1. Overview
The Tropical Crop Omics Database is a data portal that serves research on selective breeding and trait improvement for tropical crops. The database integrates the genome, variome, transcriptome, and cultivar data of 15 tropical crops, including cassava, rubber tree, coffee, and more. Using genes as the fundamental units, the database correlates multidimensional omics data to achieve the integration of various omics data within a single species. Furthermore, by leveraging homologous gene information, researchers can compare the omics characteristics among multiple species, enabling cross-species studies. Moreover, the database offers a range of online tools, such as BLAST, Genome Browser, PrimerDesign, Literature Seach, GO Enrichment, KEGG Enrichment, Synteny Viewer and Homolog Finder, to facilitate users in data mining.
2.Species
The Species page provides access to the relevant statistical results of different omics data for each species. Clicking on the data links allows for quick data retrieval.
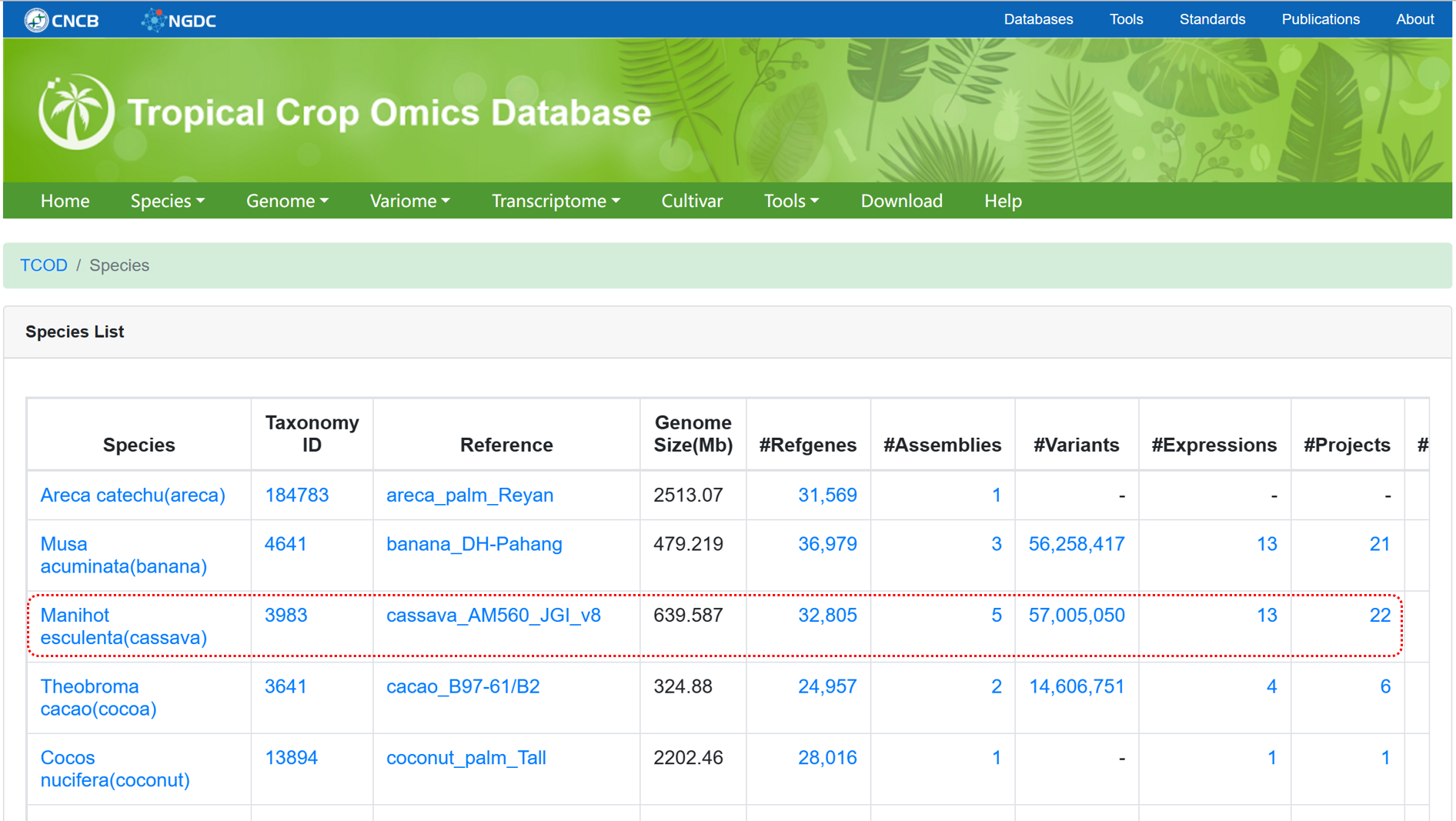
Figure 1 The overview of 'Species'

Figure 2 A scientific introduction to cassava
3.Genome
3.1. Assembly
The 'Assembly' module offers users high-quality genome sequences. Currently, a collection of 34 chromosome-level assemblies has been obtained from various sources. Specifically, the de novo assembly of cassava varieties A4047 and AM560 was provided by ITBB-CATAS, the de novo assembly of cassava variety W14 was contributed by Hainan University, and the de novo assembly of rubber tree variety CATAS8-79 was supplied by RRI-CATAS. Additional assemblies were downloaded from websites such as NGDC GWH, NCBI Genome, EnsemblPlants, and Phytozome v13.
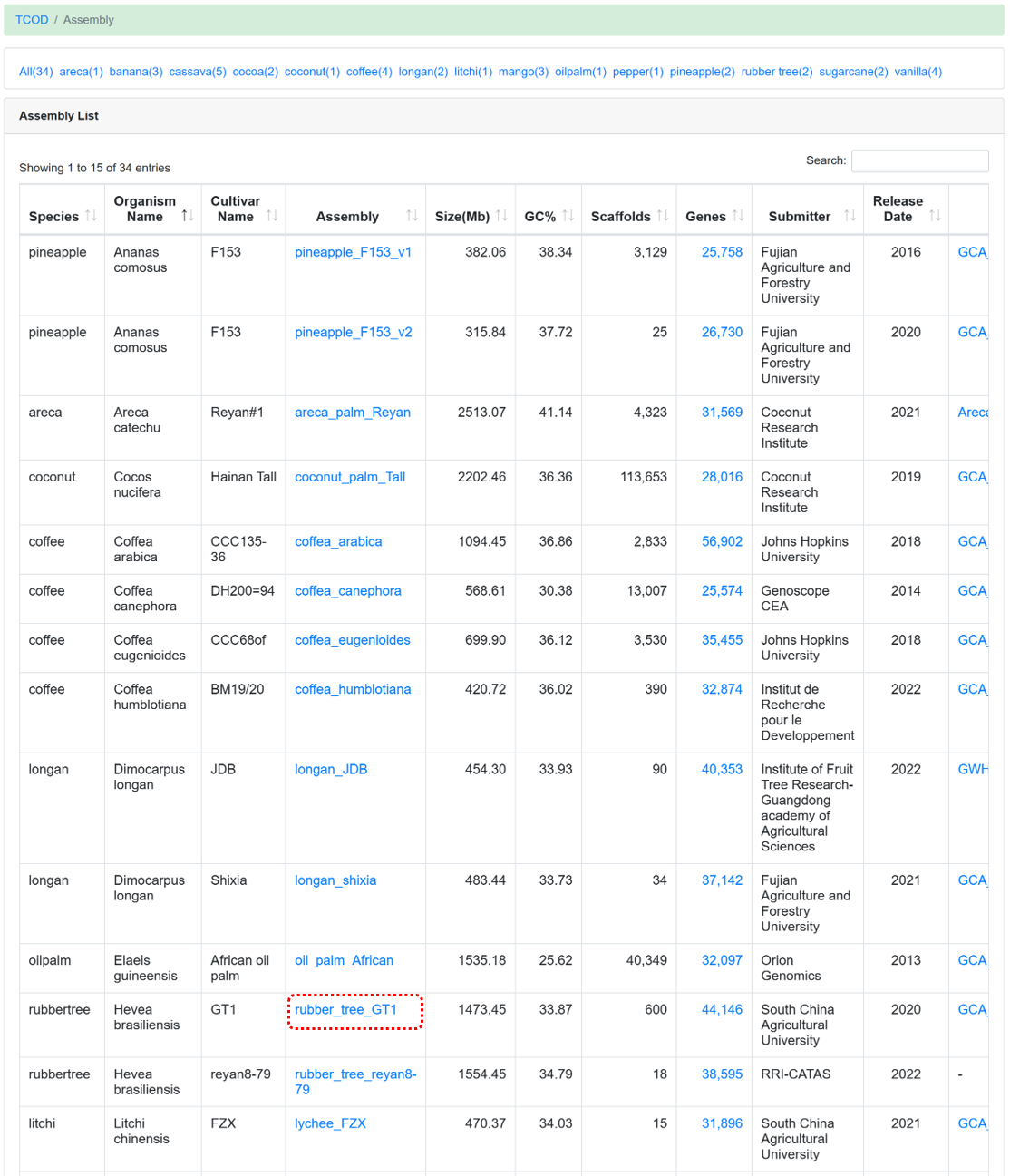
Figure 3 The overview of 'Assembly' module
Clicking on each assembly link allows you to view detailed information:
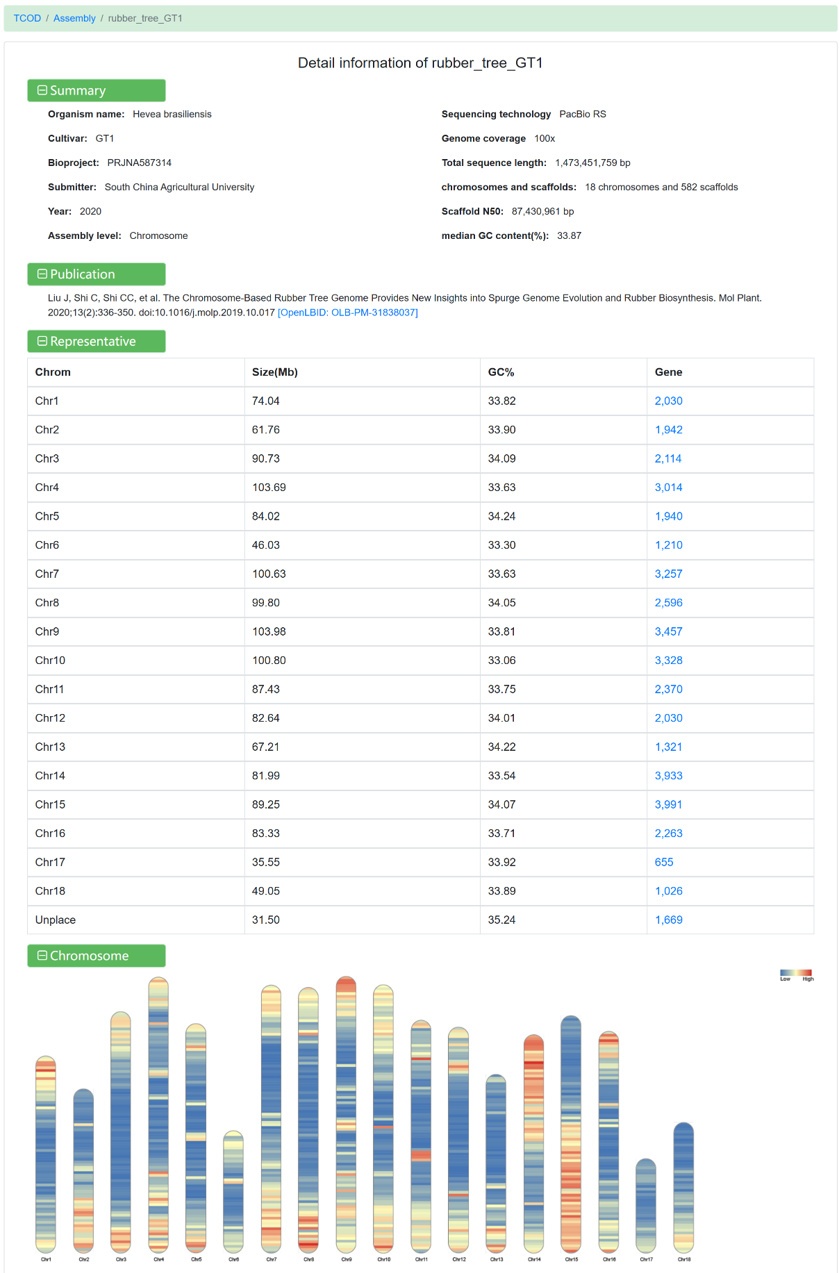
Figure 4 The detailed information for rubber_tree_GT1
3.2. Gene
The 'Gene' module integrates gene structures and functional information extracted from annotated files for each genome. We have utilized databases such as Nr, UniProt, InterPro, Pfam, and eggNOG-mapper to conduct gene annotation, ensuring comprehensive and reliable annotation information. The page supports advanced searches by selecting genome version, chromosome coordinates, gene name, and gene function.
