● About PlantPan
Numerous plant pan-genome studies have been conducted nowadays, particularly in recent years, as sequencing technology advancements have enabled high-quality whole genome assemblies for these investigations. The pan-genome of plants encompasses the full spectrum of genomic diversity, offering a wealth of genetic resources for studying evolution, domestication and breeding research, and plant improvement. Hence, developing a platform that stores plant pan-genome data is crucial. Here, we present PlantPan, a comprehensive database gathering pan-genome analysis results of 195 genomes from 11 species. PlantPan offers five levels of information, including species, genes, gene groups, genomic variation, and genome synteny. Ultimately, PlantPan serves as a comprehensive plant pan-genome database, providing valuable insights and guidance for plant breeding endeavors.
● Data Source
In total, PlantPan encompasses 11 species and 195 genomes, each featuring high-quality chromosome-level whole genome assemblies. The 11 species encompassed in this study are Arabidopsis Thaliana, Brassica Napus, Brassica Rapa, Maize, Potato, Raphanus Sativus, Rice, Sorghum, Soybean, Strawberry, and Tomato (Table 1).
Table1: Statistics of species and genomes used in PlantPan
| Species | Sub-Species | Assembled Size | N50 | N90 | #Chrom | PubMed ID |
|---|
● Data Analysis Workflow
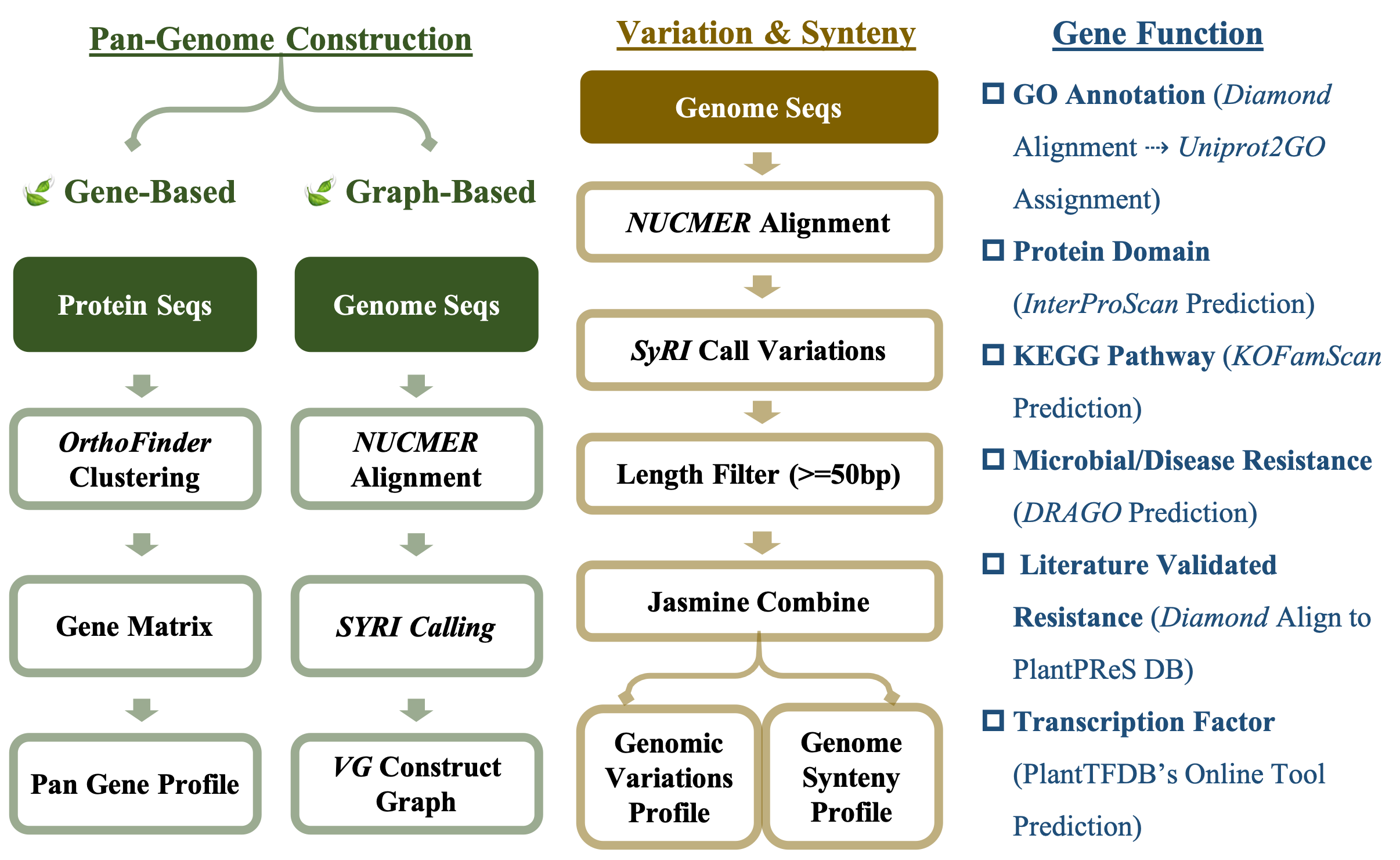
PlantPan collects genome sequences and related gene annotations from 11 species and 195 genomes to create a comprehensive plant pan-genome database. We conduct analyses in three key aspects: pan-genome construction, variations & synteny identification, gene functional annotation (Figure 1).
