Long non-coding RNA DLGAP1-AS1 facilitates tumorigenesis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma via the feedback loop of miR-26a/b-5p/IL-6/JAK2/STAT3 and Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2020 Jan 16;11(1):34. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-2188-7. PMID: 31949128; PMCID: PMC6965175.