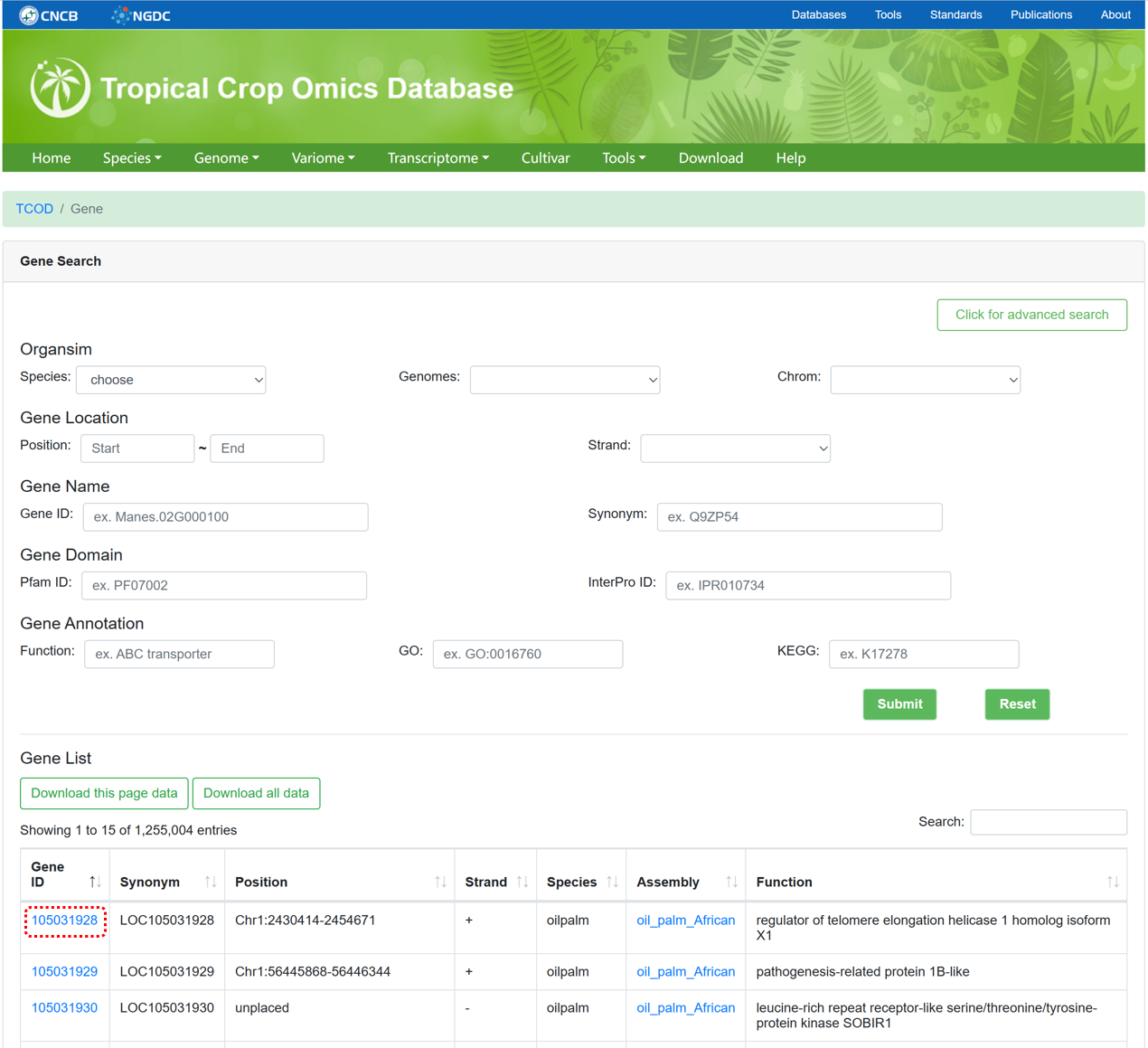
Figure 5 The overview of 'Gene' module
Clicking on each gene link allows you to view detailed information:
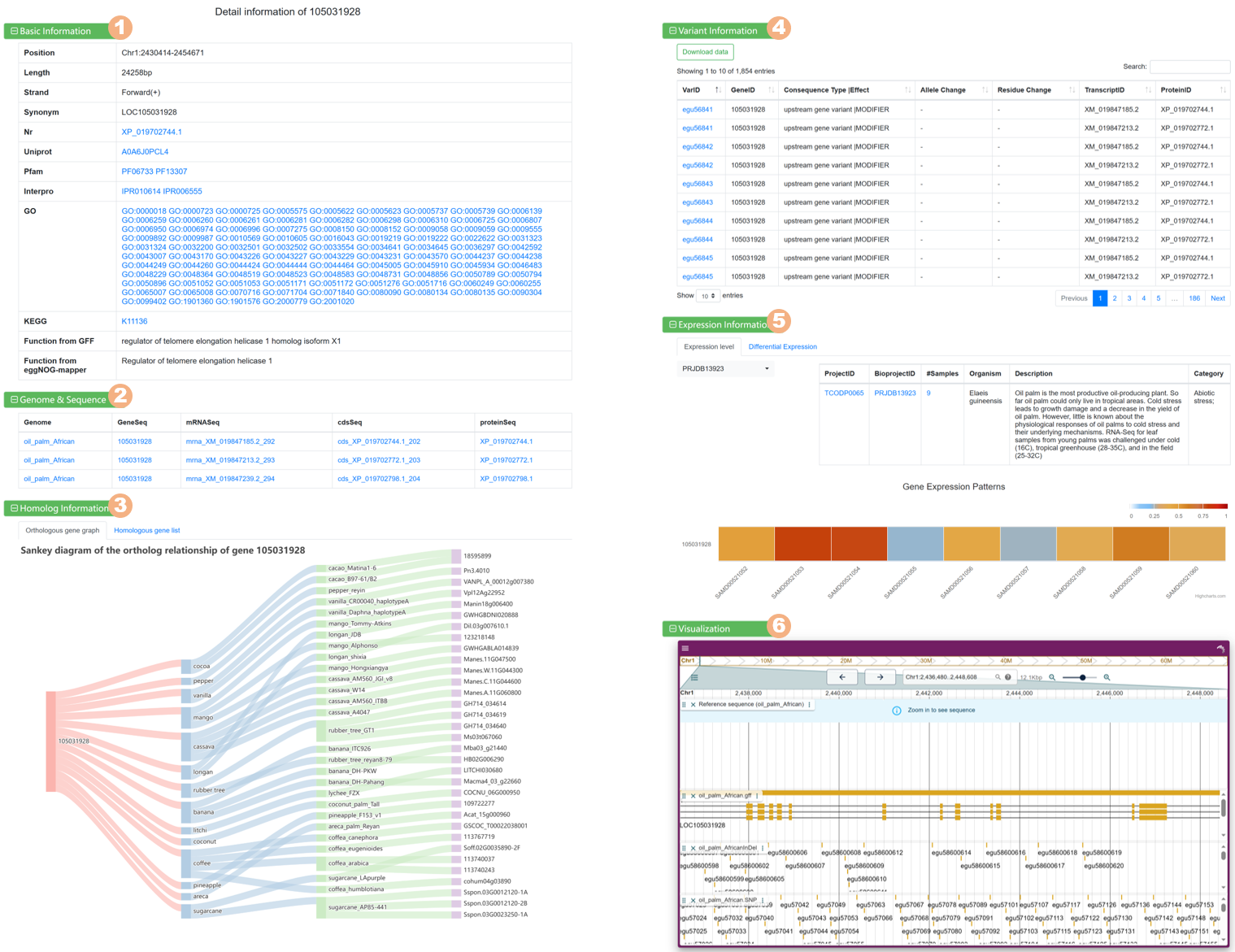
Figure 6 The detailed information for each gene
4.Variome
4.1. WGS Project
The 'WGS Project' section provides metadata information for all WGS projects used for variation analysis. The page supports advanced search, data browsing, and data downloading.
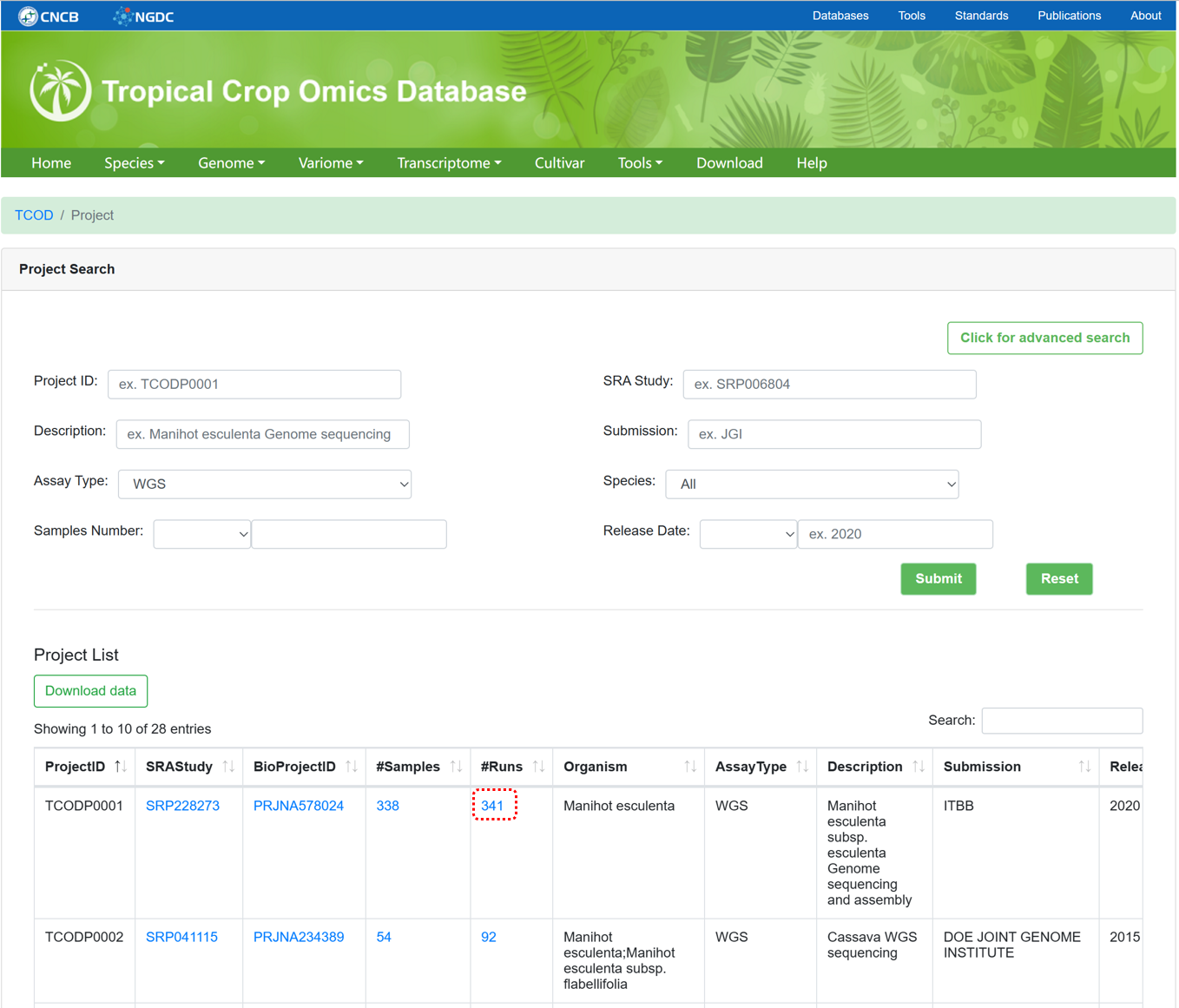
Figure 7 The overview of 'WGS Project'
4.2. WGS Sample
The 'WGS Sample' section provides metadata information for all WGS samples used for variation analysis. The page supports advanced search, data browsing, and data downloading.