1) Pan-Genome Construction
Gene-based pan-genome. We input protein sequences with only the longest transcript remaining into OrthoFinder for clustering within each species. From the clustering results, we obtain the gene presence and absence profile among sub-species. PanGP is then used to predict the openness of all and core genes to determine if the genes of these sub-species adequately represent the gene diversity of the species.
Graph-based pan-genome. Whole genomes are initially aligned against a reference genome using nucmer, followed by SyRI to call genetic variations. We select 13 types of variations from the calling results, including CPG (Copy Gain), CPL (Copy Loss), INS (Insertion), DEL (Deletion), DUP (Duplication), INVDP (Inverted Duplication), HDR (Highly Divergent Region), SNP, INV (Inversion), TRANS (Translocation), INVTR (Inverted Translocation), TDM (Tandem Repeat) and NOTAL (Un-aligned Region). By combining these variations with the reference genome, we employ VG to construct the graph-based pan-genome.
2) Variations & Synteny
Genomic variation and genome synteny identification. Firstly, whole genome sequence of each sub-species is aligned to the reference genome with nucmer. Then SyRI is used to identify genomic variations and genome synteny.
Gene copy number variations identification. Protein sequences with only longest transcript remained are mapped with each other by blastp. Then DupGen_finder.pl is used to identify gene copy number and duplicated genes.
Genomic variation and genome synteny identification group construction. Variations and genome synteny with a length of 50bp or greater have been chosen for characterizing the structural variation profile with Jasmine. Then the variation and genome synteny groups are obtained.
3) Gene Function Annotation
GO annotation. Gene protein sequences are matched to the UniProt protein sequences pool using Diamond software, and then we assign a GO ID according to UniProt protein ID. Based on the GO ID, the term, ontology, and definition are manually assigned to the corresponding gene.
Protein domain annotation. Protein sequences are input into InterProScan software, and entries with IPR IDs are chosen, with the relevant protein domain descriptions extracted.
KEGG pathway annotation. Gene sequences are entered into KOFAMSCAN software, and the corresponding ko ID is assigned to the genes. KID, K_Description, ko ID, Pathway Descrition, Level 1 and Leve2 information are assigned based on the ko ID.
Resistance genes annotation. For literature-validated resistance gene annotation, the PlantReS database curation results are utilized. By comparing protein sequences with PlantReS's findings, resistance factors, corresponding UniProt protein IDs, and related PubMed article IDs are provided. For microbial/disease resistance gene annotation, online DRAGO software is employed.
Transcription factor annotation. The PlantTFDB online software annotates transcription factors based on protein sequences.
4) Homologies identification among different species. Representative genes are first chosen from OrthoFinder clustering results for corresponding gene groups, and then these representatives are aligned using blastp. Those pairs meeting the 70% identity and 70% coverage thresholds simultaneously are considered homology with each other. All genes in these two groups are also deemed homologous to each other.
Figure 1: The workflow of pan-genome analysis.
● Module Usage
Home
The 'Home' page's quick search tool offers five search methods: species name, literature-validated resistance factor, disease/microbial resistance class, pathway, and transcription factor. The lower-left section displays the featured 11 species and the number of associated genomes included in PlantPan. The lower-right section presents the primary content of PlantPan.
