Difference between revisions of "ENST00000513868.2"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | ''PVT1'', | + | ''PVT1'', plasmacytoma variant translocation 1 gene that is involved in diabetic neuropathy and various kind of carcinomas. |
==Annotated Information== | ==Annotated Information== | ||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
===Characteristics=== | ===Characteristics=== | ||
| − | PVT1 gene harbors nine exons | + | ''PVT1'' gene is 1957 bp long intergenic non-coding RNA and harbors nine exons (GenBank), located on human chromosome 8q24.21 telomeric to the c-Myc gene and it is frequently involved in the translocations occurring in variant Burkitt's lymphomas and murine plasmacytomas<ref name="ref1" />. |
PVT1 gene contains two non canonical Myc-binding sites (E-box CACGCG) in the promoter region proximal to the transcriptional start site (−155/−95) the consensus and the surrounding sequences are conserved in the homologous mouse and rat genes<ref name="ref1" />. | PVT1 gene contains two non canonical Myc-binding sites (E-box CACGCG) in the promoter region proximal to the transcriptional start site (−155/−95) the consensus and the surrounding sequences are conserved in the homologous mouse and rat genes<ref name="ref1" />. | ||
===Function=== | ===Function=== | ||
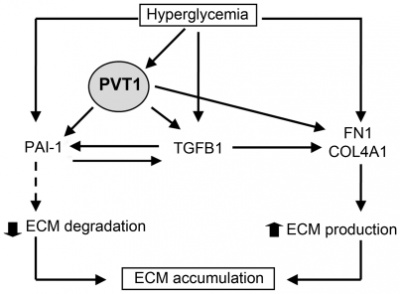
| − | ''PVT1'' is a downstream target of both c-Myc and N-Myc genes<ref name="ref1" />. | + | [[File: PVT1.jpg|right|thumb|400px|'''Schematic representation of ''PVT1'' involvement in ECM deposition.''' . Hyperglycemia causes an excessive accumulation of extracellular matrix (ECM) in the glomerular mesangium which constitutes the major pathological feature of the glomerulosclerosis |
| + | or glomerular fibrosis. Hyperglycemic conditions induce an increase in ''PVT1'' expression in MC which contributes to the increase of the two main ECM components, ''FN1'' and ''COL4A1'', as well as the two main regulators of ECM accumulation in the glomerule, ''PAI-1'' and ''TGFB1''. <ref name="ref2" />.]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''PVT1'' is a downstream target of both c-Myc and N-Myc genes <ref name="ref1" />. | ||
The E-boxes region in the ''PVT1'' proximal promoter is important for ''PVT1'' transcriptional regulation by Myc proteins and reveal a novel cross-talk between ''PVT1'' and ''N-Myc'' in neuroblastoma cells <ref name="ref1" />. | The E-boxes region in the ''PVT1'' proximal promoter is important for ''PVT1'' transcriptional regulation by Myc proteins and reveal a novel cross-talk between ''PVT1'' and ''N-Myc'' in neuroblastoma cells <ref name="ref1" />. | ||
| − | ''PVT1'' mediate the development and progression of diabetic nephropathy through mechanisms involving ECM accumulation. ''PVT1'' knockdown significantly reduced mRNA and protein levels of the major ECM proteins, FN1 and COL4A1, and two key regulators of ECM proteins, TGFB1 and PAI-1. | + | ''PVT1'' mediate the development and progression of diabetic nephropathy through mechanisms involving ECM accumulation. ''PVT1'' knockdown significantly reduced mRNA and protein levels of the major ECM proteins, FN1 and COL4A1, and two key regulators of ECM proteins, TGFB1 and PAI-1 <ref name="ref2" />. |
===Regulation=== | ===Regulation=== | ||
| Line 24: | Line 27: | ||
===Expression=== | ===Expression=== | ||
| − | ''PVT1'' expression was significantly upregulated by glucose treatment in human mesangial cells. | + | ''PVT1'' expression was significantly upregulated by glucose treatment in human mesangial cells <ref name="ref2" />.. |
{|class='wikitable' style="text-align:center" | {|class='wikitable' style="text-align:center" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 58: | Line 61: | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references> | <references> | ||
| − | <ref name="ref1">Carramusa L, Contino F, Ferro A, Minafra L, Perconti G, Giallongo A, et al. The PVT-1 oncogene is a Myc protein target that is overexpressed in transformed cells[J]. Journal of cellular physiology. 2007,213(2):511-8.</ref>(1) | + | <ref name="ref1"> Carramusa L, Contino F, Ferro A, Minafra L, Perconti G, Giallongo A, et al. The PVT-1 oncogene is a Myc protein target that is overexpressed in transformed cells[J]. Journal of cellular physiology. 2007,213(2):511-8.</ref>(1) |
| + | <ref name="ref2"> Alvarez ML & DiStefano JK. Functional characterization of the plasmacytoma variant translocation 1 gene (PVT1) in diabetic nephropathy[J]. PloS one. 2011, 6(4):e18671. | ||
| + | </ref>(2) | ||
| + | <ref name="ref3"> Zhou Q, Chen J, Feng J & Wang J. Long noncoding RNA PVT1 modulates thyroid cancer cell proliferation by recruiting EZH2 and regulating thyroid-stimulating hormone receptor (TSHR)[J]. Tumor Biology. 2016, 37(3):3105-3113. | ||
| + | </ref>(3) | ||
</references> | </references> | ||
Revision as of 04:25, 18 November 2018
PVT1, plasmacytoma variant translocation 1 gene that is involved in diabetic neuropathy and various kind of carcinomas.