Figure 8 The overview of 'WGS Sample'
4.3. Variation
By collecting WGS data from different samples and utilizing standard variation analysis pipelines from NGDC GVM, the ‘Variations’ module provides genome-wide variation maps for 10 species. The page consists of three sections:
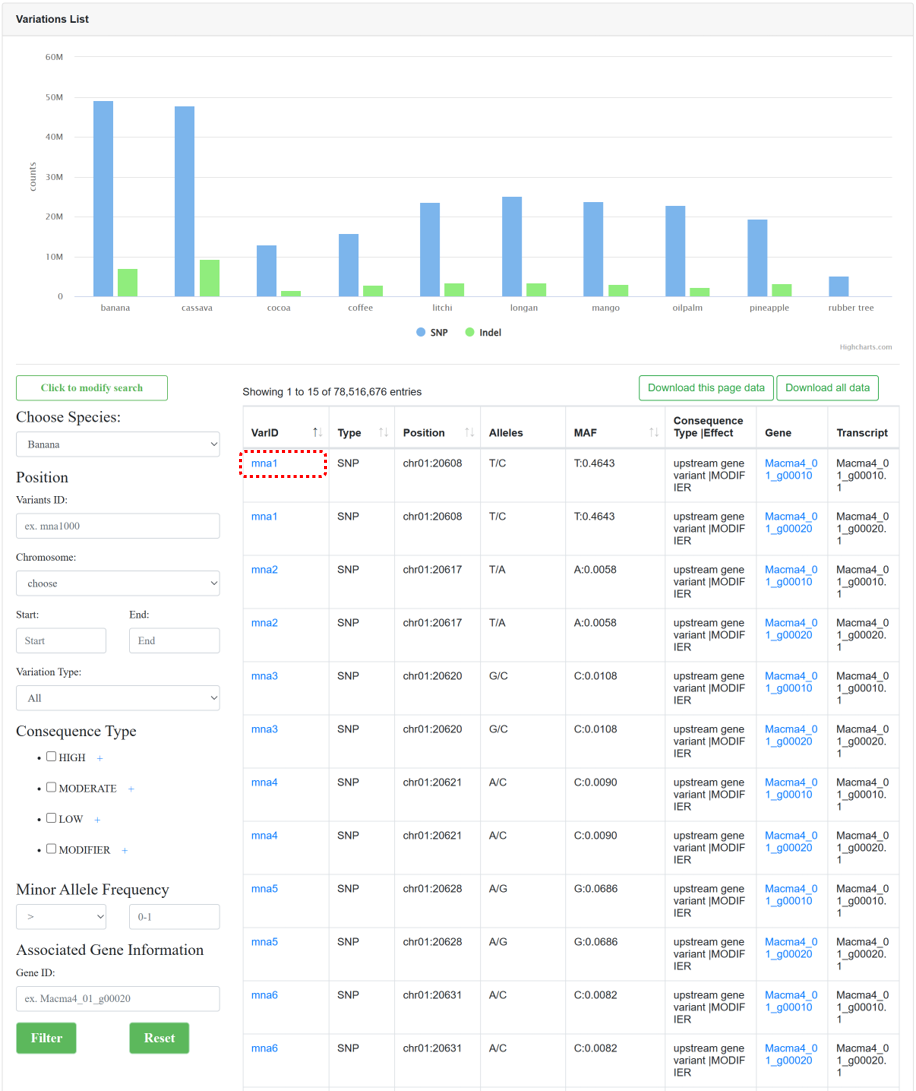
Figure 9 The overview of 'Variations' module
Clicking on each variant link allows you to view detailed information:
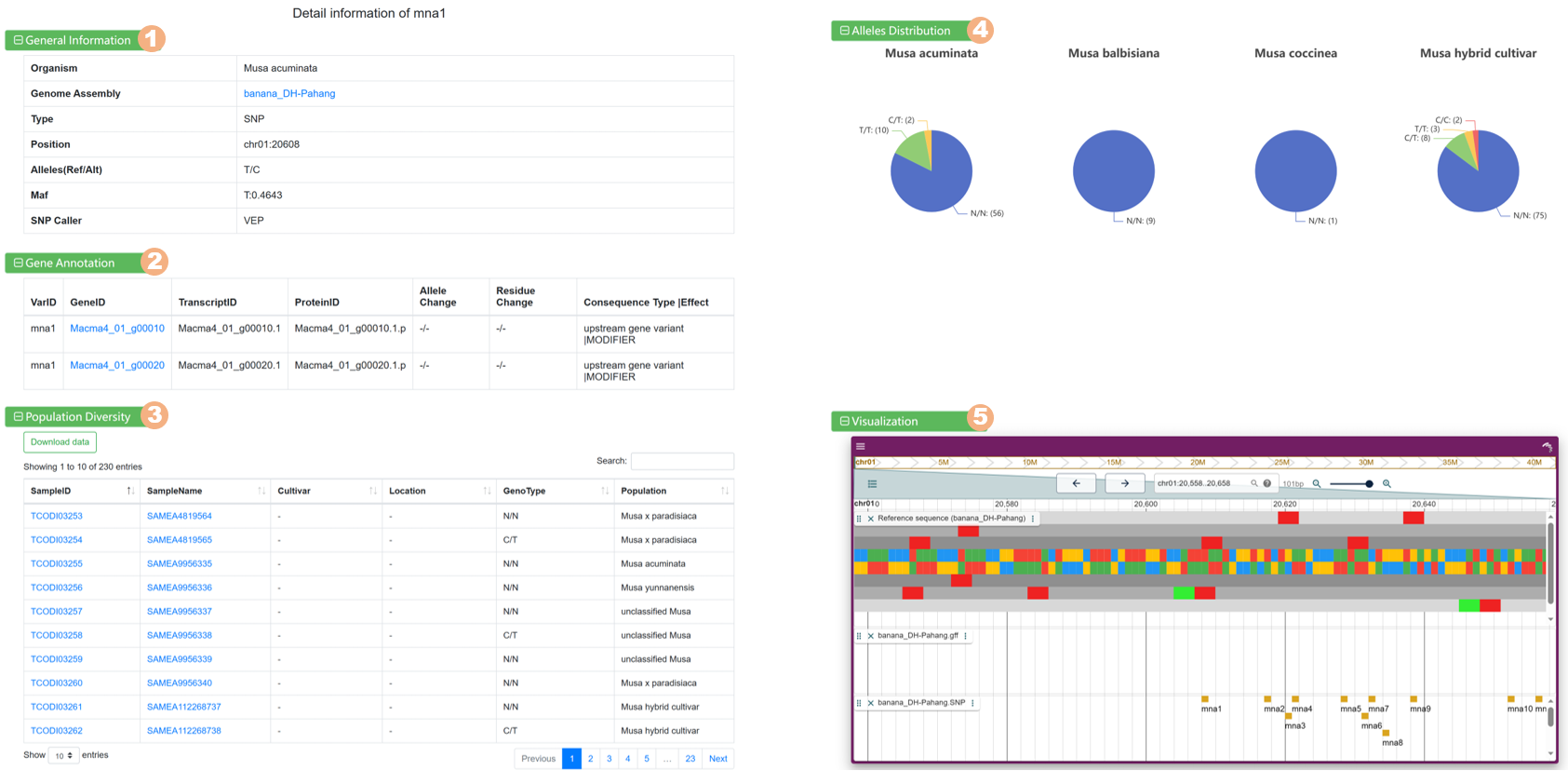
Figure 10 The detailed information for each variant
5.Transcriptome
5.1. RNASeq Project
The 'RNASeq Project' section provides metadata information for collected RNASeq projects used for whole-transcriptome analysis, similar to the design of 'WGS Project'.