Browse
The 'Browse' page comprises 11 modules: Species, Genes, Gene Groups, Genetic Variations, Genetic Variation Groups, Genome Synteny, Genome Synteny Groups, Gene Copy Number Variations, Transcription Factor, Gene Resistance and Pathway.
1) The ‘Species’ module allows users to access an overview page of all species by clicking 'Species'. Users can access detailed information pages by clicking on a specific species' name. For a particular species, the information includes sub-species description, gene-based pan-genome, resistance genes, transcription factors, metabolism pathways, genetic variations, and genome synteny.
'Sub-species Description' provides information on sub-species, including their name, assembled genome size, N50, N90, and corresponding reference PubMed ID.
'Gene-based Pan-genome' features a table of pan-gene groups, including gene group ID, pan class, sample frequency, and the number of genes in the corresponding gene group, as well as the gene openness or closeness for the species.
'Resistance' includes literature-validated plant resistance genes and microbial/disease resistance genes. For both types of resistance genes, a heatmap of gene count across sub-species and a histogram of gene count with different pan classifications are displayed. Literature-validated resistance plant genes are described with resistance factors, gene ID, corresponding UniProt ID, sub-species, gene group, pan classification, and reference PubMed ID. Microbial/disease resistance genes are described with class, domain, gene ID, location, sub-species, gene group, and pan classification.
'Transcription Factor' showcases a heatmap of transcription factor count across sub-species and a histogram of transcription factor count with different pan classifications in the top two panels. Detailed information on transcription factors includes transcription factor type, gene ID, sub-species, gene group, and pan classification.
'KEGG Pathway' presents a heatmap of metabolism pathway-related gene count across sub-species and a histogram of metabolism pathway-related gene count with different pan classifications in the top two panels. Detailed information on transcription factors includes geneID, KID, K_Description, koID, pathway description, level1, level2, sub-species, gene group ID and pan classification.
'Genetic Variation' list all of genomic variations from each sub-species and outlines the profile of structural variations with a length larger than or equal to 50bp, characterized by reference location, query location, variation type, variation length, sample frequency, and samples sharing this variation.
'Genome Synteny' gives the information of genome synteny from each sub-species and details the profile of genome synteny, characterized by reference location, query location, syntenic block length, sample frequency, and samples sharing this genome synteny.
2) In the ‘Genes’ module, the left panel displays the names of the 11 species, while the right panel presents a table containing gene information such as gene ID, sub-species, gene group ID, pan classification, and gene description. In the right table, both gene ID and gene group ID are clickable.
Clicking on the gene ID reveals detailed information about the corresponding gene, including species, sub-species, chromosome location, pan classification, sample frequency, related gene group, protein domain, GO functional annotation, metabolism pathway annotation, gene resistance, transcription factor, gene copy number variation, related genetic variations, related synteny block, and homologous genes in other species.
Clicking on the gene group ID displays detailed information about the corresponding gene group, including species, sample frequency, gene count, pan classification, genes in the group, motif of all genes in the group, phylogenetic tree, GO functional annotation, KEGG pathway annotation, literature validated resistance, microbial/disease resistance, transcription factors and homologous groups across other species.
3) ‘Gene Group’ module provides a gene group table for all 11 species containing group ID, species, sample frequency, total gene number, pan classification, sub-species list and gene list.
4) In the 'Genetic Variation' module, the left panel displays the names of the 9 species and their corresponding reference genomes. The right panel presents a table featuring 13 types of genetic, which include reference location, query genome, query location, variation type, reference variation length, query variation length, variation-related genes in the reference, and variation-related genes in the query.
5) In the 'Genetic Variation Group' module, a table including species, reference genome, reference location, query location, variation type, variation length, pan classification, sample frequency and sample list is given.
6) In the 'Genome Synteny' module, the left panel displays the names of the 9 species and their corresponding reference genomes. The right panel presents tables of genome synteny location, which include synteny ID, reference genome location, query genome, query genome location, reference syntenic block length, and query syntenic block length. Additionally, the tables show related genes in the syntenic block, featuring synteny ID, related genes in the reference genome, and related genes in the query genome. Lastly, the tables display related genetic variations in the syntenic block, including synteny ID, reference variation location, query variation location, variation type, reference variation length, and query variation length.
