Difference between revisions of "NONHSAT107640"
| (5 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | ''HULC'' : Highly upregulated in liver cancer RNA is characterized as a novel mRNA-like ncRNA which is associated with cancer progression. <ref name="ref1" /> | |
==Annotated Information== | ==Annotated Information== | ||
===Name=== | ===Name=== | ||
| − | HULC: | + | HULC: hepatocellular carcinoma up-regulated long non-coding RNA [https://www.genenames.org/data/gene-symbol-report/#!/hgnc_id/HGNC:34232 (HGNC:34232)] |
| + | ===Aliases=== | ||
| + | NCRNA00078: non-protein coding RNA 78, LINC00078: long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 78, HCCAT1: hepatocellular carcinoma associated transcript 1 (non-protein coding) [https://www.genenames.org/data/gene-symbol-report/#!/hgnc_id/HGNC:34232 (HGNC:34232)] | ||
===Characteristics=== | ===Characteristics=== | ||
| − | + | [[File: HULC.jpg|right|thumb|400px|'''Characterization of the HULC transcriptional unit. (A) Northern blot analysis of HULC RNA. Ten micrograms of total RNA were loaded per lane. A positive signal at 500 nt indicates specific overexpression in different tumorous tissues. H, HCC; F, focal nodular hyperplasia (FNH); N, non-neoplastic liver. 18S and 28S rRNA were used as a control for the quantity and quality of RNA loaded. (B) The HULC gene locus. HULC RNA sequence including the polyA tail showing the location of the intron and the polyadenylation signals (boxes). (C) Diagram of the HULC gene locus. The HULC gene consists of 2 exons, 182 nt and 303 nt long, with 1 standard AATAAA and 2 noncanonical AATTAA polyadenylation signals occurring 21 nt, 32 nt, and 47 nt, respectively, upstream from the polyA tail.''' <ref name="ref1" />.]] | |
| + | |||
| + | ''HULC'' RNA is ~500nuc, spliced and polyadenlyated,localized on human chromosome 6p24.3 and resembles the mammalian LTR transposon 1A. One striking feature of the ''HULC'' RNA sequence is the high density of stop codons in the small potential reading frames scattered throughout the ''HULC'' gene. It does not contain substantial open reading frames, and no protein product was detected. ''HULC'' is present in the cytoplasm, where it copurifies with ribosomes. The ''HULC'' gene includes a single intron and carries 1 canonical and 2 noncanonical polyadenylation signals 21 nt, 32 nt, and 47 nt, respectively, upstream from the polyA tail <ref name="ref1" /> | ||
===Function=== | ===Function=== | ||
| − | + | ''HULC'' has a role in post-transcriptional modulation of gene expression. First clues about the function of ''HULC'' were obtained from siRNA-mediated knockdown of ''HULC'' in Hep3B and HepG2 cells, which resulted in a significant up- and down-regulation of several genes. <ref name="ref1" /> | |
| + | ''HULC'' may act as an endogenous ‘sponge’, which down-regulates a series of microRNAs (miRNAs) activities, including miR-372. Inhibition of miR-372 leads to reducing translational repression of its target gene, ''PRKACB'', which in turn induces phosphorylation of ''CREB''. <ref name="ref2" /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Regulation=== | ||
| + | PKA pathway may involved in up-regulation of HULC. <ref name="ref2" /> | ||
===Expression=== | ===Expression=== | ||
| − | + | ''HULC'' Is specifically expressed in Hepatocytes and highly up-regulated in HCC. ''HULC'' is the first ncRNA with highly specific up-regulation in HCC. It was detected in blood of HCC patients therefore can be used as a potential biomarker. In contrast to the liver tumors, ''HULC'' is only slightly up-regulated in cirrhotic liver tissue and only barely detectable in most of the normal tissues. In situ hybridization revealed the specific and strong expression of ''HULC'' RNA in the cytoplasm of HCC, whereas it was not detected in tumor stroma and non-neoplastic liver cells. <ref name="ref1" /> | |