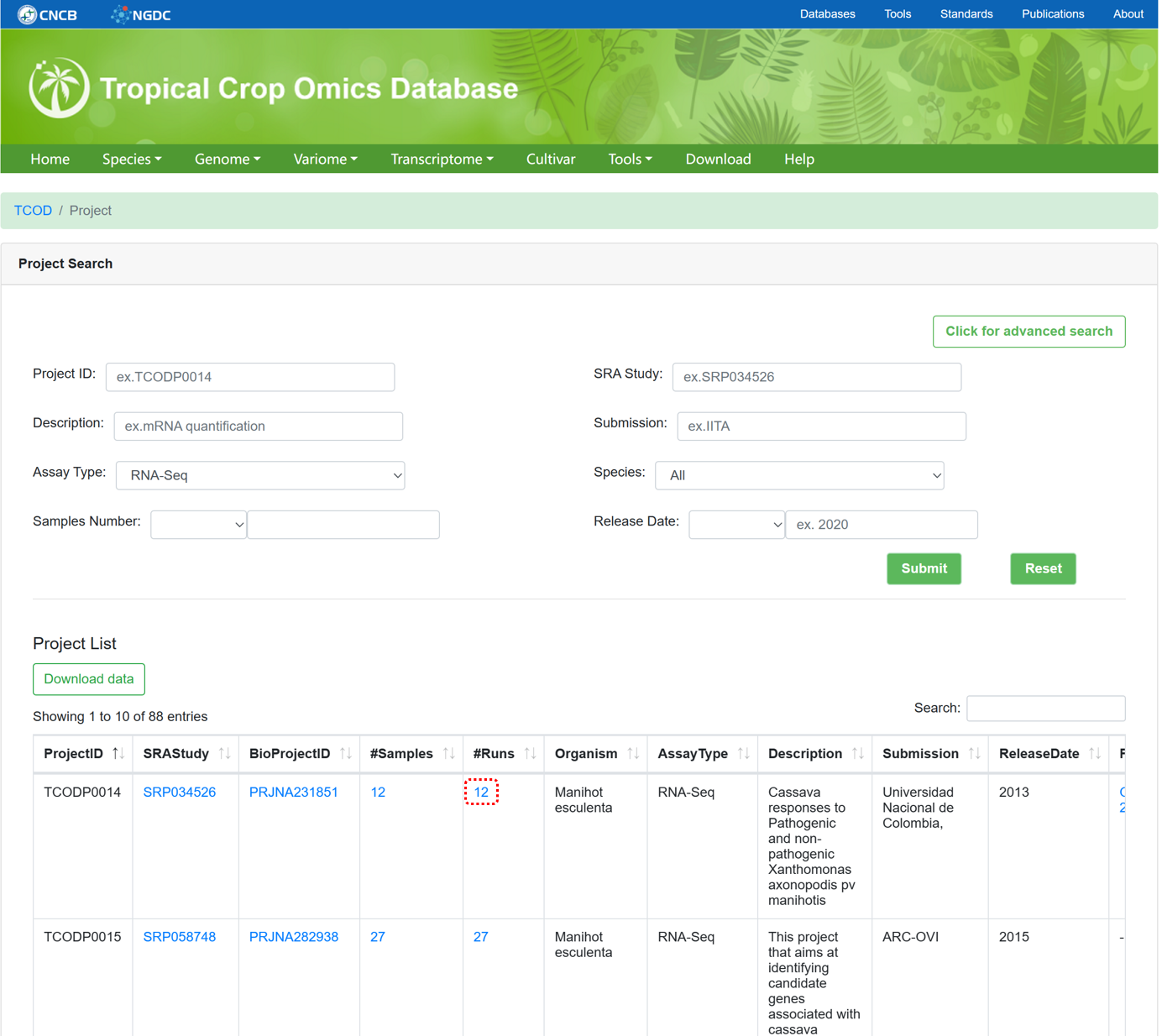
Figure 11 The overview of 'RNASeq Project'
5.2. RNASeq Sample
The 'RNASeq Sample' section provides metadata information for collected RNASeq samples used for whole-transcriptome analysis. It is similar to the design of 'WGS Sample', but provides more detailed descriptions of the sample and overall alignment rate.
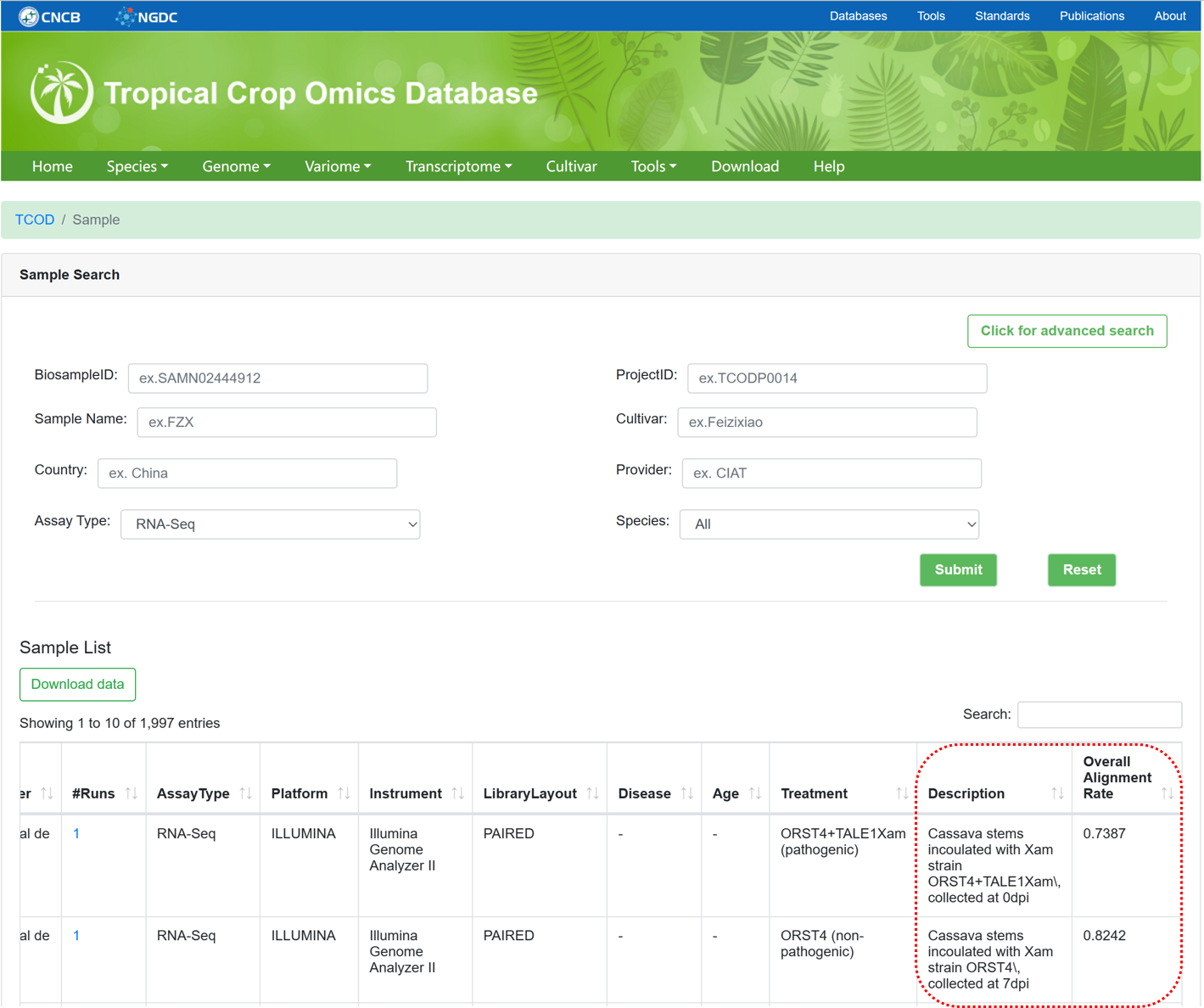
Figure 12 The overview of 'RNASeq Sample'
5.3. Expression
By using standard transcriptome analysis pipelines from NGDC GEN on different RNA-Seq sequencing projects, the ‘Expressions’ module provides transcriptome profiles of 13 species under diverse experimental conditions. In addition, according to the description for each project, category tags (such as biotic stress, abiotic stress, etc.) were added to make it easier for users to find interested datasets.
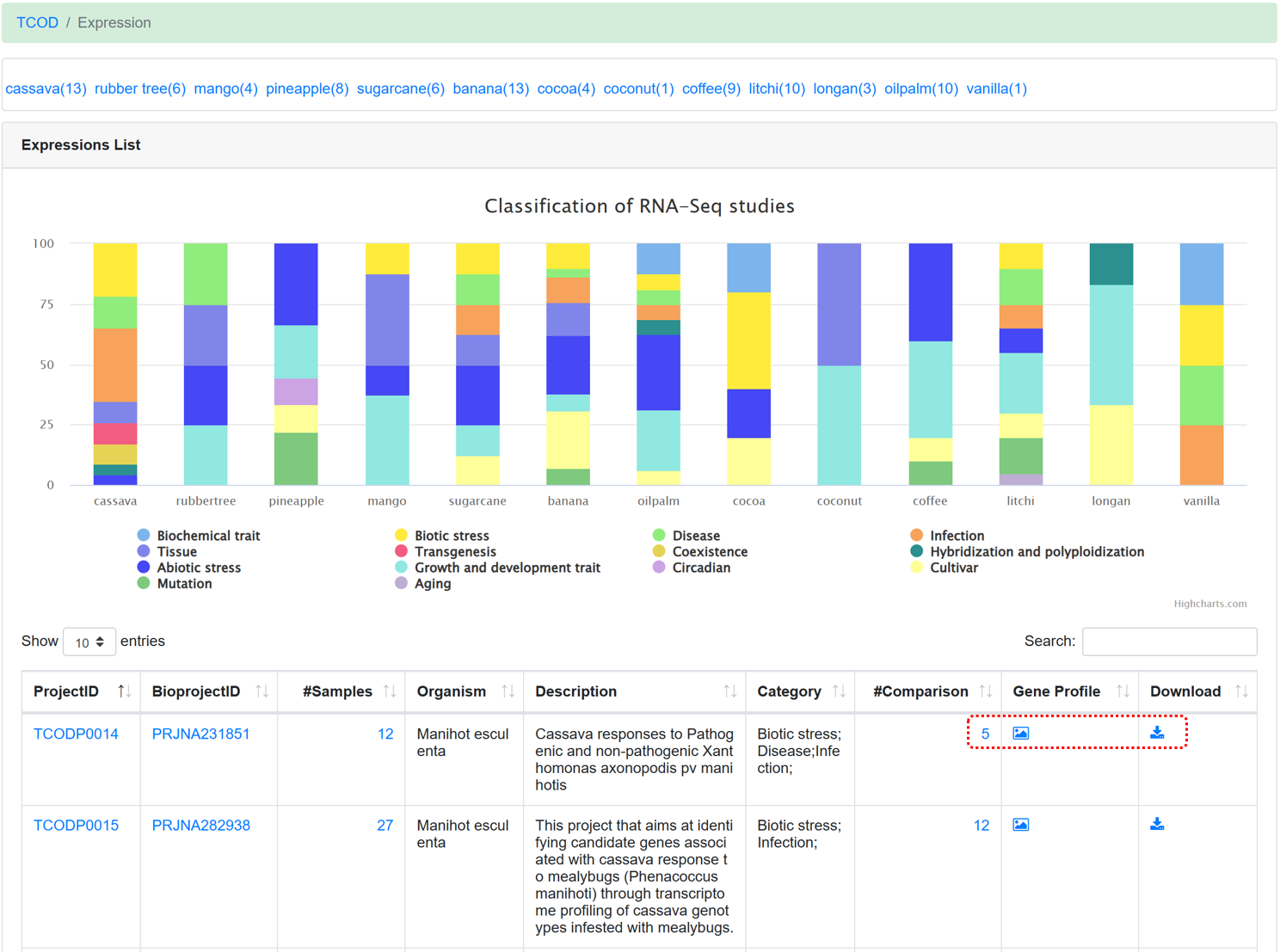
Figure 13 The overview of 'Expression' module