Contents
Annotated Information
Name
PVT1:Pvt1 oncogene (HGNC nomenclature)
LINC00079, "long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 79", NCRNA00079, "non-protein coding RNA 79"[1]
Characteristics
PVT1 gene is 1957 bp long intergenic non-coding RNA and harbors nine exons (GenBank), located on human chromosome 8q24.21 telomeric to the c-Myc gene and it is frequently involved in the translocations occurring in variant Burkitt's lymphomas and murine plasmacytomas[1].
PVT1 gene contains two non canonical Myc-binding sites (E-box CACGCG) in the promoter region proximal to the transcriptional start site (−155/−95) the consensus and the surrounding sequences are conserved in the homologous mouse and rat genes[1].
Function
PVT1 is a downstream target of both c-Myc and N-Myc genes [1].
The E-boxes region in the PVT1 proximal promoter is important for PVT1 transcriptional regulation by Myc proteins and reveal a novel cross-talk between PVT1 and N-Myc in neuroblastoma cells [1].
PVT1 mediate the development and progression of diabetic nephropathy through mechanisms involving ECM accumulation. PVT1 knockdown significantly reduced mRNA and protein levels of the major ECM proteins, FN1 and COL4A1, and two key regulators of ECM proteins, TGFB1 and PAI-1 [2].
Regulation
The E-boxes region in the PVT-1 proximal promoter is important for PVT-1 transcriptional regulation by Myc proteins[1].

Expression
PVT1 expression was significantly upregulated by glucose treatment in human mesangial cells [2]..
| Primer | Forward | Reverse |
|---|---|---|
| PVT1 | CAT GGT TCC ACC AGC GTT ATT C | TCC TTG CGG AAA GGA TGT TGG[1] |
| c-Myc | CAG CAG AGC GAG CTG CAG CC | CTG TCT TTG CGC GCA GCC TG[1] |
| N-Myc | CAG CAG AGC GAG CTG CAG CC | CTG TCT TTG CGC GCA GCC TG[1] |
| GAPDH | TGA CAT CAA GAA GGT GGT GA | TCC ACC ACC CTG TTG CTG TA[1] |
Evolution
A computer-assisted alignment of the human PVT-1 promoter nucleotidesequence with the homologous mouse and rat sequences,indicates the existence of a significant evolutionary conservation both at the nucleotide level and in the spacing ofthe E-boxes relative to the transcriptional start site.
Disease
neuroblastoma
Labs working on this lncRNA
- Dipartimento di Oncologia Sperimentale e Applicazioni Cliniche, Università di Palermo, Palermo, Italy[1].
References
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.11 Carramusa L, Contino F, Ferro A, Minafra L, Perconti G, Giallongo A, et al. The PVT-1 oncogene is a Myc protein target that is overexpressed in transformed cells[J]. Journal of cellular physiology. 2007,213(2):511-8.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Alvarez ML & DiStefano JK. Functional characterization of the plasmacytoma variant translocation 1 gene (PVT1) in diabetic nephropathy[J]. PloS one. 2011, 6(4):e18671.
Cite error: <ref> tag with name "ref3" defined in <references> is not used in prior text.