| − | === | + | ''HULC'' was overexpressed in colorectal carcinomas that metastasize to the liver indicating that ''HULC'' expression is not confined to HCC. <ref name="ref3" /> |
| − | + | {| class='wikitable' style="text-align:center" | |
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! | Experiment | ||
| + | ! | Forward primer | ||
| + | ! | Reverse primer | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | rowspan="1"|Quantiative RT-PCR | ||
| + | | | 5'-atctgcaagccaggaagagtc- 3' | ||
| + | | | 5'-cttgcttgatgctttggtctgt- 3'<ref name="ref1" /> | ||
| + | |} | ||
| − | === | + | ===Diseases=== |
| − | + | * Colorectal Carcinomas <ref name="ref3" /> | |
| + | * Hepatocellular Carcinoma <ref name="ref1" /> | ||
| − | === | + | ===Conservation=== |
| − | + | ''HLUC'' also present in other primates, gene shows good conservation above that of surrounding sequence. Not detected in rodents so may be primate specific <ref name="ref1" /> | |
| − | == | + | ==Labs working on this lncRNA== |
| − | + | * Institute of Pathology, Medical University of Graz, Graz, Austria | |
| + | * Oridis-Biomed, Graz, Austria | ||
| + | * Max F. Perutz Laboratories, Vienna, Austria | ||
| + | * Laboratory of Experimental and Molecular Hepatology, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Medical University of Graz, Graz, Austria | ||
| + | * Department of Biology, Science and Technology, Alquds Abu-Dis University, Jerusalem, Israel. | ||
| + | * Department of Laboratory Medicine, Ruijin Hospital, Faculty of Medical Laboratory Science, Department of Pathology, Ruijin Hospital, Shanghai Jiaotong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200025 | ||
| − | == | + | ==References== |
| − | + | <references> | |
| − | + | <ref name="ref1"> Panzitt K, Tschernatsch MMO, Guelly C, Moustafa T, Stradner M, Strohmaier HM et al. Characterization of HULC, a Novel Gene With Striking Up-Regulation in Hepatocellular Carcinoma, as Noncoding RNA[J]. Gastroenterology. 2007, 132(1):330-342.</ref>(1) | |
| − | = | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | = | + | <ref name="ref2"> Wang J, Liu X, Wu H, Ni P, Gu Z, Qiao Y et al. CREB up-regulates long non-coding RNA, HULC expression through interaction with microRNA-372 in liver cancer[J]. Nucleic acids research. 2010, 38(16):5366-5383.</ref>(2) |
| − | |||
| − | = | + | <ref name="ref3"> Matouk IJ, Abbasi I, Hochberg A, Galun E, Dweik H & Akkawi M. Highly upregulated in liver cancer noncoding RNA is overexpressed in hepatic colorectal metastasis[J]. European Journal of gastroenterology & hepatology. 2009, 21(6):688-692.</ref>(3) |
| − | + | </references> | |
{{basic| | {{basic| | ||
Latest revision as of 07:26, 23 November 2018
HULC : Highly upregulated in liver cancer RNA is characterized as a novel mRNA-like ncRNA which is associated with cancer progression. [1]
Contents
Annotated Information
Name
HULC: hepatocellular carcinoma up-regulated long non-coding RNA (HGNC:34232)
Aliases
NCRNA00078: non-protein coding RNA 78, LINC00078: long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 78, HCCAT1: hepatocellular carcinoma associated transcript 1 (non-protein coding) (HGNC:34232)
Characteristics
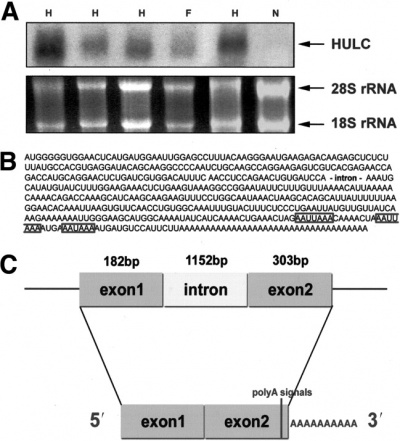
HULC RNA is ~500nuc, spliced and polyadenlyated,localized on human chromosome 6p24.3 and resembles the mammalian LTR transposon 1A. One striking feature of the HULC RNA sequence is the high density of stop codons in the small potential reading frames scattered throughout the HULC gene. It does not contain substantial open reading frames, and no protein product was detected. HULC is present in the cytoplasm, where it copurifies with ribosomes. The HULC gene includes a single intron and carries 1 canonical and 2 noncanonical polyadenylation signals 21 nt, 32 nt, and 47 nt, respectively, upstream from the polyA tail [1]
Function