For each dataset, the following information is avaliable:
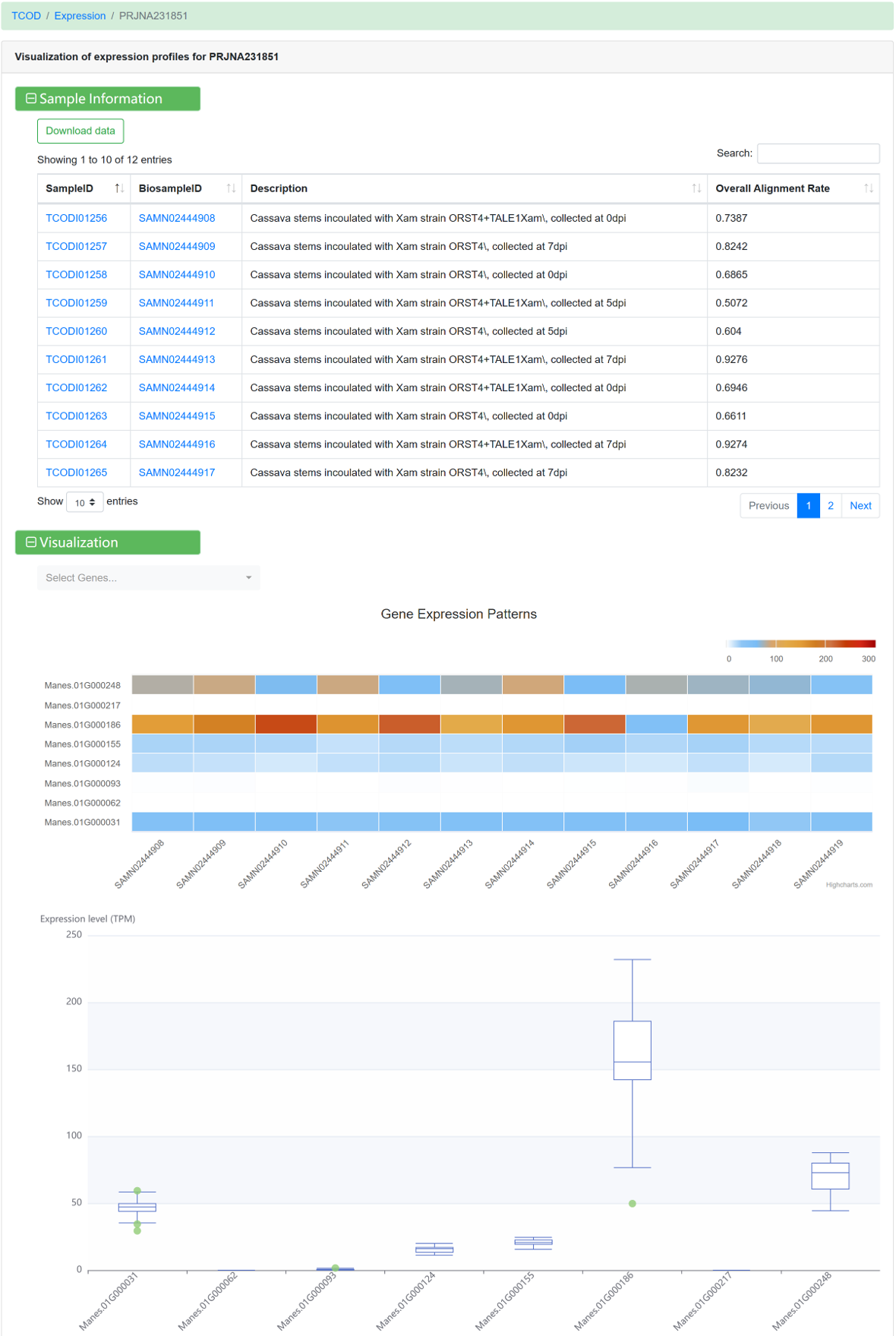
Figure 14 Visualization of gene expression profile
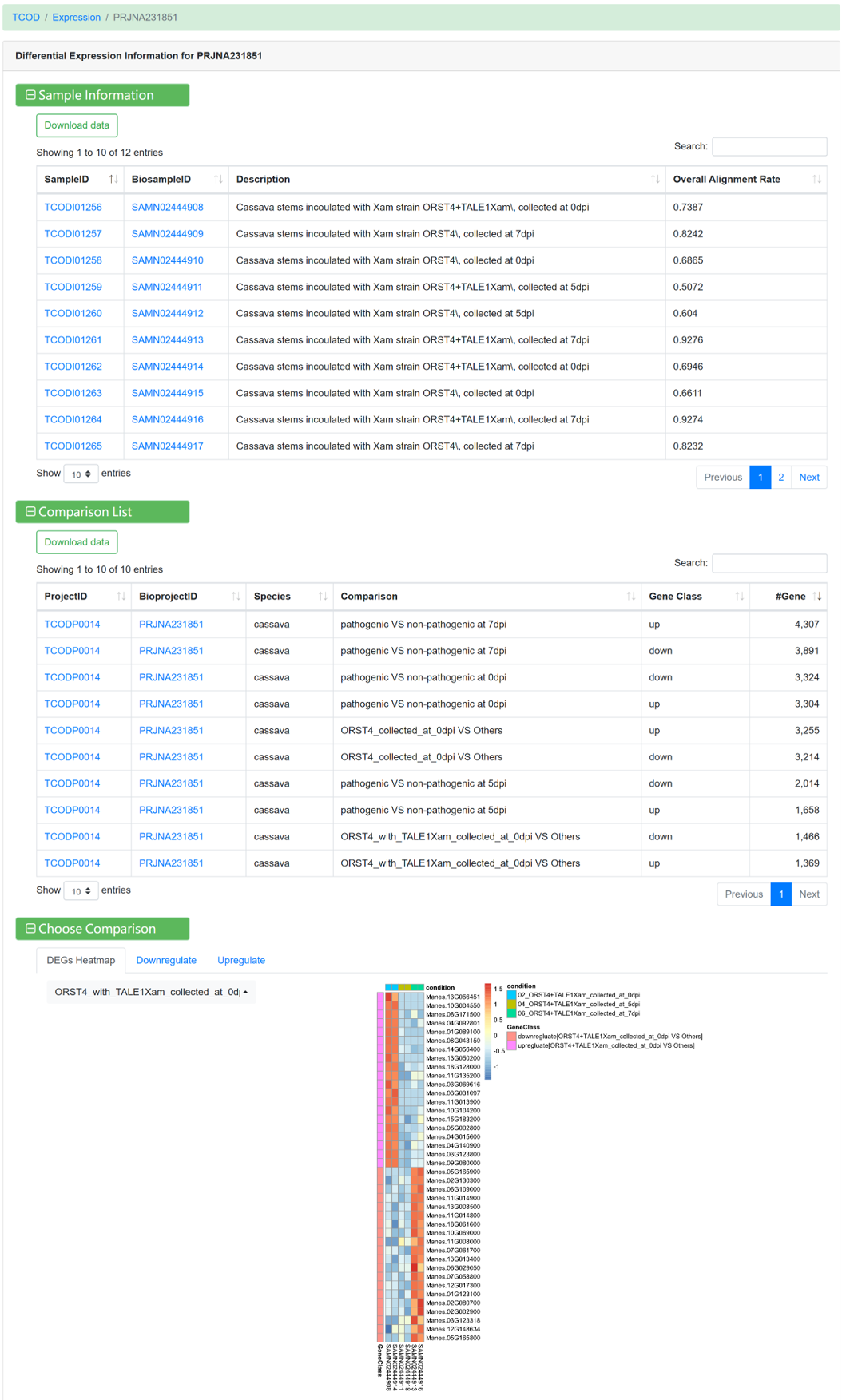
Figure 15 Differential expression information under different comparison conditions
6.Cultivar
The 'Cultivars' module currently includes 13,122 germplasm entries of 15 species, integrated from CIAT , IITA and GRIN. The page consists of the following three sections:

Figure 16 The overview of 'Cultivars' module
Clicking on each cultivarID link allows you to view detailed information:
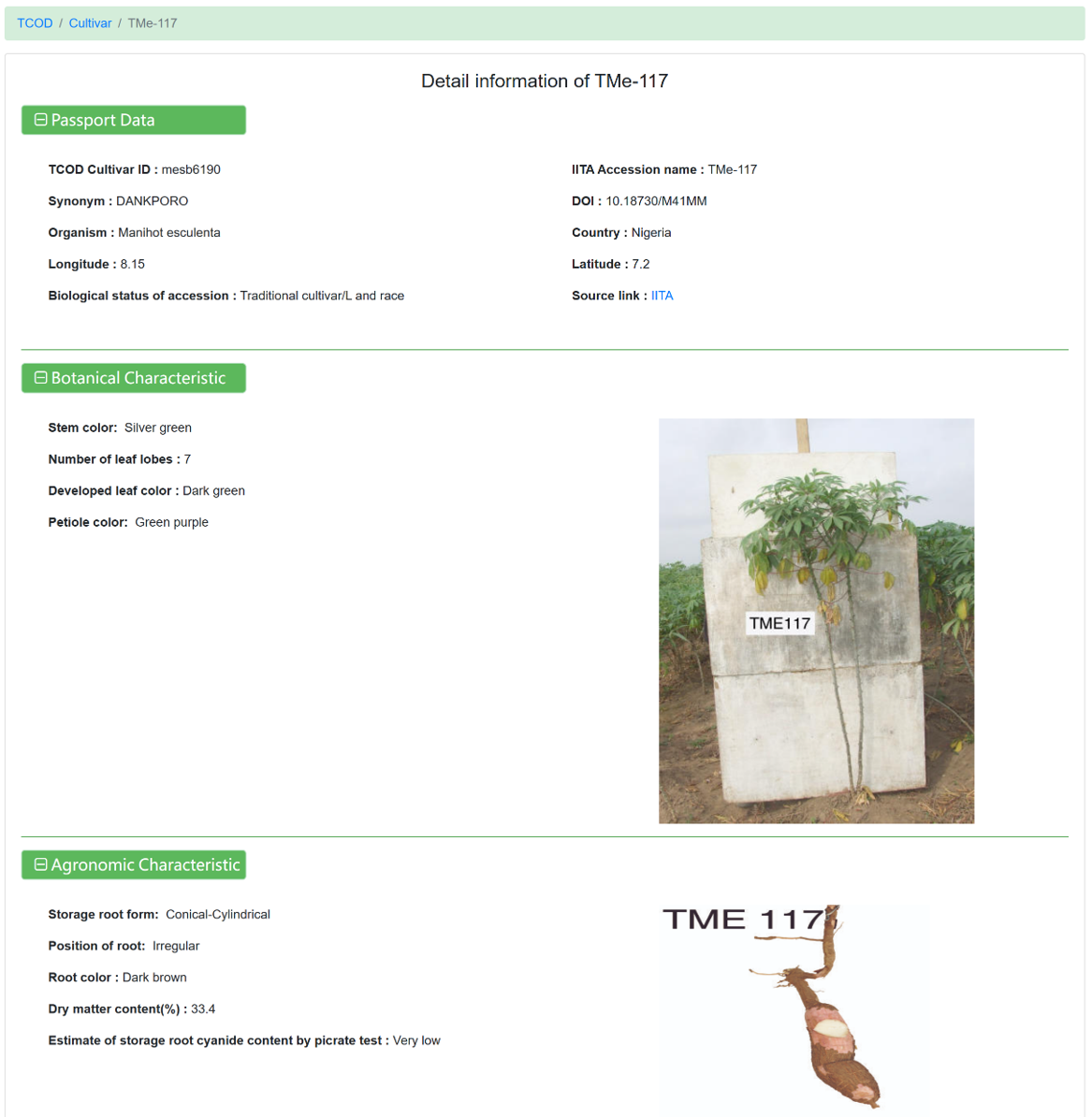
Figure 17 The detailed information for each cultivar
7.Tools
7.1. BLAST
The BLAST tool provides alignment databases for 15 species, including genome, CDS, and protein sequences. Users can choose single or multiple species alignment databases to find similar sequences, or submit their own sequences for pairwise alignment.