sequence
>gi|5820|ref|NR_003367.3| Homo sapiens Pvt1 oncogene (PVT1), long non-coding RNA
000081 CGACGACGAG CTGCGAGCAA AGATGTGCCC CGGGACCCCC GGCACCTTCC AGTGGATTTC CTTGCGGAAA GGATGTTGGC 000160
000161 GGTCCCTGTG ACCTGTGGAG ACACGGCCAG ATCTGCCCTC CAGCCTGATC TTTTGGCCAG AAGGAGATTA AAAAGATGCC 000240
000241 CCTCAAGATG GCTGTGCCTG TCAGCTGCAT GGAGCTTCGT TCAAGTATTT TCTGAGCCTG ATGGATTTAC AGTGATCTTC 000320
000321 AGTGGTCTGG GGAATAACGC TGGTGGAACC ATGCACTGGA ATGACACACG CCCGGCACAT TTCAGGATAC TAAAAGTGGT 000400
000401 TTTAAGGGAG GCTGTGGCTG AATGCCTCAT GGATTCTTAC AGCTTGGATG TCCATGGGGG ACGAAGGACT GCAGCTGGCT 000480
000481 GAGAGGGTTG AGATCTCTGT TTACTTAGAT CTCTGCCAAC TTCCTTTGGG TCTCCCTATG GAATGTAAGA CCCCGACTCT 000560
000561 TCCTGGTGAA GCATCTGATG CACGTTCCAT CCGGCGCTCA GCTGGGCTTG AGCTGACCAT ACTCCCTGGA GCCTTCTCCC 000640
000641 GAGGTGCGCG GGTGACCTTG GCACATACAG CCATCATGAT GGTACTTTAA GTGGAGGCTG AATCATCTCC CCTTTGAGCT 000720
000721 GCTTGGCACG TGGCTCCCTT GGTGTTCCCC TTTTACTGCC AGGACACTGA GATTTGGAGA GAGTCTCACT CTGTGGTCCA 000800
000801 GGCTGAAGTA CAGTGGCATG ATCCCAGGTC ACTGCAACCC CCACCTCCCG GGTTCAAGTG ATCCTCCTGC CTCAGCCTCC 000880
000881 CGAGTAGCTG GTATTACAGG CGTGTGCCAC AAAGCCTGGC TAAGTTTTGT ATTTTTAGTA GAGACGGGGT TTCACCATGT 000960
000961 TGGCCAGGTT GGTCTCGAAC TCCTGACCTC AAGTGATCCA CTCACTTTGG CCTTTCAACG TGCTGGGATT ACAGGCGAGA 001040
001041 GTCACCGCAC CCGGACGACT CTGACATTTT TGAAGAGTCC AGAATCCTGT TACACCTGGG ATTTAGGCAC TTTCAATCTG 001120
001121 AAAAAATACA TATCCTTTCA GCACTCTGGA CGGACTTGAG AACTGTCCTT ACGTGACCTA AAGCTGGAGT ATTTTGAGAT 001200
001201 TGGAGAATTA AGAGCCAGTC TTGGTGCTCT GTGTTCACCT GGTTCATCTG AGGAGCTGCA TCTACCCTGC CCATGCCATA 001280
001281 GATCCTGCCC TGTTTGCTTC TCCTGTTGCT GCTAGTGGAC ATGAGAAGGA CAGAATAACG GGCTCCCAGA TTCACAAGCC 001360
001361 CCACCAAGAG GATCACCCCA GGAACGCTTG GAGGCTGAGG AGTTCACTGA GGCTACTGCA TCTTGAGACT CAGGATGAAG 001440
001441 ACCCAGCTTG GGGCTGTCAA AGAGGCCTGA AGAGGCAGAA CACCCCAGAG GAGCCTGGGG CCACCACCCA GCATCACTGT 001520
001521 GGGAAAACGG CAGCAGGAAA TGTCCTCTCG CCTGCGTGCT CCACCTCGGT CCACGCCTTC CCTCCTTCTG GAAGCCTTGC 001600
001601 CTGACCACTG GCCTGCCCCT TCTATGGGAA TCACTACTGA CCTTGCAGCT TATTATAGAC TTATATGTTT TTTGCATGTC 001680
001681 TGACACCCAT GACTCCACCT GGACCTTATG GCTCCACCCA GAAGCAATTC AGCCCAACAG GAGGACAGCT TCAACCCATT 001760
001761 ACGATTTCAT CTCTGCCCCA ACCACTCAGC AGCAAGCACC TGTTACCTGT CCACCCCCAC CCCTTCCCCC AAACTGCCTT 001840
001841 TGAAAAATCC CTAACCTATG AGCTTTGAAT AAGATGAGTA CGAACTTCAT CGCCCACGTG GCGTGGCCGG CCTCGTGTCT 001920
001921 ATTAAATTCT TTTTCTACTA AAAAAAAAAA AAAAAAA
Predicted Small Protein
| Name | ENST00000513868.2_smProtein_206:448 |
| Length | 81 |
| Molecular weight | 8571.0033 |
| Aromaticity | 0.025 |
| Instability index | 49.55375 |
| Isoelectric point | 5.18756103516 |
| Runs | 12 |
| Runs residual | 0.0111842105263 |
| Runs probability | 0.0499838073367 |
| Amino acid sequence | MSMGDEGLQLAERVEISVYLDLCQLPLGLPMECKTPTLPGEASDARSIRRSAGLELTILP GAFSRGARVTLAHTAIMMVL |
| Secondary structure | LLLLHHHHLHHHHEEEEEEELLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLHHHHHHHLLLEEEELL LLLLLLLLHHHHHHHHHHHL |
| PRMN | - |
| PiMo | - |