7) In the 'Genome Synteny Group' module, a table including species, reference genome, reference location, query location, length, pan classification, sample frequency and sample list is given.
8) In 'Gene Copy Number Variation' module, the left panel displays the names of the 11 species, while the right panel presents a table containing gene copy number variation information including gene ID, copy number and duplicated genes.
9) The 'Transcription Factor' module provides a table that includes information such as transcription factor, geneID, sub-species, group, pan classification, and species name from 11 species.
10) The 'Gene Resistance' module presents 2 table format containing items related to literature-validated resistance and predicted microbial/disease resistance respectively from 11 species.
11) The 'Pathway' module provides a table that includes information such as geneID, KID, K_Description, koID, pathway description, level1, level2, sub-species, gene group ID, pan classification and species name from 11 species.
Search
There are four methods to search PlantPan: Species, Genes, Genomic Variation, and Genome Synteny.
1) In the 'Search Species' module, users can select a species name from the drop-down menu, and the search result displays detailed information about the corresponding species.
2) In the 'Search Genes' module, users can choose from six search types in the left drop-down menu, including gene ID, keyword, transcription factor, resistance factor, microbial resistance type, and KEGG pathway type. Next, a detailed search term can be entered or selected from the right drop-down menu. The search results for gene ID or keyword display a table containing gene ID, sub-species, gene group ID, gene pan classification, and gene description. The other four search methods return three figures at the top panel, showcasing gene and gene group count of different pan classification counts, genes overlapping with variations or not count, and gene copy number variation distribution. The bottom panel features a table displaying related gene ID, search type, gene ID, group ID, pan classification, genetic variations, and gene copy number.
3) In the 'Search Genetic Variations' module, users can specify species, sub-species, variation type, chromosome, reference start location, and reference end location. PlantPan then returns a table containing reference chromosome, reference start, reference end, query, query chromosome, query start, query end, variation type, reference variation length, query variation length, reference related genes, and query related genes. Gene IDs in the table are clickable, providing access to detailed gene information.
4) In the 'Search Genome Synteny' module, users can specify species, sub-species, chromosome, reference start location, and reference end location. PlantPan then returns a table containing synteny ID, reference chromosome, reference start, reference end, query, query chromosome, query start, query end, variation type, reference variation length, query variation length, reference related genes, query related genes, and variations in the synteny block. Gene IDs in the table are clickable, allowing users to access detailed gene information.
5) In the 'Search Structural Variation Group’ module, users can specify species, pan classification, reference chromosome, reference start location, and reference end location. PlantPan then returns a table containing species, reference chromosome, reference start, reference end, query, query chromosome, query start, query end, variation type, variation length, sample list.
6) In the 'Search Genome Synteny Group' module, users can specify species, pan-classification, reference chromosome, reference start location, and reference end location. PlantPan then returns a table containing species, reference chromosome, reference start, reference end, query, query chromosome, query start, query end, length, sample frequency and sample frequency.
Genome Browser
In this module, users can select genes, transcription factors, literature-validated resistance genes, microbial/disease resistance genes, KEGG pathway-related genes for each sub-species within a species into JBrowser for visualization. In addition, genomic variation and genome synteny for all sub-species of a single species can be loaded once to be visualized.
Download
In this module, users can access 'Genome & Gene' data (featuring genome sequences for all sub-species, gene annotation gff files and protein sequences), 'Gene Group' (including gene clusters in matrix and associated gene sequences for each group), 'Genetic Variations' (with genetic variations for each sub-species within a species in vcf format, as well as gene copy number variation annotation files), 'Gene Functions' (comprising transcription factors, literature-validated resistance genes, microbial/disease resistance genes, KEGG pathway-related genes, GO annotations, and protein domain annotations), 'Graph Pan-Genome' in vg format and Genome Synteny in vcf format for download.
● Contact Us
If you would like to learn more about NGDC, explore the opportunity for collaboration, or to have a visit, please feel free to contact us.
Address
National Genomics Data Center
Beijing Institute of Genomics, Chinese Academy of Sciences
China National Center for Bioinformation
Beichen West Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing 100101, China
Telephone: +86 (10) 8409-7298
Fax: +86 (10) 8409-7720
Email: plantpan@big.ac.cn


 Browse
Browse

 Tools
Tools