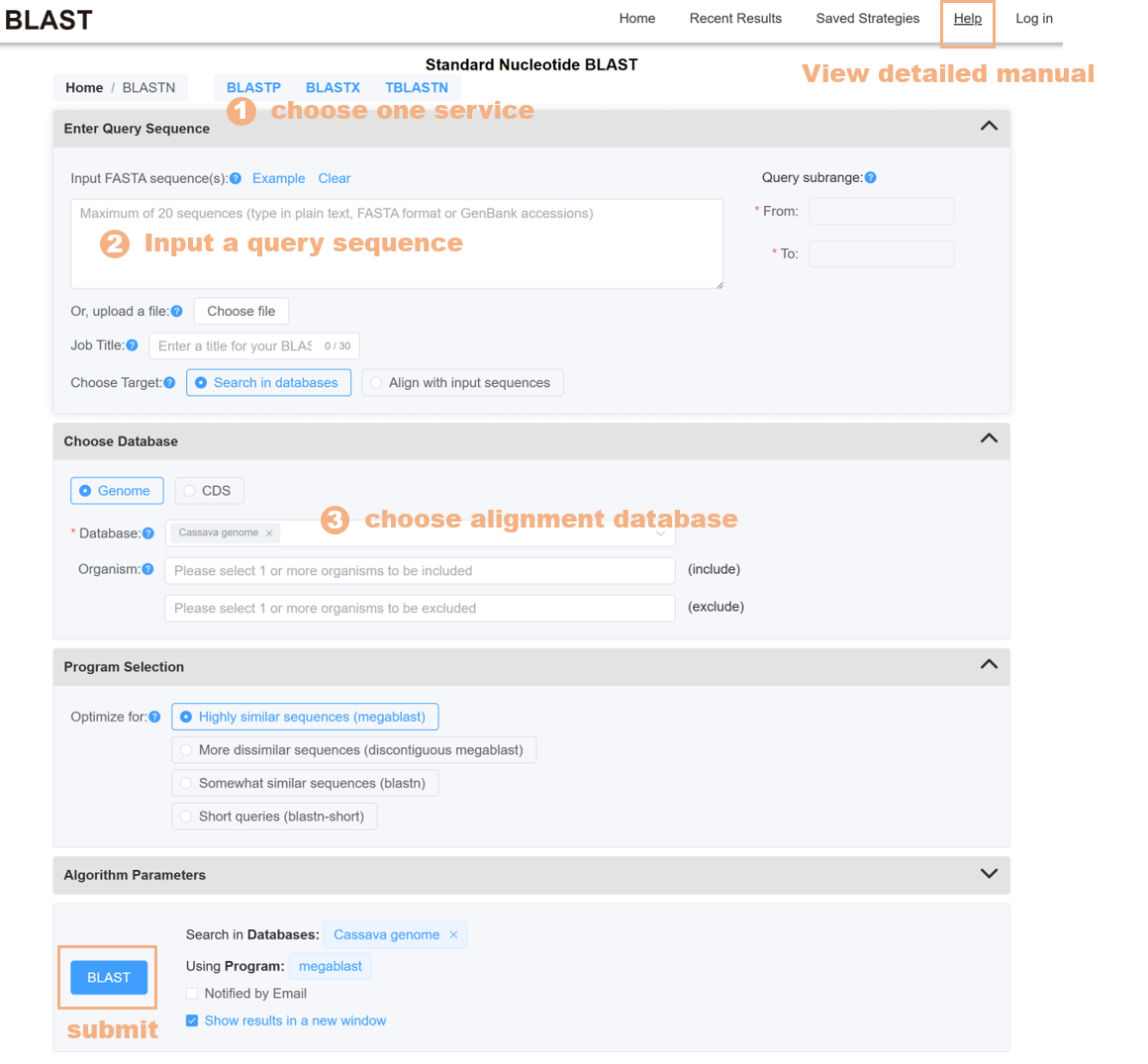
Figure 18 The BLAST tool
7.2. Genome Browser
The Genome Browser calls the jbrowse plug-in to support the visualization of the genome sequence, gene structure, SNPs and InDels on the genes, and supports exporting the visualization results of selected regions to images.
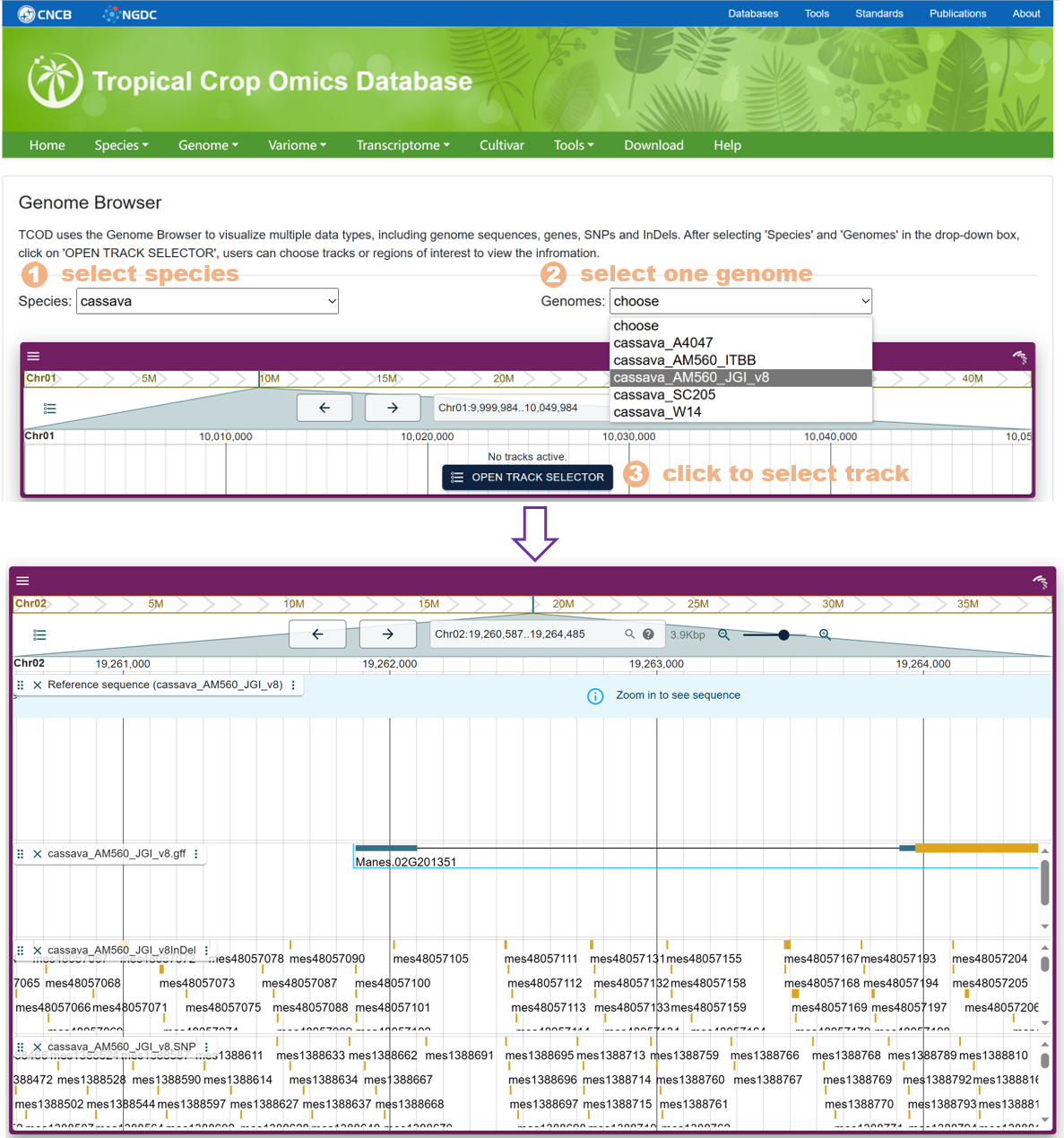
Figure 19 The Genome Browser tool
7.3. Primer Design
The Primer Design tool is designed to assist users in designing primers for subsequent experimental validation. It is a secondary development based on Primer3web. The specific steps are as follows:
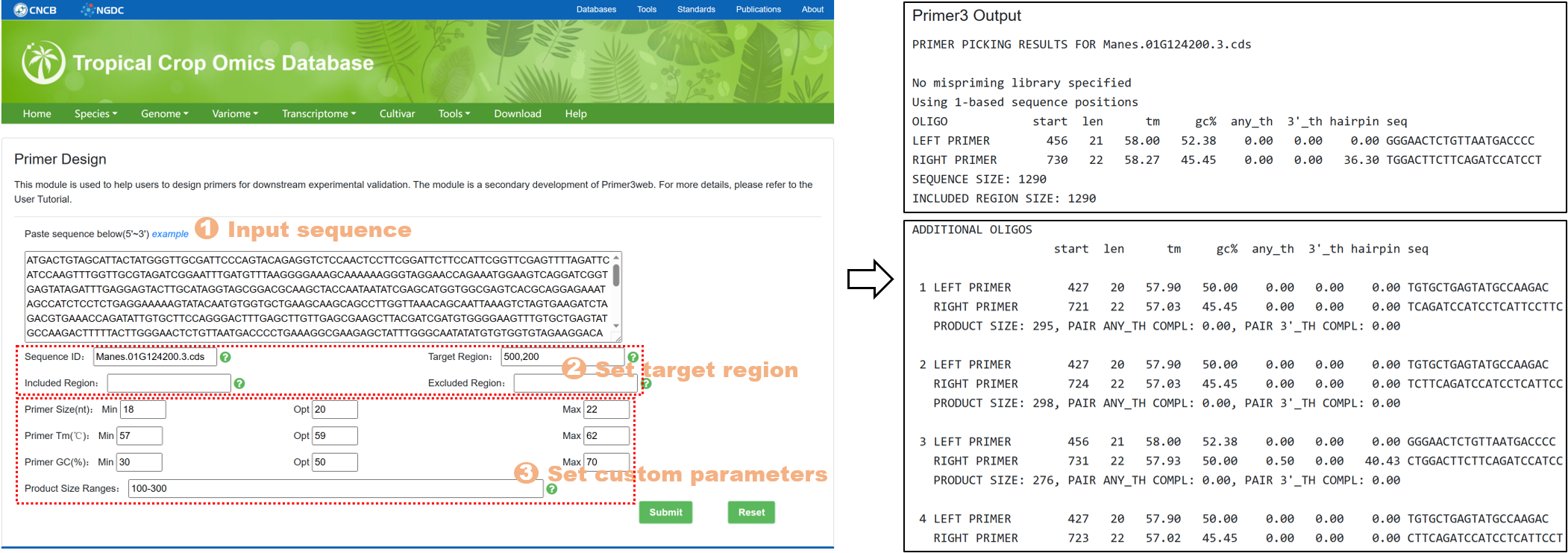
Figure 20 The Primer Design tool
7.4. Literature Search
The Literature Search tool utilizes the data interface provided by NGDC OpenLB to facilitate rapid literature searches based on selected journals, publication years, publication types.