HULC has a role in post-transcriptional modulation of gene expression. First clues about the function of HULC were obtained from siRNA-mediated knockdown of HULC in Hep3B and HepG2 cells, which resulted in a significant up- and down-regulation of several genes. [1] HULC may act as an endogenous ‘sponge’, which down-regulates a series of microRNAs (miRNAs) activities, including miR-372. Inhibition of miR-372 leads to reducing translational repression of its target gene, PRKACB, which in turn induces phosphorylation of CREB. [2]
Regulation
PKA pathway may involved in up-regulation of HULC. [2]
Expression
HULC Is specifically expressed in Hepatocytes and highly up-regulated in HCC. HULC is the first ncRNA with highly specific up-regulation in HCC. It was detected in blood of HCC patients therefore can be used as a potential biomarker. In contrast to the liver tumors, HULC is only slightly up-regulated in cirrhotic liver tissue and only barely detectable in most of the normal tissues. In situ hybridization revealed the specific and strong expression of HULC RNA in the cytoplasm of HCC, whereas it was not detected in tumor stroma and non-neoplastic liver cells. [1]
HULC was overexpressed in colorectal carcinomas that metastasize to the liver indicating that HULC expression is not confined to HCC. [3]
| Experiment | Forward primer | Reverse primer |
|---|---|---|
| Quantiative RT-PCR | 5'-atctgcaagccaggaagagtc- 3' | 5'-cttgcttgatgctttggtctgt- 3'[1] |
Diseases
Conservation
HLUC also present in other primates, gene shows good conservation above that of surrounding sequence. Not detected in rodents so may be primate specific [1]
Labs working on this lncRNA
- Institute of Pathology, Medical University of Graz, Graz, Austria
- Oridis-Biomed, Graz, Austria
- Max F. Perutz Laboratories, Vienna, Austria
- Laboratory of Experimental and Molecular Hepatology, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Medical University of Graz, Graz, Austria
- Department of Biology, Science and Technology, Alquds Abu-Dis University, Jerusalem, Israel.
- Department of Laboratory Medicine, Ruijin Hospital, Faculty of Medical Laboratory Science, Department of Pathology, Ruijin Hospital, Shanghai Jiaotong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200025
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 Panzitt K, Tschernatsch MMO, Guelly C, Moustafa T, Stradner M, Strohmaier HM et al. Characterization of HULC, a Novel Gene With Striking Up-Regulation in Hepatocellular Carcinoma, as Noncoding RNA[J]. Gastroenterology. 2007, 132(1):330-342.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Wang J, Liu X, Wu H, Ni P, Gu Z, Qiao Y et al. CREB up-regulates long non-coding RNA, HULC expression through interaction with microRNA-372 in liver cancer[J]. Nucleic acids research. 2010, 38(16):5366-5383.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Matouk IJ, Abbasi I, Hochberg A, Galun E, Dweik H & Akkawi M. Highly upregulated in liver cancer noncoding RNA is overexpressed in hepatic colorectal metastasis[J]. European Journal of gastroenterology & hepatology. 2009, 21(6):688-692.
Basic Information
| Transcript ID |
NONHSAT107640 |
| Source |
NONCODE4.0 |
| Same with |
, |
| Classification |
intergenic |
| Length |
500 nt |
| Genomic location |
chr6+:8652442..8654459 |
| Exon number |
3 |
| Exons |
8652442..8652623,8653778..8654079,8654444..8654459 |
| Genome context |
|
| Sequence |
000001 ATGGGGGTGG AACTCATGAT GGAATTGGAG CCTTTACAAG GGAATGAAGA GACAAGAGCT CTCTTTATGC CACGTGAGGA 000080
000081 TACAGCAAGG CCCCAATCTG CAAGCCAGGA AGAGTCGTCA CGAGAACCAG ACCATGCAGG AACTCTGATC GTGGACATTT 000160 000161 CAACCTCCAG AACTGTGATC CAAAATGCAT ATGTATCTTT GGAAGAAACT CTGAAGTAAA GGCCGGAATA TTCTTTGTTT 000240 000241 AAAACATTAA AAACAAAACA GACCAAAGCA TCAAGCAAGA AGTTTCCTGG CAATAAACTA AGCACAGCAT TATTTTTTAA 000320 000321 GGAACACAAA TTAAGTGTTC AACCTGTGGC AAATTTGTAC TTTCTCCCTG AATTATGTTG TTATCAAAGA AAAAAATTGG 000400 000401 GAAGCATGGC AAAATATCAT CAAAACTGAA ACTAGAATTA AACAAAACTA AATTAAAATG AAATAAAATG ATGTCCATTC 000480 000481 TTAAAAAAAA AAAAAAAAAA |