LINC02620
LINC02620,a long non-coding RNA, promotes breast cancer progression by targeting miR-1303/PTBP3 axis.[1]
Contents
Annotated Information
Name
Approved symbol:LINC02620
HGNC ID:54097
Approved name:long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 2620
Alias symbol:BCRT1
RefSeq ID:NR_120624
Characteristics
location:10q25.1
Function
LINC02620 could competitively bind with miR-1303 to prevent the degradation of its target gene PTBP3, which acts as a tumor-promoter in breast cancer. [1]
Regulation
LINC02620 could bind with miR-1303 to prevent the degradation of its target gene PTBP3, which acts as a tumor-promoter in breast cancer.[1]
Expression
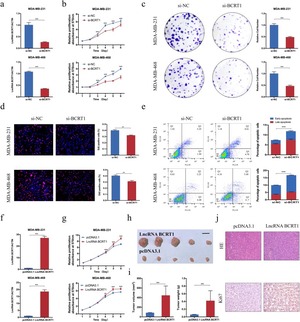
LncRNA LINC02620 was significantly upregulated in breast cancer tissues, which was correlated with poor prognosis in breast cancer patients.[1] LncRNA LINC02620 overexpression could promote M2 polarization of macrophages, mediated by exosomes, which further accelerated breast cancer progression.LINC02620 was upregulated in response to hypoxia, which was attributed to the binding of HIF-1α to HREs in the lncRNA LINC02620 promoter. [1]
Diseases
Breast cancer[1]
Labs working on this lncRNA
- Department of Breast Surgery, Qilu Hospital of Shandong University, Jinan, Shandong, 250012, People's Republic of China.[1]
- Pathology Tissue Bank, Qilu Hospital of Shandong University, Jinan, Shandong, 250012, People's Republic of China.[1]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 Liang Y, Song X, Li Y, Chen B, Zhao W, Wang L, Zhang H, Liu Y, Han D, Zhang N, Ma T, Wang Y, Ye F, Luo D, Li X, Yang Q. LncRNA BCRT1 promotes breast cancer progression by targeting miR-1303/PTBP3 axis. Mol Cancer. 2020 May 8;19(1):85. doi: 10.1186/s12943-020-01206-5. PMID: 32384893; PMCID: PMC7206728.