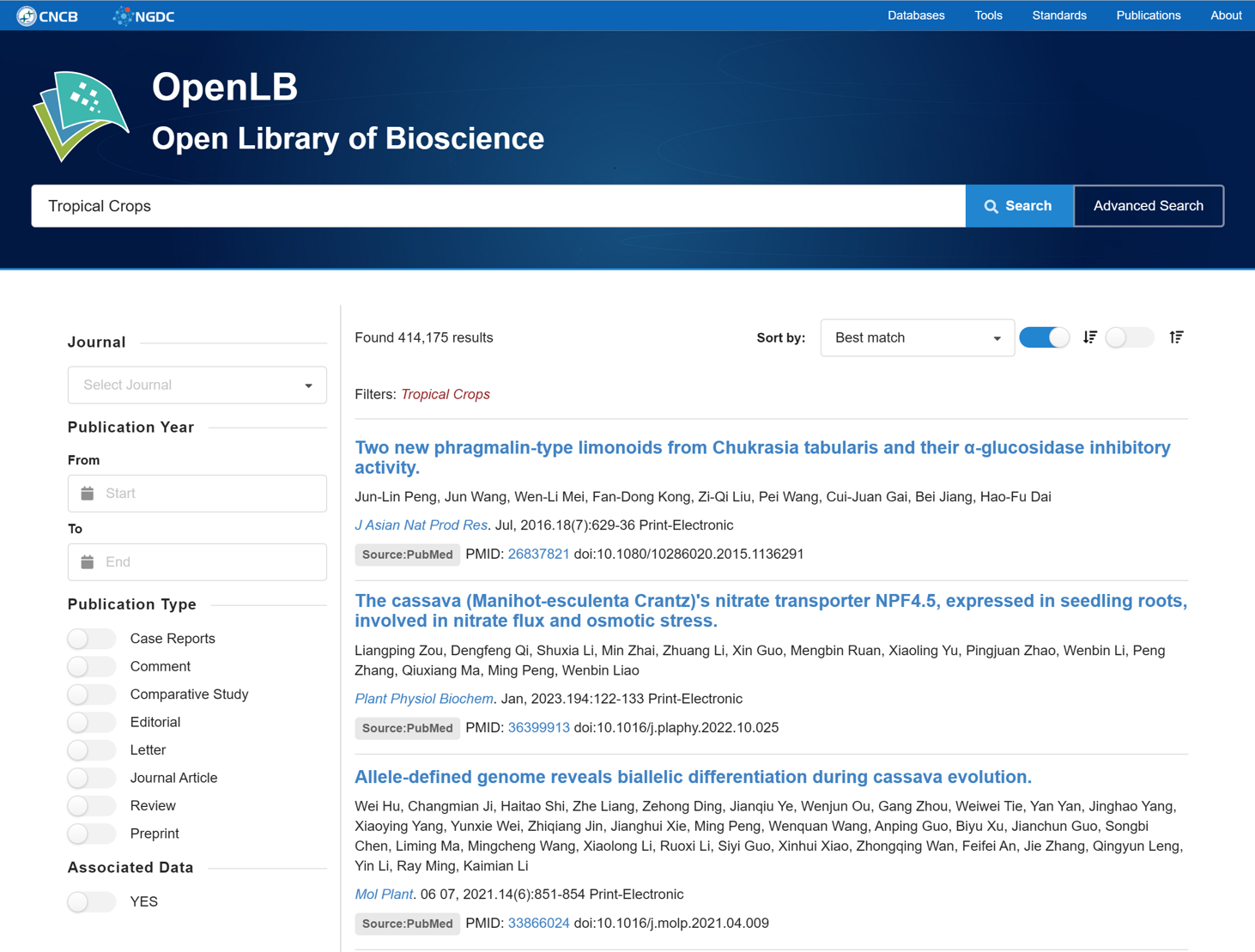
Figure 21 The Literature Search tool
7.5. GO Enrichment
The GO Enrichment tool is used to help users carry out GO pathway enrichment analysis on the target gene set. The specific steps are as follows:
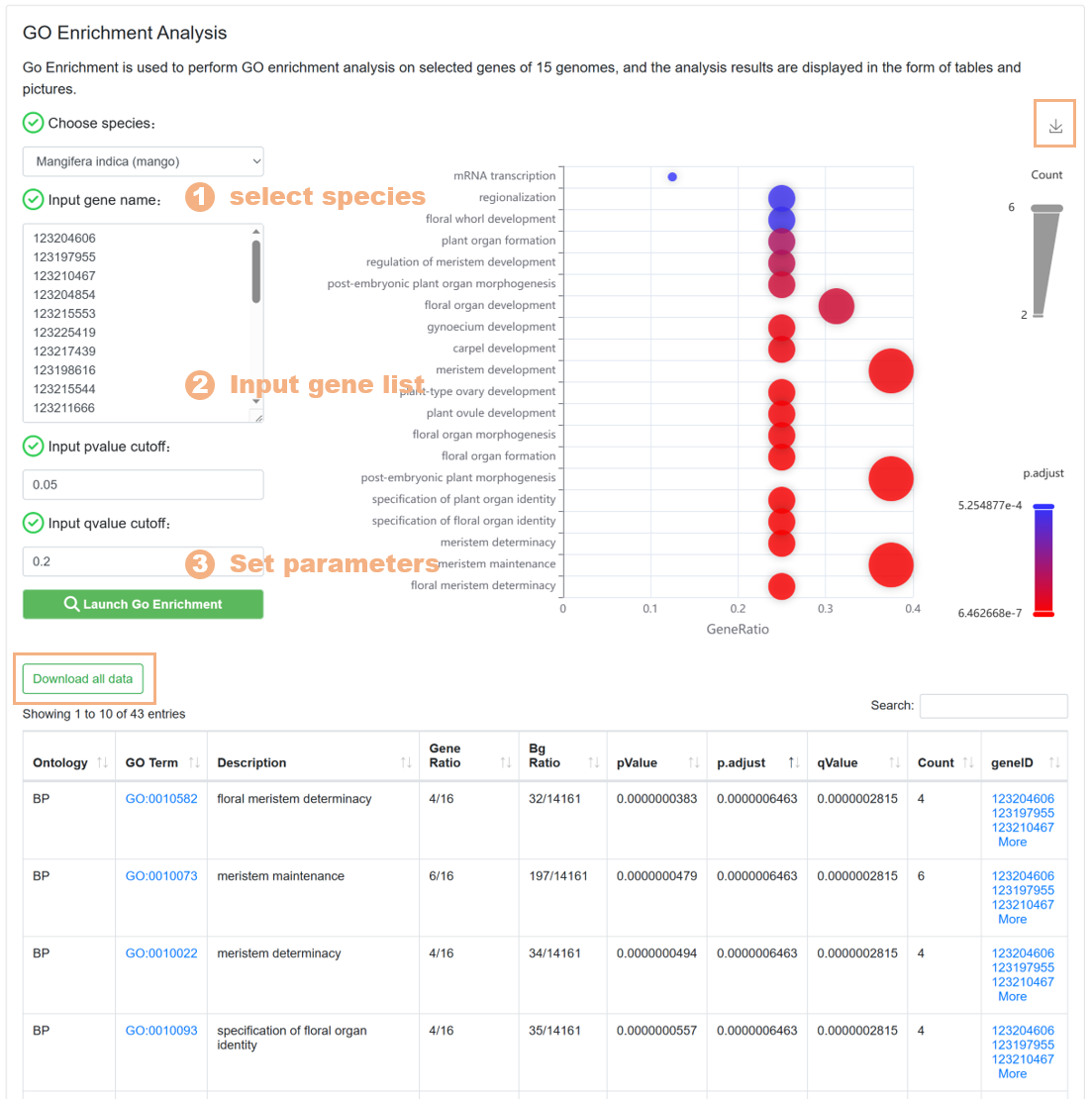
Figure 22 The GO Enrichment tool
7.6. KEGG Enrichment
The KEGG Enrichment tool is used to help users carry out KEGG pathway enrichment analysis on the target gene set, similar to the design of the GO Enrichment tool. The specific steps are as follows:
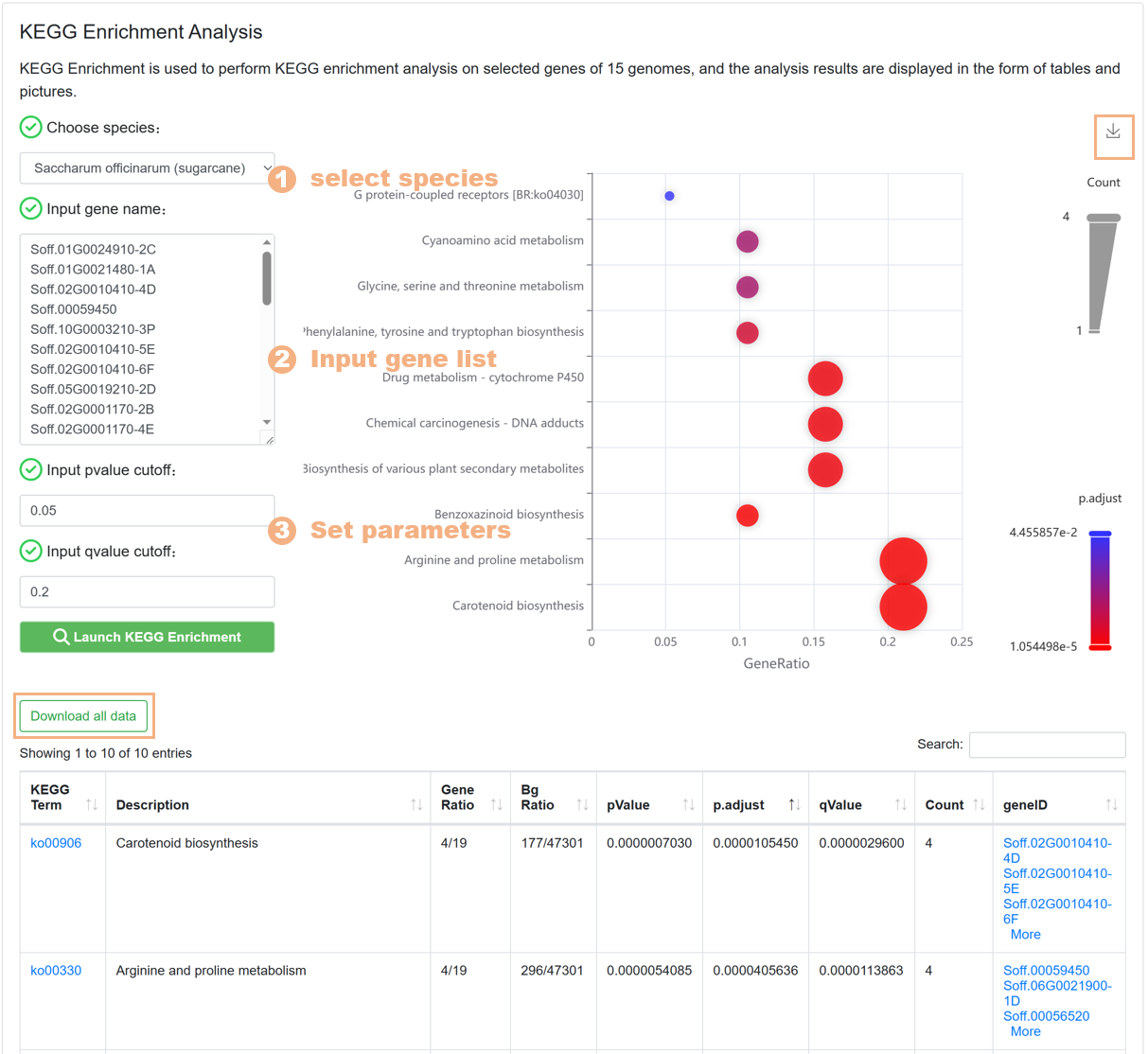
Figure 23 The KEGG Enrichment tool
7.7. Synteny Viewer
We utilized the Mummer software to conduct synteny analysis on the whole genome sequences of 15 species. The Synteny Viewer allows users to visualize the synteny results between different species, as well as between different subspecies of the same species. The specific steps are as follows:
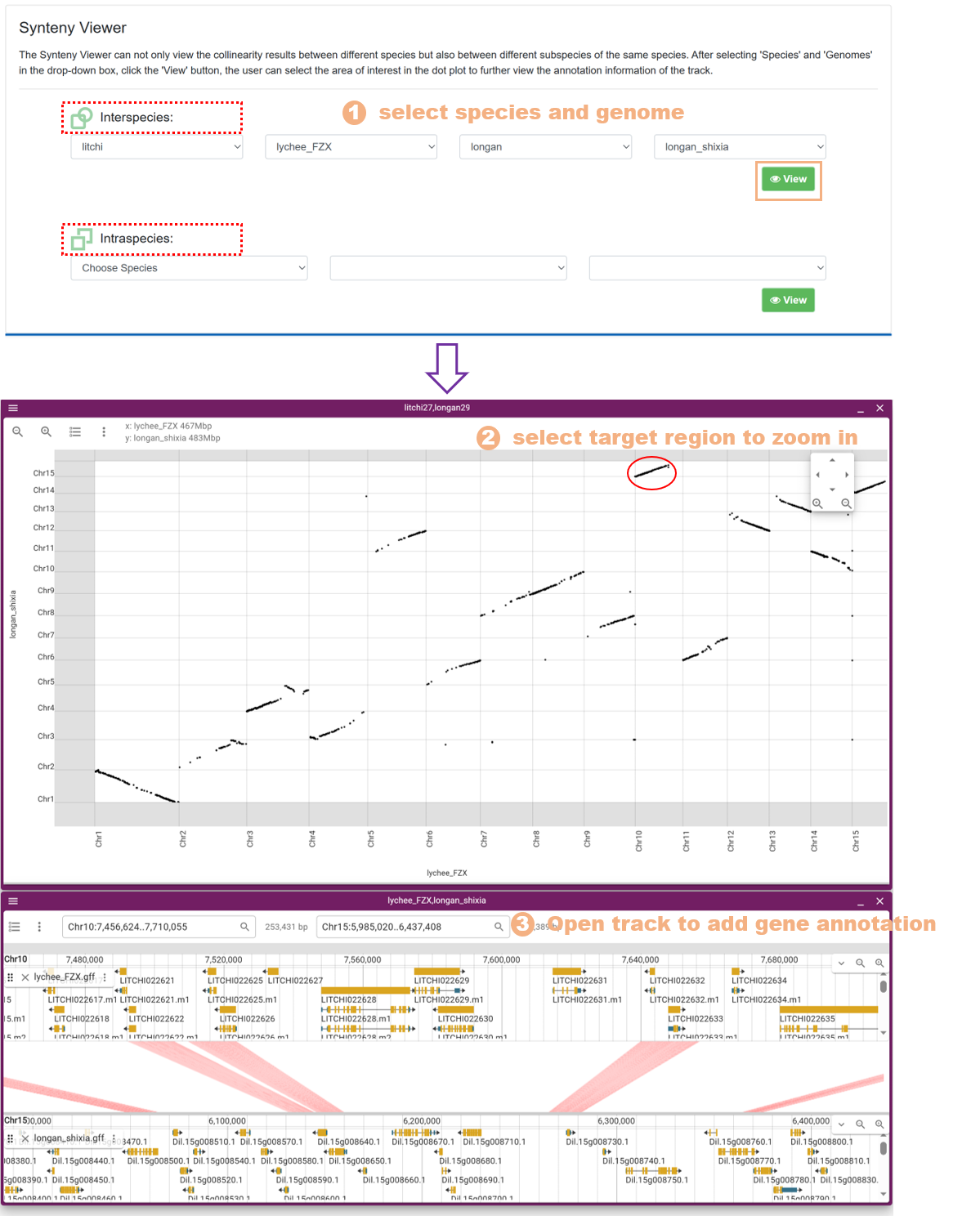
Figure 24 The Synteny Viewer tool
7.8. Homolog Finder
The Homolog Finder tool aids users in swiftly searching homologous genes. The page primarily encompasses:
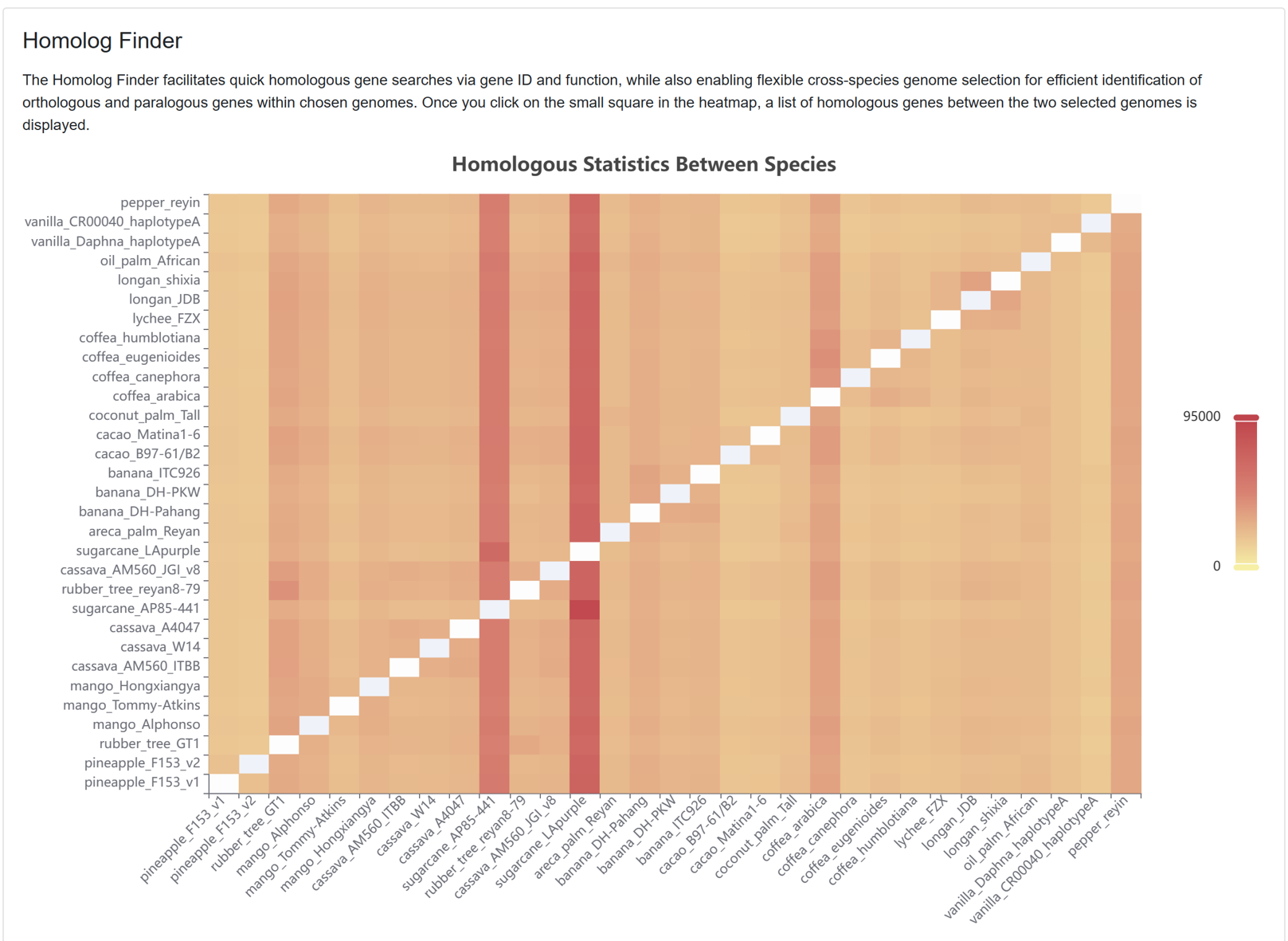
Figure 25 The homologous gene entries between pairs of genomes for each species
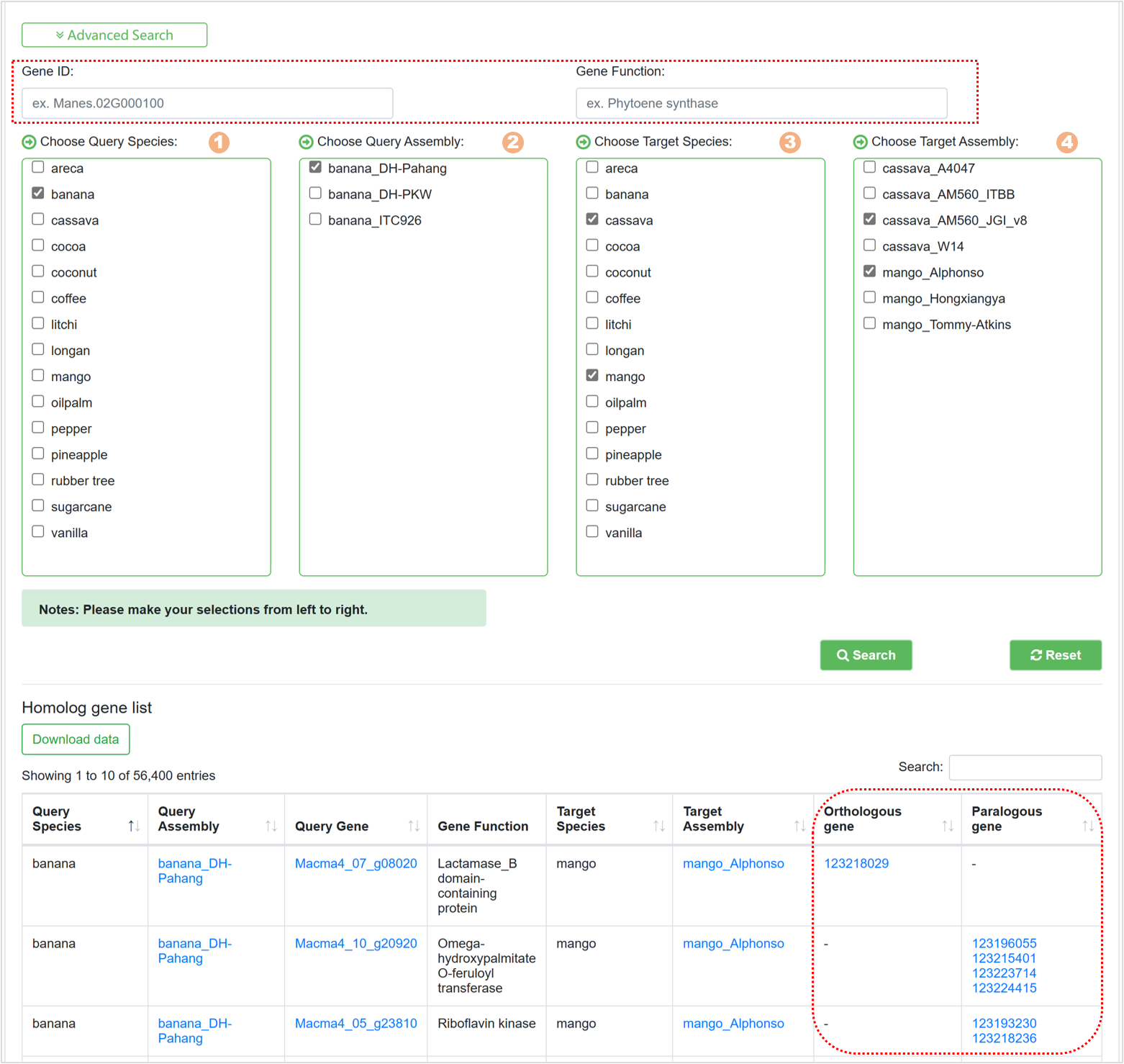
Figure 26 Advanced search for homologous genes
8.Download
For the diverse omics data resources integrated into the database, we offer the direct download for all available data except those that are yet to be released. The downloadable data encompass a wide range of information, including 30 genome sequences along with their corresponding annotation infromation, genome-wide variation data for 9 different species, transcriptome profiling results for 13 species, and germplasm items for 15 species.
9.Tutorial video
This video file provides a brief introduction to the TCOD and demonstrates how to effectively mine the data contained within it.